Shlomo Zilberstein
University of Massachuetts Amherst
Verification Required: The Impact of Information Credibility on AI Persuasion
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Agents powered by large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in settings where communication shapes high-stakes decisions, making a principled understanding of strategic communication essential. Prior work largely studies either unverifiable cheap-talk or fully verifiable disclosure, failing to capture realistic domains in which information has probabilistic credibility. We introduce MixTalk, a strategic communication game for LLM-to-LLM interaction that models information credibility. In MixTalk, a sender agent strategically combines verifiable and unverifiable claims to communicate private information, while a receiver agent allocates a limited budget to costly verification and infers the underlying state from prior beliefs, claims, and verification outcomes. We evaluate state-of-the-art LLM agents in large-scale tournaments across three realistic deployment settings, revealing their strengths and limitations in reasoning about information credibility and the explicit behavior that shapes these interactions. Finally, we propose Tournament Oracle Policy Distillation (TOPD), an offline method that distills tournament oracle policy from interaction logs and deploys it in-context at inference time. Our results show that TOPD significantly improves receiver robustness to persuasion.
Persuasion Propagation in LLM Agents
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Modern AI agents increasingly combine conversational interaction with autonomous task execution, such as coding and web research, raising a natural question: what happens when an agent engaged in long-horizon tasks is subjected to user persuasion? We study how belief-level intervention can influence downstream task behavior, a phenomenon we name \emph{persuasion propagation}. We introduce a behavior-centered evaluation framework that distinguishes between persuasion applied during or prior to task execution. Across web research and coding tasks, we find that on-the-fly persuasion induces weak and inconsistent behavioral effects. In contrast, when the belief state is explicitly specified at task time, belief-prefilled agents conduct on average 26.9\% fewer searches and visit 16.9\% fewer unique sources than neutral-prefilled agents. These results suggest that persuasion, even in prior interaction, can affect the agent's behavior, motivating behavior-level evaluation in agentic systems.
Terrarium: Revisiting the Blackboard for Multi-Agent Safety, Privacy, and Security Studies
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:A multi-agent system (MAS) powered by large language models (LLMs) can automate tedious user tasks such as meeting scheduling that requires inter-agent collaboration. LLMs enable nuanced protocols that account for unstructured private data, user constraints, and preferences. However, this design introduces new risks, including misalignment and attacks by malicious parties that compromise agents or steal user data. In this paper, we propose the Terrarium framework for fine-grained study on safety, privacy, and security in LLM-based MAS. We repurpose the blackboard design, an early approach in multi-agent systems, to create a modular, configurable testbed for multi-agent collaboration. We identify key attack vectors such as misalignment, malicious agents, compromised communication, and data poisoning. We implement three collaborative MAS scenarios with four representative attacks to demonstrate the framework's flexibility. By providing tools to rapidly prototype, evaluate, and iterate on defenses and designs, Terrarium aims to accelerate progress toward trustworthy multi-agent systems.
Aligning LLMs on a Budget: Inference-Time Alignment with Heuristic Reward Models
Aug 07, 2025



Abstract:Aligning LLMs with user preferences is crucial for real-world use but often requires costly fine-tuning or expensive inference, forcing trade-offs between alignment quality and computational cost. Existing inference-time methods typically ignore this balance, focusing solely on the optimized policy's performance. We propose HIA (Heuristic-Guided Inference-time Alignment), a tuning-free, black-box-compatible approach that uses a lightweight prompt optimizer, heuristic reward models, and two-stage filtering to reduce inference calls while preserving alignment quality. On real-world prompt datasets, HelpSteer and ComPRed, HIA outperforms best-of-N sampling, beam search, and greedy search baselines in multi-objective, goal-conditioned tasks under the same inference budget. We also find that HIA is effective under low-inference budgets with as little as one or two response queries, offering a practical solution for scalable, personalized LLM deployment.
Proceedings of 1st Workshop on Advancing Artificial Intelligence through Theory of Mind
Apr 28, 2025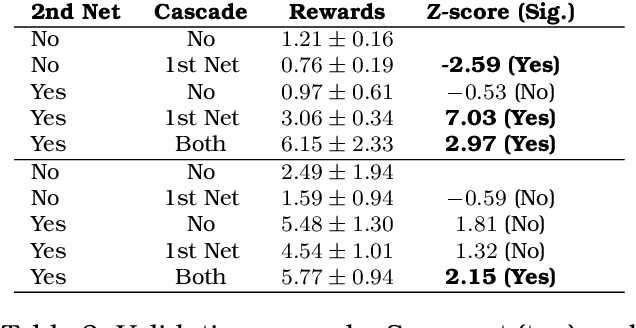
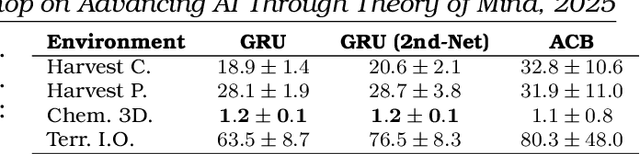
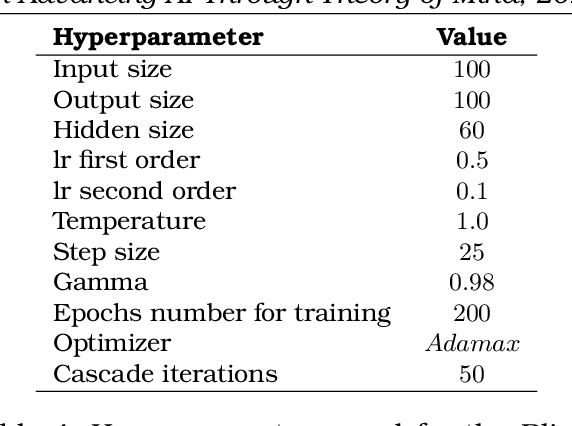
Abstract:This volume includes a selection of papers presented at the Workshop on Advancing Artificial Intelligence through Theory of Mind held at AAAI 2025 in Philadelphia US on 3rd March 2025. The purpose of this volume is to provide an open access and curated anthology for the ToM and AI research community.
Distributed Multi-Agent Coordination Using Multi-Modal Foundation Models
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Distributed Constraint Optimization Problems (DCOPs) offer a powerful framework for multi-agent coordination but often rely on labor-intensive, manual problem construction. To address this, we introduce VL-DCOPs, a framework that takes advantage of large multimodal foundation models (LFMs) to automatically generate constraints from both visual and linguistic instructions. We then introduce a spectrum of agent archetypes for solving VL-DCOPs: from a neuro-symbolic agent that delegates some of the algorithmic decisions to an LFM, to a fully neural agent that depends entirely on an LFM for coordination. We evaluate these agent archetypes using state-of-the-art LLMs (large language models) and VLMs (vision language models) on three novel VL-DCOP tasks and compare their respective advantages and drawbacks. Lastly, we discuss how this work extends to broader frontier challenges in the DCOP literature.
MAPLE: A Framework for Active Preference Learning Guided by Large Language Models
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:The advent of large language models (LLMs) has sparked significant interest in using natural language for preference learning. However, existing methods often suffer from high computational burdens, taxing human supervision, and lack of interpretability. To address these issues, we introduce MAPLE, a framework for large language model-guided Bayesian active preference learning. MAPLE leverages LLMs to model the distribution over preference functions, conditioning it on both natural language feedback and conventional preference learning feedback, such as pairwise trajectory rankings. MAPLE also employs active learning to systematically reduce uncertainty in this distribution and incorporates a language-conditioned active query selection mechanism to identify informative and easy-to-answer queries, thus reducing human burden. We evaluate MAPLE's sample efficiency and preference inference quality across two benchmarks, including a real-world vehicle route planning benchmark using OpenStreetMap data. Our results demonstrate that MAPLE accelerates the learning process and effectively improves humans' ability to answer queries.
RL$^3$: Boosting Meta Reinforcement Learning via RL inside RL$^2$
Jun 28, 2023



Abstract:Meta reinforcement learning (meta-RL) methods such as RL$^2$ have emerged as promising approaches for learning data-efficient RL algorithms tailored to a given task distribution. However, these RL algorithms struggle with long-horizon tasks and out-of-distribution tasks since they rely on recurrent neural networks to process the sequence of experiences instead of summarizing them into general RL components such as value functions. Moreover, even transformers have a practical limit to the length of histories they can efficiently reason about before training and inference costs become prohibitive. In contrast, traditional RL algorithms are data-inefficient since they do not leverage domain knowledge, but they do converge to an optimal policy as more data becomes available. In this paper, we propose RL$^3$, a principled hybrid approach that combines traditional RL and meta-RL by incorporating task-specific action-values learned through traditional RL as an input to the meta-RL neural network. We show that RL$^3$ earns greater cumulative reward on long-horizon and out-of-distribution tasks compared to RL$^2$, while maintaining the efficiency of the latter in the short term. Experiments are conducted on both custom and benchmark discrete domains from the meta-RL literature that exhibit a range of short-term, long-term, and complex dependencies.
Adaptive Rollout Length for Model-Based RL Using Model-Free Deep RL
Jun 07, 2022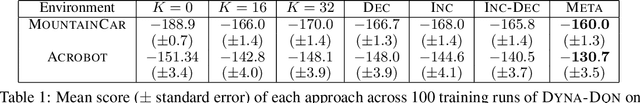
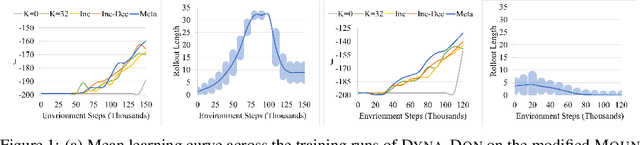
Abstract:Model-based reinforcement learning promises to learn an optimal policy from fewer interactions with the environment compared to model-free reinforcement learning by learning an intermediate model of the environment in order to predict future interactions. When predicting a sequence of interactions, the rollout length, which limits the prediction horizon, is a critical hyperparameter as accuracy of the predictions diminishes in the regions that are further away from real experience. As a result, with a longer rollout length, an overall worse policy is learned in the long run. Thus, the hyperparameter provides a trade-off between quality and efficiency. In this work, we frame the problem of tuning the rollout length as a meta-level sequential decision-making problem that optimizes the final policy learned by model-based reinforcement learning given a fixed budget of environment interactions by adapting the hyperparameter dynamically based on feedback from the learning process, such as accuracy of the model and the remaining budget of interactions. We use model-free deep reinforcement learning to solve the meta-level decision problem and demonstrate that our approach outperforms common heuristic baselines on two well-known reinforcement learning environments.
Dense Crowd Flow-Informed Path Planning
Jun 01, 2022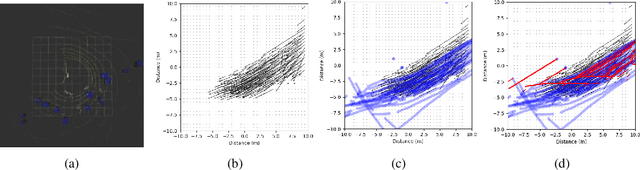
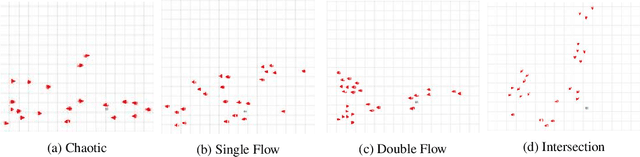
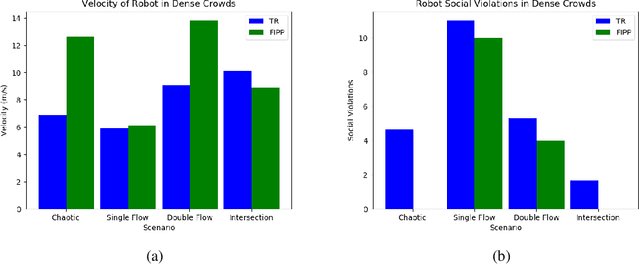
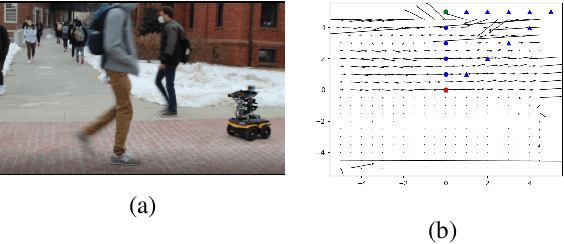
Abstract:Both pedestrian and robot comfort are of the highest priority whenever a robot is placed in an environment containing human beings. In the case of pedestrian-unaware mobile robots this desire for safety leads to the freezing robot problem, where a robot confronted with a large dynamic group of obstacles (such as a crowd of pedestrians) would determine all forward navigation unsafe causing the robot to stop in place. In order to navigate in a socially compliant manner while avoiding the freezing robot problem we are interested in understanding the flow of pedestrians in crowded scenarios. By treating the pedestrians in the crowd as particles moved along by the crowd itself we can model the system as a time dependent flow field. From this flow field we can extract different flow segments that reflect the motion patterns emerging from the crowd. These motion patterns can then be accounted for during the control and navigation of a mobile robot allowing it to move safely within the flow of the crowd to reach a desired location within or beyond the flow. We combine flow-field extraction with a discrete heuristic search to create Flow-Informed path planning (FIPP). We provide empirical results showing that when compared against a trajectory-rollout local path planner, a robot using FIPP was able not only to reach its goal more quickly but also was shown to be more socially compliant than a robot using traditional techniques both in simulation and on real robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge