Sebastian Monka
Enhancing Manufacturing Knowledge Access with LLMs and Context-aware Prompting
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) have transformed data management within the manufacturing industry, offering effective means for integrating disparate data sources through shared and structured conceptual schemas. However, harnessing the power of KGs can be daunting for non-experts, as it often requires formulating complex SPARQL queries to retrieve specific information. With the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs), there is a growing potential to automatically translate natural language queries into the SPARQL format, thus bridging the gap between user-friendly interfaces and the sophisticated architecture of KGs. The challenge remains in adequately informing LLMs about the relevant context and structure of domain-specific KGs, e.g., in manufacturing, to improve the accuracy of generated queries. In this paper, we evaluate multiple strategies that use LLMs as mediators to facilitate information retrieval from KGs. We focus on the manufacturing domain, particularly on the Bosch Line Information System KG and the I40 Core Information Model. In our evaluation, we compare various approaches for feeding relevant context from the KG to the LLM and analyze their proficiency in transforming real-world questions into SPARQL queries. Our findings show that LLMs can significantly improve their performance on generating correct and complete queries when provided only the adequate context of the KG schema. Such context-aware prompting techniques help LLMs to focus on the relevant parts of the ontology and reduce the risk of hallucination. We anticipate that the proposed techniques help LLMs to democratize access to complex data repositories and empower informed decision-making in manufacturing settings.
Visual Representation Learning Guided By Multi-modal Prior Knowledge
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:Despite the remarkable success of deep neural networks (DNNs) in computer vision, they fail to remain high-performing when facing distribution shifts between training and testing data. In this paper, we propose Knowledge-Guided Visual representation learning (KGV), a distribution-based learning approach leveraging multi-modal prior knowledge, to improve generalization under distribution shift. We use prior knowledge from two distinct modalities: 1) a knowledge graph (KG) with hierarchical and association relationships; and 2) generated synthetic images of visual elements semantically represented in the KG. The respective embeddings are generated from the given modalities in a common latent space, i.e., visual embeddings from original and synthetic images as well as knowledge graph embeddings (KGEs). These embeddings are aligned via a novel variant of translation-based KGE methods, where the node and relation embeddings of the KG are modeled as Gaussian distributions and translations respectively. We claim that incorporating multi-model prior knowledge enables more regularized learning of image representations. Thus, the models are able to better generalize across different data distributions. We evaluate KGV on different image classification tasks with major or minor distribution shifts, namely road sign classification across datasets from Germany, China, and Russia, image classification with the mini-ImageNet dataset and its variants, as well as the DVM-CAR dataset. The results demonstrate that KGV consistently exhibits higher accuracy and data efficiency than the baselines across all experiments.
nuScenes Knowledge Graph -- A comprehensive semantic representation of traffic scenes for trajectory prediction
Dec 15, 2023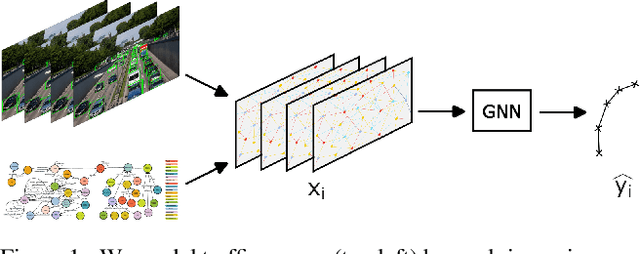
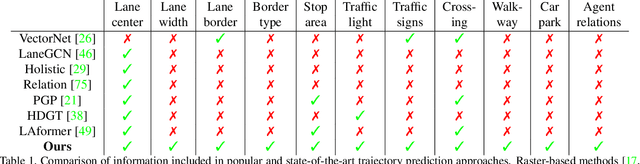
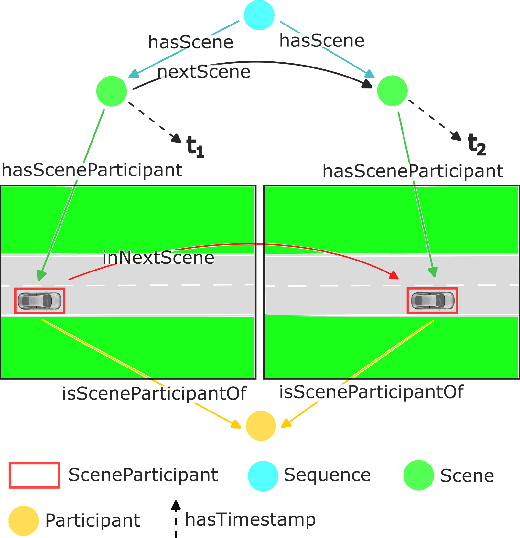
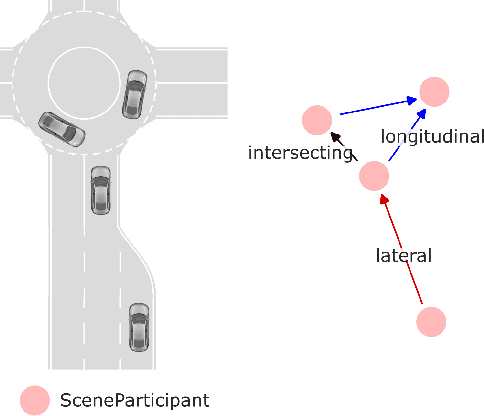
Abstract:Trajectory prediction in traffic scenes involves accurately forecasting the behaviour of surrounding vehicles. To achieve this objective it is crucial to consider contextual information, including the driving path of vehicles, road topology, lane dividers, and traffic rules. Although studies demonstrated the potential of leveraging heterogeneous context for improving trajectory prediction, state-of-the-art deep learning approaches still rely on a limited subset of this information. This is mainly due to the limited availability of comprehensive representations. This paper presents an approach that utilizes knowledge graphs to model the diverse entities and their semantic connections within traffic scenes. Further, we present nuScenes Knowledge Graph (nSKG), a knowledge graph for the nuScenes dataset, that models explicitly all scene participants and road elements, as well as their semantic and spatial relationships. To facilitate the usage of the nSKG via graph neural networks for trajectory prediction, we provide the data in a format, ready-to-use by the PyG library. All artefacts can be found here: https://github.com/boschresearch/nuScenes_Knowledge_Graph
Context-driven Visual Object Recognition based on Knowledge Graphs
Oct 20, 2022
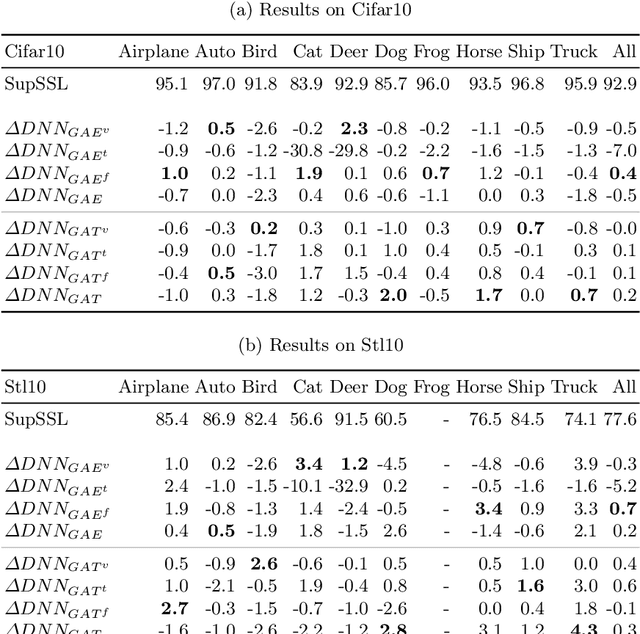
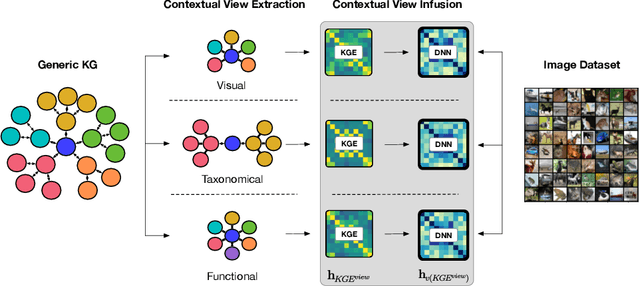
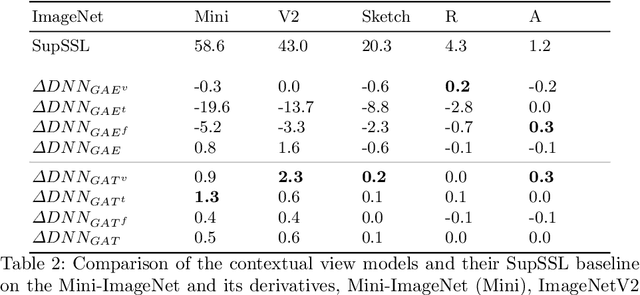
Abstract:Current deep learning methods for object recognition are purely data-driven and require a large number of training samples to achieve good results. Due to their sole dependence on image data, these methods tend to fail when confronted with new environments where even small deviations occur. Human perception, however, has proven to be significantly more robust to such distribution shifts. It is assumed that their ability to deal with unknown scenarios is based on extensive incorporation of contextual knowledge. Context can be based either on object co-occurrences in a scene or on memory of experience. In accordance with the human visual cortex which uses context to form different object representations for a seen image, we propose an approach that enhances deep learning methods by using external contextual knowledge encoded in a knowledge graph. Therefore, we extract different contextual views from a generic knowledge graph, transform the views into vector space and infuse it into a DNN. We conduct a series of experiments to investigate the impact of different contextual views on the learned object representations for the same image dataset. The experimental results provide evidence that the contextual views influence the image representations in the DNN differently and therefore lead to different predictions for the same images. We also show that context helps to strengthen the robustness of object recognition models for out-of-distribution images, usually occurring in transfer learning tasks or real-world scenarios.
A Survey on Visual Transfer Learning using Knowledge Graphs
Jan 27, 2022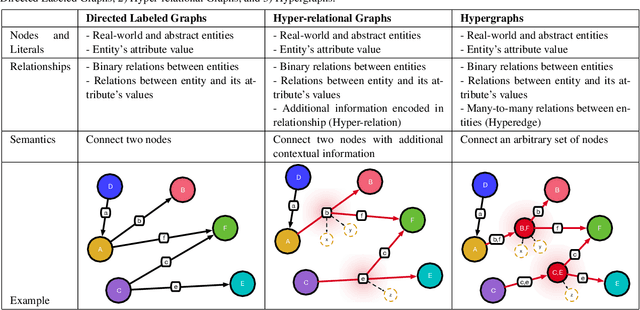
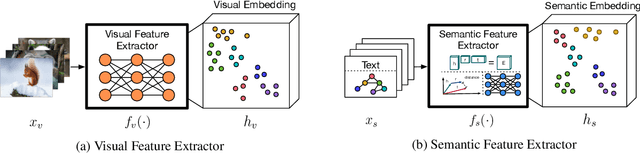
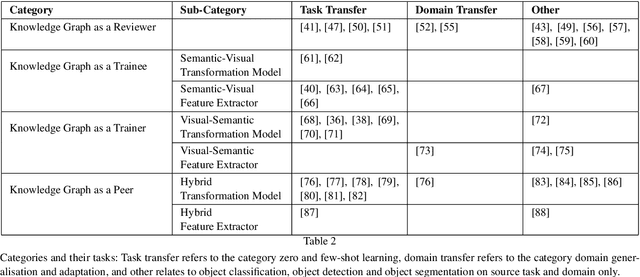
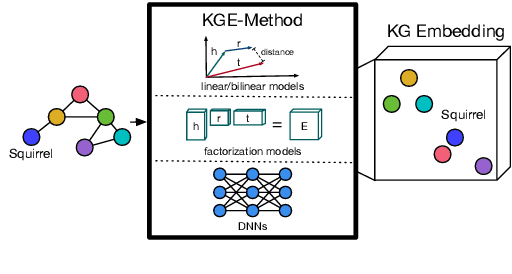
Abstract:Recent approaches of computer vision utilize deep learning methods as they perform quite well if training and testing domains follow the same underlying data distribution. However, it has been shown that minor variations in the images that occur when using these methods in the real world can lead to unpredictable errors. Transfer learning is the area of machine learning that tries to prevent these errors. Especially, approaches that augment image data using auxiliary knowledge encoded in language embeddings or knowledge graphs (KGs) have achieved promising results in recent years. This survey focuses on visual transfer learning approaches using KGs. KGs can represent auxiliary knowledge either in an underlying graph-structured schema or in a vector-based knowledge graph embedding. Intending to enable the reader to solve visual transfer learning problems with the help of specific KG-DL configurations we start with a description of relevant modeling structures of a KG of various expressions, such as directed labeled graphs, hypergraphs, and hyper-relational graphs. We explain the notion of feature extractor, while specifically referring to visual and semantic features. We provide a broad overview of knowledge graph embedding methods and describe several joint training objectives suitable to combine them with high dimensional visual embeddings. The main section introduces four different categories on how a KG can be combined with a DL pipeline: 1) Knowledge Graph as a Reviewer; 2) Knowledge Graph as a Trainee; 3) Knowledge Graph as a Trainer; and 4) Knowledge Graph as a Peer. To help researchers find evaluation benchmarks, we provide an overview of generic KGs and a set of image processing datasets and benchmarks including various types of auxiliary knowledge. Last, we summarize related surveys and give an outlook about challenges and open issues for future research.
ConTraKG: Contrastive-based Transfer Learning for Visual Object Recognition using Knowledge Graphs
Feb 17, 2021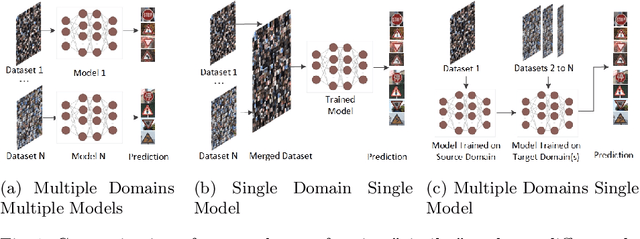
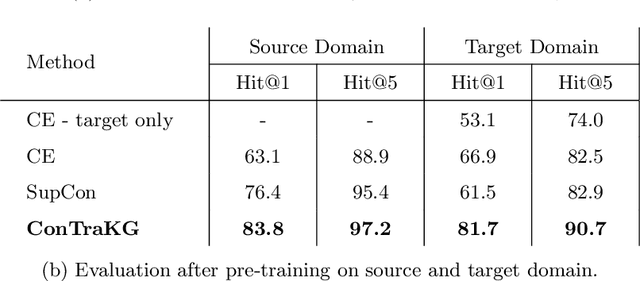
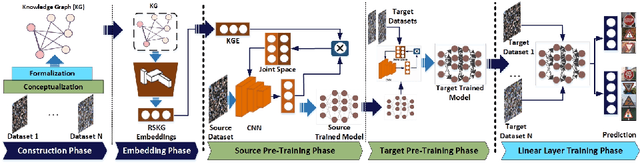
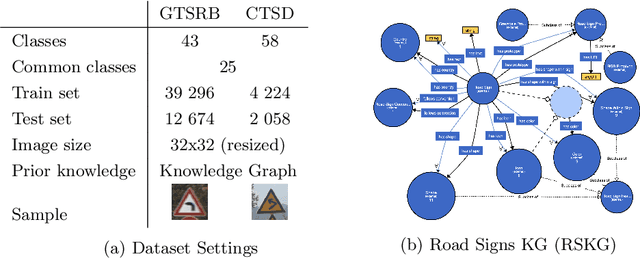
Abstract:Deep learning techniques achieve high accuracy in computer vision tasks. However, their accuracy suffers considerably when they face a domain change, i.e., as soon as they are used in a domain that differs from their training domain. For example, a road sign recognition model trained to recognize road signs in Germany performs poorly in countries with different road sign standards like China. We propose ConTraKG, a neuro-symbolic approach that enables cross-domain transfer learning based on prior knowledge about the domain or context. A knowledge graph serves as a medium for encoding such prior knowledge, which is then transformed into a dense vector representation via embedding methods. Using a five-phase training pipeline, we train the deep neural network to adjust its visual embedding space according to the domain-invariant embedding space of the knowledge graph based on a contrastive loss function. This allows the neural network to incorporate training data from different target domains that are already represented in the knowledge graph. We conduct a series of empirical evaluations to determine the accuracy of our approach. The results show that ConTraKG is significantly more accurate than the conventional approach for dealing with domain changes. In a transfer learning setup, where the network is trained on both domains, ConTraKG achieves 21% higher accuracy when tested on the source domain and 15% when tested on the target domain compared to the standard approach. Moreover, with only 10% of the target data for training, it achieves the same accuracy as the cross-entropy-based model trained on the full target data.
Real-time on-board obstacle avoidance for UAVs based on embedded stereo vision
Jul 17, 2018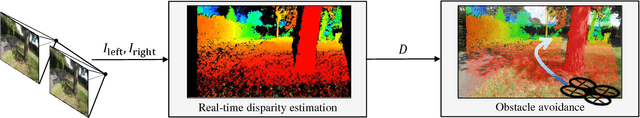
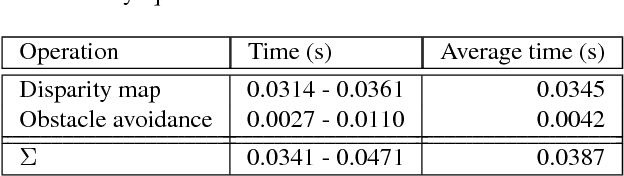
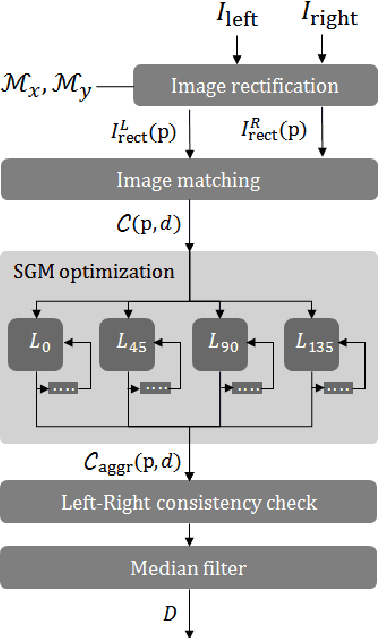
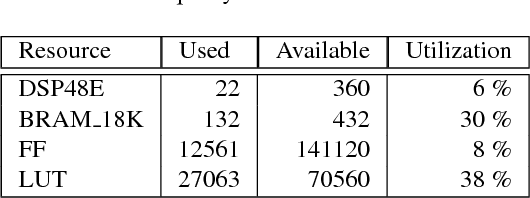
Abstract:In order to improve usability and safety, modern unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are equipped with sensors to monitor the environment, such as laser-scanners and cameras. One important aspect in this monitoring process is to detect obstacles in the flight path in order to avoid collisions. Since a large number of consumer UAVs suffer from tight weight and power constraints, our work focuses on obstacle avoidance based on a lightweight stereo camera setup. We use disparity maps, which are computed from the camera images, to locate obstacles and to automatically steer the UAV around them. For disparity map computation we optimize the well-known semi-global matching (SGM) approach for the deployment on an embedded FPGA. The disparity maps are then converted into simpler representations, the so called U-/V-Maps, which are used for obstacle detection. Obstacle avoidance is based on a reactive approach which finds the shortest path around the obstacles as soon as they have a critical distance to the UAV. One of the fundamental goals of our work was the reduction of development costs by closing the gap between application development and hardware optimization. Hence, we aimed at using high-level synthesis (HLS) for porting our algorithms, which are written in C/C++, to the embedded FPGA. We evaluated our implementation of the disparity estimation on the KITTI Stereo 2015 benchmark. The integrity of the overall realtime reactive obstacle avoidance algorithm has been evaluated by using Hardware-in-the-Loop testing in conjunction with two flight simulators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge