Shengfeng Liu
Joint Landmark and Structure Learning for Automatic Evaluation of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
Jun 10, 2021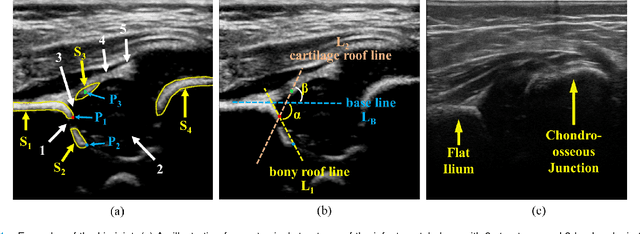
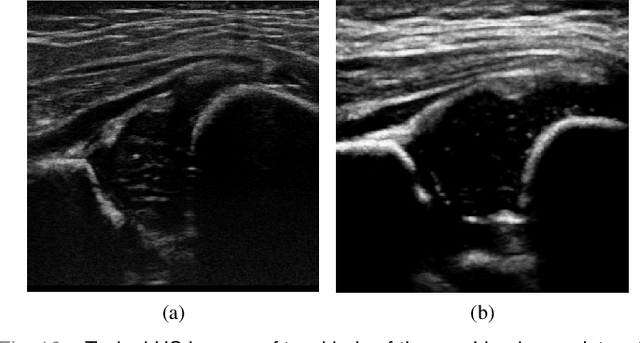
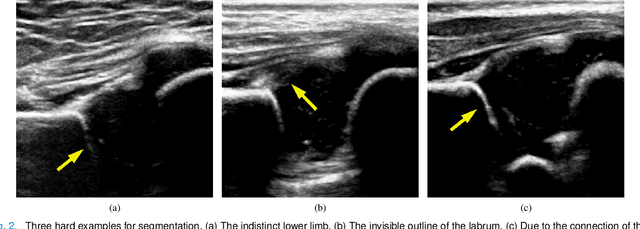
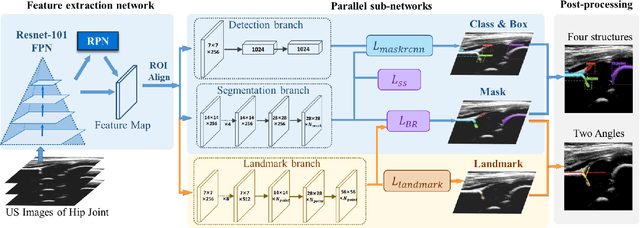
Abstract:The ultrasound (US) screening of the infant hip is vital for the early diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). The US diagnosis of DDH refers to measuring alpha and beta angles that quantify hip joint development. These two angles are calculated from key anatomical landmarks and structures of the hip. However, this measurement process is not trivial for sonographers and usually requires a thorough understanding of complex anatomical structures. In this study, we propose a multi-task framework to learn the relationships among landmarks and structures jointly and automatically evaluate DDH. Our multi-task networks are equipped with three novel modules. Firstly, we adopt Mask R-CNN as the basic framework to detect and segment key anatomical structures and add one landmark detection branch to form a new multi-task framework. Secondly, we propose a novel shape similarity loss to refine the incomplete anatomical structure prediction robustly and accurately. Thirdly, we further incorporate the landmark-structure consistent prior to ensure the consistency of the bony rim estimated from the segmented structure and the detected landmark. In our experiments, 1,231 US images of the infant hip from 632 patients are collected, of which 247 images from 126 patients are tested. The average errors in alpha and beta angles are 2.221 degrees and 2.899 degrees. About 93% and 85% estimates of alpha and beta angles have errors less than 5 degrees, respectively. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can accurately and robustly realize the automatic evaluation of DDH, showing great potential for clinical application.
Region Proposal Network with Graph Prior and IoU-Balance Loss for Landmark Detection in 3D Ultrasound
Apr 01, 2020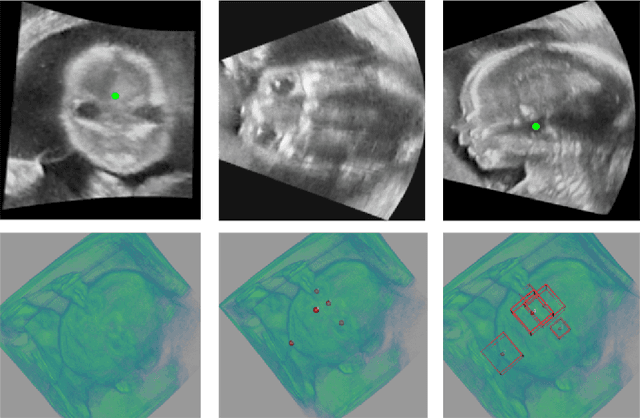
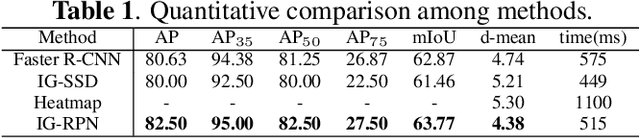
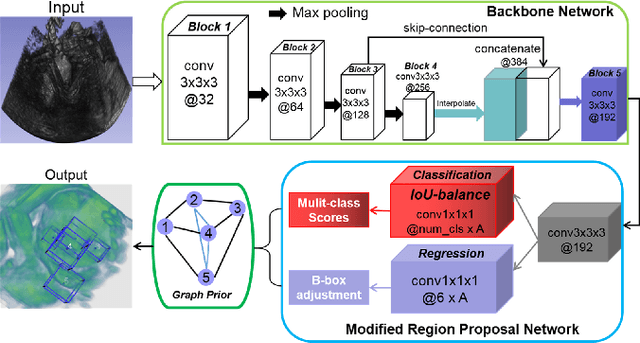
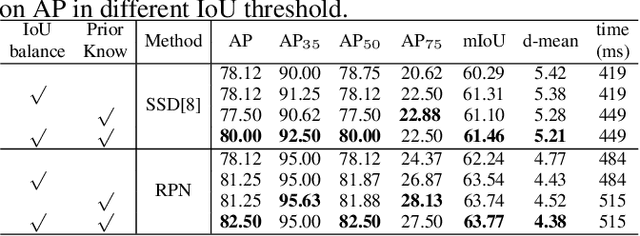
Abstract:3D ultrasound (US) can facilitate detailed prenatal examinations for fetal growth monitoring. To analyze a 3D US volume, it is fundamental to identify anatomical landmarks of the evaluated organs accurately. Typical deep learning methods usually regress the coordinates directly or involve heatmap-matching. However, these methods struggle to deal with volumes with large sizes and the highly-varying positions and orientations of fetuses. In this work, we exploit an object detection framework to detect landmarks in 3D fetal facial US volumes. By regressing multiple parameters of the landmark-centered bounding box (B-box) with a strict criteria, the proposed model is able to pinpoint the exact location of the targeted landmarks. Specifically, the model uses a 3D region proposal network (RPN) to generate 3D candidate regions, followed by several 3D classification branches to select the best candidate. It also adopts an IoU-balance loss to improve communications between branches that benefits the learning process. Furthermore, it leverages a distance-based graph prior to regularize the training and helps to reduce false positive predictions. The performance of the proposed framework is evaluated on a 3D US dataset to detect five key fetal facial landmarks. Results showed the proposed method outperforms some of the state-of-the-art methods in efficacy and efficiency.
Remove Appearance Shift for Ultrasound Image Segmentation via Fast and Universal Style Transfer
Feb 14, 2020



Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) suffer from the performance degradation when image appearance shift occurs, especially in ultrasound (US) image segmentation. In this paper, we propose a novel and intuitive framework to remove the appearance shift, and hence improve the generalization ability of DNNs. Our work has three highlights. First, we follow the spirit of universal style transfer to remove appearance shifts, which was not explored before for US images. Without sacrificing image structure details, it enables the arbitrary style-content transfer. Second, accelerated with Adaptive Instance Normalization block, our framework achieved real-time speed required in the clinical US scanning. Third, an efficient and effective style image selection strategy is proposed to ensure the target-style US image and testing content US image properly match each other. Experiments on two large US datasets demonstrate that our methods are superior to state-of-the-art methods on making DNNs robust against various appearance shifts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge