Pivot calibration concept for sensor attached mobile c-arms
Paper and Code
Jan 09, 2020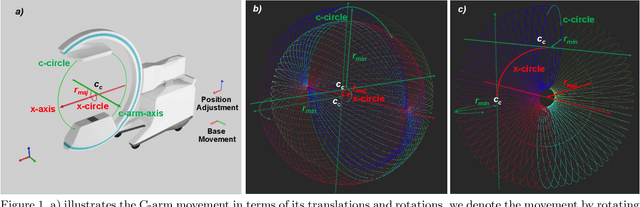
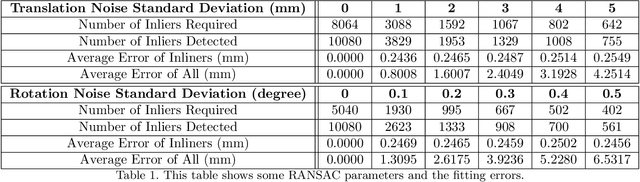


Medical augmented reality has been actively studied for decades and many methods have been proposed torevolutionize clinical procedures. One example is the camera augmented mobile C-arm (CAMC), which providesa real-time video augmentation onto medical images by rigidly mounting and calibrating a camera to the imagingdevice. Since then, several CAMC variations have been suggested by calibrating 2D/3D cameras, trackers, andmore recently a Microsoft HoloLens to the C-arm. Different calibration methods have been applied to establishthe correspondence between the rigidly attached sensor and the imaging device. A crucial step for these methodsis the acquisition of X-Ray images or 3D reconstruction volumes; therefore, requiring the emission of ionizingradiation. In this work, we analyze the mechanical motion of the device and propose an alternatative methodto calibrate sensors to the C-arm without emitting any radiation. Given a sensor is rigidly attached to thedevice, we introduce an extended pivot calibration concept to compute the fixed translation from the sensor tothe C-arm rotation center. The fixed relationship between the sensor and rotation center can be formulated as apivot calibration problem with the pivot point moving on a locus. Our method exploits the rigid C-arm motiondescribing a Torus surface to solve this calibration problem. We explain the geometry of the C-arm motion andits relation to the attached sensor, propose a calibration algorithm and show its robustness against noise, as wellas trajectory and observed pose density by computer simulations. We discuss this geometric-based formulationand its potential extensions to different C-arm applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge