Shikha Bordia
Bonafide at LegalLens 2024 Shared Task: Using Lightweight DeBERTa Based Encoder For Legal Violation Detection and Resolution
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we present two systems -- Named Entity Resolution (NER) and Natural Language Inference (NLI) -- for detecting legal violations within unstructured textual data and for associating these violations with potentially affected individuals, respectively. Both these systems are lightweight DeBERTa based encoders that outperform the LLM baselines. The proposed NER system achieved an F1 score of 60.01\% on Subtask A of the LegalLens challenge, which focuses on identifying violations. The proposed NLI system achieved an F1 score of 84.73\% on Subtask B of the LegalLens challenge, which focuses on resolving these violations by matching them with pre-existing legal complaints of class action cases. Our NER system ranked sixth and NLI system ranked fifth on the LegalLens leaderboard. We release the trained models and inference scripts.
HoVer: A Dataset for Many-Hop Fact Extraction And Claim Verification
Nov 16, 2020
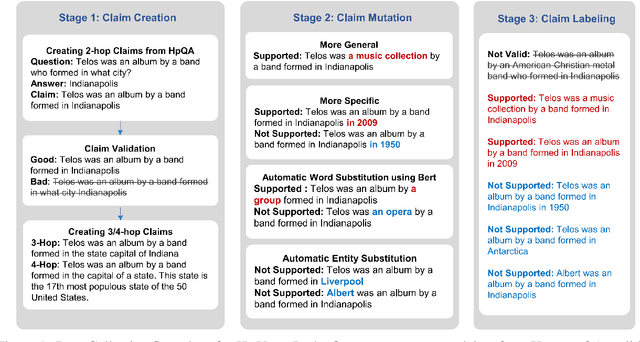
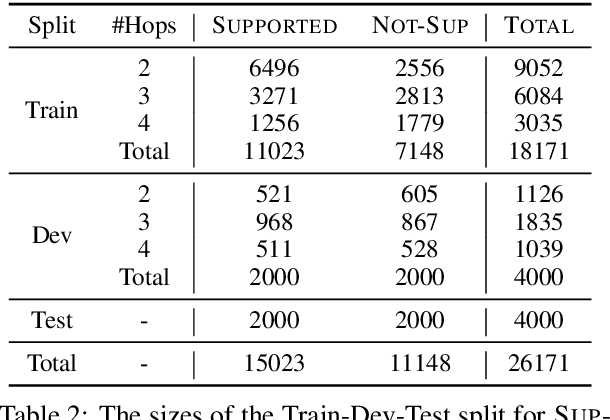
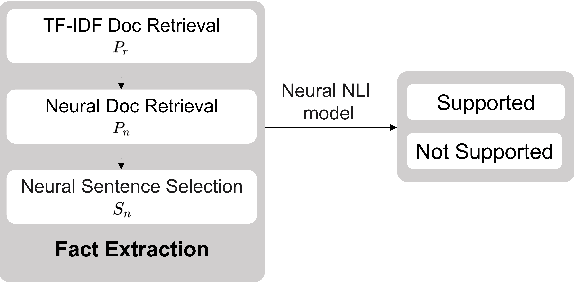
Abstract:We introduce HoVer (HOppy VERification), a dataset for many-hop evidence extraction and fact verification. It challenges models to extract facts from several Wikipedia articles that are relevant to a claim and classify whether the claim is Supported or Not-Supported by the facts. In HoVer, the claims require evidence to be extracted from as many as four English Wikipedia articles and embody reasoning graphs of diverse shapes. Moreover, most of the 3/4-hop claims are written in multiple sentences, which adds to the complexity of understanding long-range dependency relations such as coreference. We show that the performance of an existing state-of-the-art semantic-matching model degrades significantly on our dataset as the number of reasoning hops increases, hence demonstrating the necessity of many-hop reasoning to achieve strong results. We hope that the introduction of this challenging dataset and the accompanying evaluation task will encourage research in many-hop fact retrieval and information verification. We make the HoVer dataset publicly available at https://hover-nlp.github.io
Do Attention Heads in BERT Track Syntactic Dependencies?
Nov 27, 2019



Abstract:We investigate the extent to which individual attention heads in pretrained transformer language models, such as BERT and RoBERTa, implicitly capture syntactic dependency relations. We employ two methods---taking the maximum attention weight and computing the maximum spanning tree---to extract implicit dependency relations from the attention weights of each layer/head, and compare them to the ground-truth Universal Dependency (UD) trees. We show that, for some UD relation types, there exist heads that can recover the dependency type significantly better than baselines on parsed English text, suggesting that some self-attention heads act as a proxy for syntactic structure. We also analyze BERT fine-tuned on two datasets---the syntax-oriented CoLA and the semantics-oriented MNLI---to investigate whether fine-tuning affects the patterns of their self-attention, but we do not observe substantial differences in the overall dependency relations extracted using our methods. Our results suggest that these models have some specialist attention heads that track individual dependency types, but no generalist head that performs holistic parsing significantly better than a trivial baseline, and that analyzing attention weights directly may not reveal much of the syntactic knowledge that BERT-style models are known to learn.
Investigating BERT's Knowledge of Language: Five Analysis Methods with NPIs
Sep 19, 2019
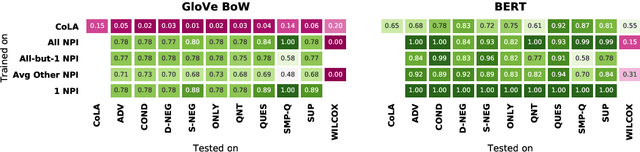

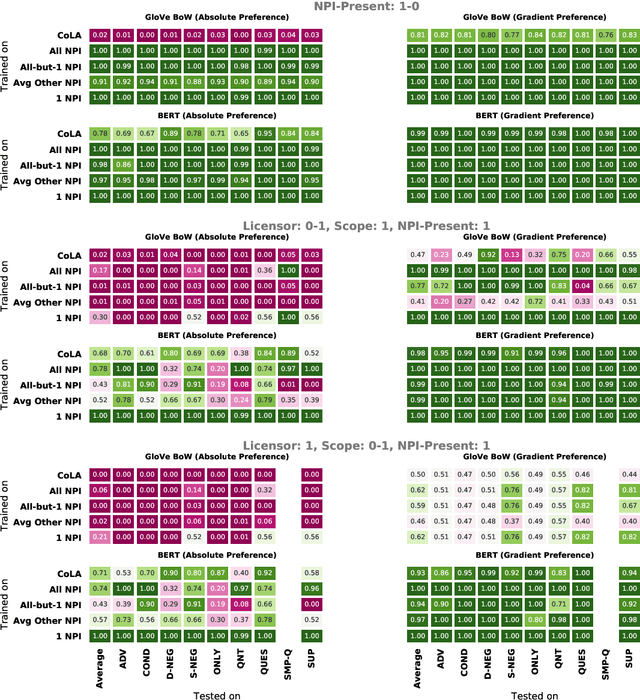
Abstract:Though state-of-the-art sentence representation models can perform tasks requiring significant knowledge of grammar, it is an open question how best to evaluate their grammatical knowledge. We explore five experimental methods inspired by prior work evaluating pretrained sentence representation models. We use a single linguistic phenomenon, negative polarity item (NPI) licensing in English, as a case study for our experiments. NPIs like "any" are grammatical only if they appear in a licensing environment like negation ("Sue doesn't have any cats" vs. "Sue has any cats"). This phenomenon is challenging because of the variety of NPI licensing environments that exist. We introduce an artificially generated dataset that manipulates key features of NPI licensing for the experiments. We find that BERT has significant knowledge of these features, but its success varies widely across different experimental methods. We conclude that a variety of methods is necessary to reveal all relevant aspects of a model's grammatical knowledge in a given domain.
Identifying and Reducing Gender Bias in Word-Level Language Models
Apr 05, 2019



Abstract:Many text corpora exhibit socially problematic biases, which can be propagated or amplified in the models trained on such data. For example, doctor cooccurs more frequently with male pronouns than female pronouns. In this study we (i) propose a metric to measure gender bias; (ii) measure bias in a text corpus and the text generated from a recurrent neural network language model trained on the text corpus; (iii) propose a regularization loss term for the language model that minimizes the projection of encoder-trained embeddings onto an embedding subspace that encodes gender; (iv) finally, evaluate efficacy of our proposed method on reducing gender bias. We find this regularization method to be effective in reducing gender bias up to an optimal weight assigned to the loss term, beyond which the model becomes unstable as the perplexity increases. We replicate this study on three training corpora---Penn Treebank, WikiText-2, and CNN/Daily Mail---resulting in similar conclusions.
On Measuring Social Biases in Sentence Encoders
Mar 25, 2019



Abstract:The Word Embedding Association Test shows that GloVe and word2vec word embeddings exhibit human-like implicit biases based on gender, race, and other social constructs (Caliskan et al., 2017). Meanwhile, research on learning reusable text representations has begun to explore sentence-level texts, with some sentence encoders seeing enthusiastic adoption. Accordingly, we extend the Word Embedding Association Test to measure bias in sentence encoders. We then test several sentence encoders, including state-of-the-art methods such as ELMo and BERT, for the social biases studied in prior work and two important biases that are difficult or impossible to test at the word level. We observe mixed results including suspicious patterns of sensitivity that suggest the test's assumptions may not hold in general. We conclude by proposing directions for future work on measuring bias in sentence encoders.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge