Shimao Chen
HySparse: A Hybrid Sparse Attention Architecture with Oracle Token Selection and KV Cache Sharing
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:This work introduces Hybrid Sparse Attention (HySparse), a new architecture that interleaves each full attention layer with several sparse attention layers. While conceptually simple, HySparse strategically derives each sparse layer's token selection and KV caches directly from the preceding full attention layer. This architecture resolves two fundamental limitations of prior sparse attention methods. First, conventional approaches typically rely on additional proxies to predict token importance, introducing extra complexity and potentially suboptimal performance. In contrast, HySparse uses the full attention layer as a precise oracle to identify important tokens. Second, existing sparse attention designs often reduce computation without saving KV cache. HySparse enables sparse attention layers to reuse the full attention KV cache, thereby reducing both computation and memory. We evaluate HySparse on both 7B dense and 80B MoE models. Across all settings, HySparse consistently outperforms both full attention and hybrid SWA baselines. Notably, in the 80B MoE model with 49 total layers, only 5 layers employ full attention, yet HySparse achieves substantial performance gains while reducing KV cache storage by nearly 10x.
MiMo-V2-Flash Technical Report
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present MiMo-V2-Flash, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 309B total parameters and 15B active parameters, designed for fast, strong reasoning and agentic capabilities. MiMo-V2-Flash adopts a hybrid attention architecture that interleaves Sliding Window Attention (SWA) with global attention, with a 128-token sliding window under a 5:1 hybrid ratio. The model is pre-trained on 27 trillion tokens with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), employing a native 32k context length and subsequently extended to 256k. To efficiently scale post-training compute, MiMo-V2-Flash introduces a novel Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation (MOPD) paradigm. In this framework, domain-specialized teachers (e.g., trained via large-scale reinforcement learning) provide dense and token-level reward, enabling the student model to perfectly master teacher expertise. MiMo-V2-Flash rivals top-tier open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3.2 and Kimi-K2, despite using only 1/2 and 1/3 of their total parameters, respectively. During inference, by repurposing MTP as a draft model for speculative decoding, MiMo-V2-Flash achieves up to 3.6 acceptance length and 2.6x decoding speedup with three MTP layers. We open-source both the model weights and the three-layer MTP weights to foster open research and community collaboration.
MiMo-Audio: Audio Language Models are Few-Shot Learners
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Existing audio language models typically rely on task-specific fine-tuning to accomplish particular audio tasks. In contrast, humans are able to generalize to new audio tasks with only a few examples or simple instructions. GPT-3 has shown that scaling next-token prediction pretraining enables strong generalization capabilities in text, and we believe this paradigm is equally applicable to the audio domain. By scaling MiMo-Audio's pretraining data to over one hundred million of hours, we observe the emergence of few-shot learning capabilities across a diverse set of audio tasks. We develop a systematic evaluation of these capabilities and find that MiMo-Audio-7B-Base achieves SOTA performance on both speech intelligence and audio understanding benchmarks among open-source models. Beyond standard metrics, MiMo-Audio-7B-Base generalizes to tasks absent from its training data, such as voice conversion, style transfer, and speech editing. MiMo-Audio-7B-Base also demonstrates powerful speech continuation capabilities, capable of generating highly realistic talk shows, recitations, livestreaming and debates. At the post-training stage, we curate a diverse instruction-tuning corpus and introduce thinking mechanisms into both audio understanding and generation. MiMo-Audio-7B-Instruct achieves open-source SOTA on audio understanding benchmarks (MMSU, MMAU, MMAR, MMAU-Pro), spoken dialogue benchmarks (Big Bench Audio, MultiChallenge Audio) and instruct-TTS evaluations, approaching or surpassing closed-source models. Model checkpoints and full evaluation suite are available at https://github.com/XiaomiMiMo/MiMo-Audio.
Fairy$\pm i$: the First 2-bit Complex LLM with All Parameters in $\{\pm1, \pm i\}$
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Quantization-Aware Training (QAT) integrates quantization into the training loop, enabling LLMs to learn robust low-bit representations, and is widely recognized as one of the most promising research directions. All current QAT research focuses on minimizing quantization error on full-precision models, where the full-precision accuracy acts as an upper bound (accuracy ceiling). No existing method has even attempted to surpass this ceiling. To break this ceiling, we propose a new paradigm: raising the ceiling (full-precision model), and then still quantizing it efficiently into 2 bits. We propose Fairy$\pm i$, the first 2-bit quantization framework for complex-valued LLMs. Specifically, our method leverages the representational advantages of the complex domain to boost full-precision accuracy. We map weights to the fourth roots of unity $\{\pm1, \pm i\}$, forming a perfectly symmetric and information-theoretically optimal 2-bit representation. Importantly, each quantized weight has either a zero real or imaginary part, enabling multiplication-free inference using only additions and element swaps. Experimental results show that Fairy$\pm i$ outperforms the ceiling of existing 2-bit quantization approaches in terms of both PPL and downstream tasks, while maintaining strict storage and compute efficiency. This work opens a new direction for building highly accurate and practical LLMs under extremely low-bit constraints.
MiMo: Unlocking the Reasoning Potential of Language Model -- From Pretraining to Posttraining
May 12, 2025Abstract:We present MiMo-7B, a large language model born for reasoning tasks, with optimization across both pre-training and post-training stages. During pre-training, we enhance the data preprocessing pipeline and employ a three-stage data mixing strategy to strengthen the base model's reasoning potential. MiMo-7B-Base is pre-trained on 25 trillion tokens, with additional Multi-Token Prediction objective for enhanced performance and accelerated inference speed. During post-training, we curate a dataset of 130K verifiable mathematics and programming problems for reinforcement learning, integrating a test-difficulty-driven code-reward scheme to alleviate sparse-reward issues and employing strategic data resampling to stabilize training. Extensive evaluations show that MiMo-7B-Base possesses exceptional reasoning potential, outperforming even much larger 32B models. The final RL-tuned model, MiMo-7B-RL, achieves superior performance on mathematics, code and general reasoning tasks, surpassing the performance of OpenAI o1-mini. The model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/xiaomimimo/MiMo.
INT-FlashAttention: Enabling Flash Attention for INT8 Quantization
Sep 26, 2024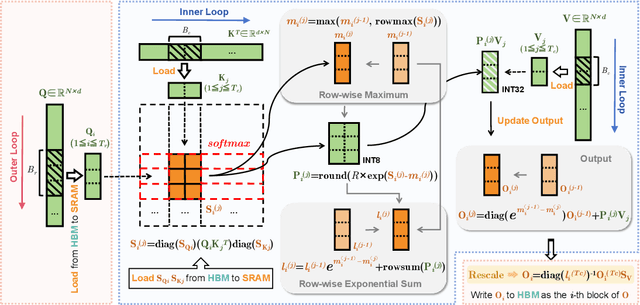
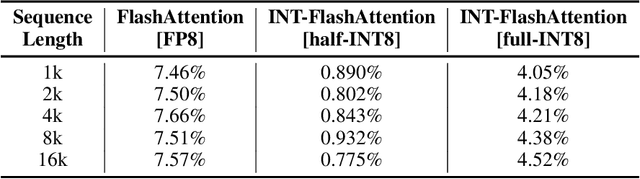
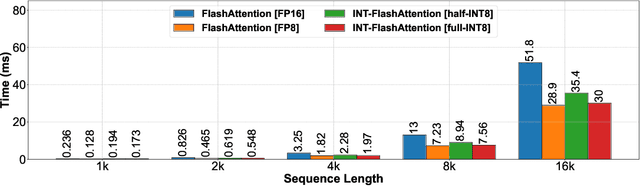
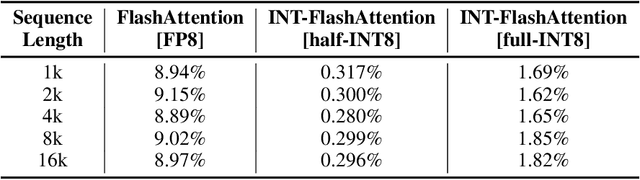
Abstract:As the foundation of large language models (LLMs), self-attention module faces the challenge of quadratic time and memory complexity with respect to sequence length. FlashAttention accelerates attention computation and reduces its memory usage by leveraging the GPU memory hierarchy. A promising research direction is to integrate FlashAttention with quantization methods. This paper introduces INT-FlashAttention, the first INT8 quantization architecture compatible with the forward workflow of FlashAttention, which significantly improves the inference speed of FlashAttention on Ampere GPUs. We implement our INT-FlashAttention prototype with fully INT8 activations and general matrix-multiplication (GEMM) kernels, making it the first attention operator with fully INT8 input. As a general token-level post-training quantization framework, INT-FlashAttention is also compatible with other data formats like INT4, etc. Experimental results show INT-FlashAttention achieves 72% faster inference speed and 82% smaller quantization error compared to standard FlashAttention with FP16 and FP8 data format.
Prediction Is All MoE Needs: Expert Load Distribution Goes from Fluctuating to Stabilizing
Apr 25, 2024Abstract:MoE facilitates the development of large models by making the computational complexity of the model no longer scale linearly with increasing parameters. The learning sparse gating network selects a set of experts for each token to be processed; however, this may lead to differences in the number of tokens processed by each expert over several successive iterations, i.e., the expert load fluctuations, which reduces computational parallelization and resource utilization. To this end, we traced and analyzed loads of each expert in the training iterations for several large language models in this work, and defined the transient state with "obvious load fluctuation" and the stable state with "temporal locality". Moreover, given the characteristics of these two states and the computational overhead, we deployed three classical prediction algorithms that achieve accurate expert load prediction results. For the GPT3 350M model, the average error rates for predicting the expert load proportion over the next 1,000 and 2,000 steps are approximately 1.3% and 1.8%, respectively. This work can provide valuable guidance for expert placement or resource allocation for MoE model training. Based on this work, we will propose an expert placement scheme for transient and stable states in our coming work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge