Peizhuang Cong
LPFQA: A Long-Tail Professional Forum-based Benchmark for LLM Evaluation
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have made rapid progress in reasoning, question answering, and professional applications; however, their true capabilities remain difficult to evaluate using existing benchmarks. Current datasets often focus on simplified tasks or artificial scenarios, overlooking long-tail knowledge and the complexities of real-world applications. To bridge this gap, we propose LPFQA, a long-tail knowledge-based benchmark derived from authentic professional forums across 20 academic and industrial fields, covering 502 tasks grounded in practical expertise. LPFQA introduces four key innovations: fine-grained evaluation dimensions that target knowledge depth, reasoning, terminology comprehension, and contextual analysis; a hierarchical difficulty structure that ensures semantic clarity and unique answers; authentic professional scenario modeling with realistic user personas; and interdisciplinary knowledge integration across diverse domains. We evaluated 12 mainstream LLMs on LPFQA and observed significant performance disparities, especially in specialized reasoning tasks. LPFQA provides a robust, authentic, and discriminative benchmark for advancing LLM evaluation and guiding future model development.
Rank Also Matters: Hierarchical Configuration for Mixture of Adapter Experts in LLM Fine-Tuning
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable success across various tasks, accompanied by a continuous increase in their parameter size. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods, such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), address the challenges of fine-tuning LLMs by significantly reducing the number of trainable parameters. Recent studies have integrated LoRA with Mixture of Experts (MoE) architectures, leveraging multiple adapter experts and gating mechanisms to further improve fine-tuning performance. However, existing approaches primarily focus on adjusting the allocations of adapter experts per layer to optimize the introduced trainable parameter size, while neglecting a critical factor of adapters' rank. To this end, we propose a hierarchical scheme for expert allocation and rank configuration, HILO, which dynamically adjusts the number and rank of adapter experts across layers, matching the varying representational complexity of model layers in adapter-granularity. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark tasks demonstrate that HILO outperforms existing methods in accuracy while introducing fewer trainable parameters, providing an efficient and practical solution for fine-tuning LLMs.
BATON: Enhancing Batch-wise Inference Efficiency for Large Language Models via Dynamic Re-batching
Oct 24, 2024Abstract:The advanced capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) have inspired the development of various interactive web services or applications, such as ChatGPT, which offer query inference services for users. Unlike traditional DNN model, the inference of LLM entails different iterations of forward computation for different queries, which result in efficiency challenges for existing run-to-completion batch-wise inference. Hence, some methods refine batch-wise inference to iteration-level by duplicating all nonlinear layers of LLM. However, this approach not only increases resource usage but also introduces idle computations to the batch due to the prefilling of newly added queries. Therefore, we propose BATON, an efficient batch-wise LLM inference scheme by dynamically adjusting processing batch, which can achieve near-zero idle computations without incurring additional resource consumption. To do so, BATON 1) shapes the vectors involved in the inference of the newly inserted query and processing batch to align dimensions and generates a new attention mask based on vector shaping to ensure inference correctness, which enables query inserting without consuming additional resource; 2) embeds prefilled Keys and Values of the new query into the KV_Cache of the processing batch by leveraging the prefilling and decoding separation mechanism, eliminating idle computations to the batch introduced by the prefilling process of the new query. Experimental results show that compared to the state-of-the-art solution Orca, BATON improves query processing by up to 1.75 times.
INT-FlashAttention: Enabling Flash Attention for INT8 Quantization
Sep 26, 2024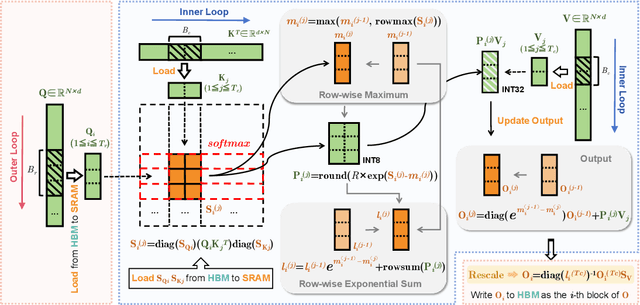
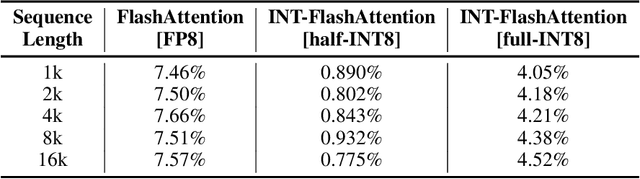
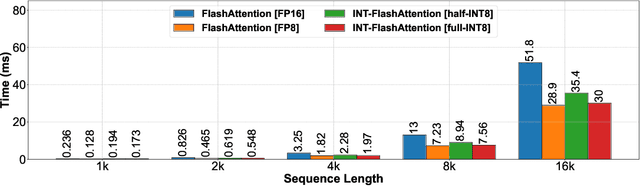
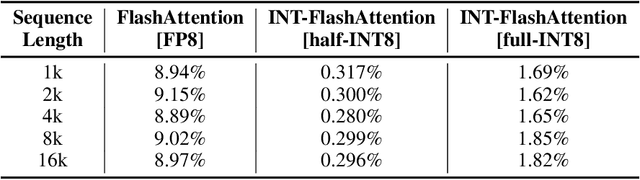
Abstract:As the foundation of large language models (LLMs), self-attention module faces the challenge of quadratic time and memory complexity with respect to sequence length. FlashAttention accelerates attention computation and reduces its memory usage by leveraging the GPU memory hierarchy. A promising research direction is to integrate FlashAttention with quantization methods. This paper introduces INT-FlashAttention, the first INT8 quantization architecture compatible with the forward workflow of FlashAttention, which significantly improves the inference speed of FlashAttention on Ampere GPUs. We implement our INT-FlashAttention prototype with fully INT8 activations and general matrix-multiplication (GEMM) kernels, making it the first attention operator with fully INT8 input. As a general token-level post-training quantization framework, INT-FlashAttention is also compatible with other data formats like INT4, etc. Experimental results show INT-FlashAttention achieves 72% faster inference speed and 82% smaller quantization error compared to standard FlashAttention with FP16 and FP8 data format.
Prediction Is All MoE Needs: Expert Load Distribution Goes from Fluctuating to Stabilizing
Apr 25, 2024Abstract:MoE facilitates the development of large models by making the computational complexity of the model no longer scale linearly with increasing parameters. The learning sparse gating network selects a set of experts for each token to be processed; however, this may lead to differences in the number of tokens processed by each expert over several successive iterations, i.e., the expert load fluctuations, which reduces computational parallelization and resource utilization. To this end, we traced and analyzed loads of each expert in the training iterations for several large language models in this work, and defined the transient state with "obvious load fluctuation" and the stable state with "temporal locality". Moreover, given the characteristics of these two states and the computational overhead, we deployed three classical prediction algorithms that achieve accurate expert load prediction results. For the GPT3 350M model, the average error rates for predicting the expert load proportion over the next 1,000 and 2,000 steps are approximately 1.3% and 1.8%, respectively. This work can provide valuable guidance for expert placement or resource allocation for MoE model training. Based on this work, we will propose an expert placement scheme for transient and stable states in our coming work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge