Context-driven Visual Object Recognition based on Knowledge Graphs
Paper and Code
Oct 20, 2022
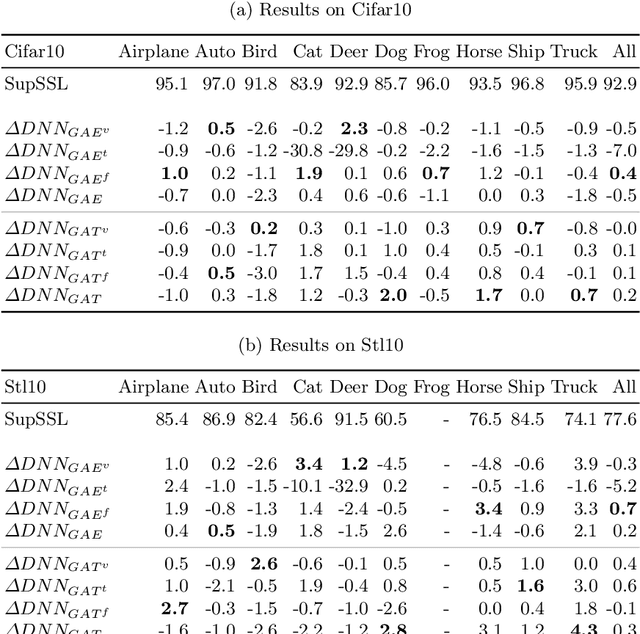
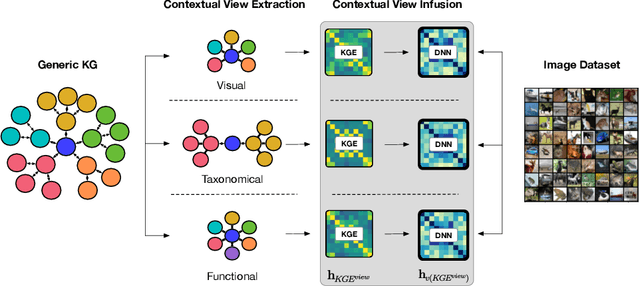
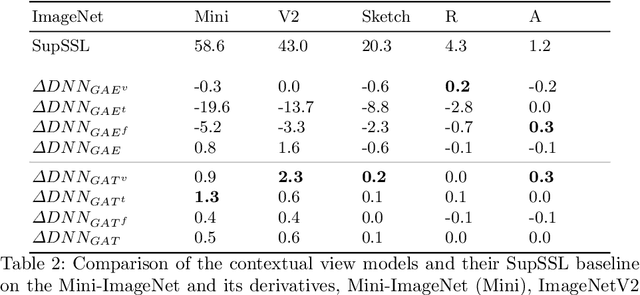
Current deep learning methods for object recognition are purely data-driven and require a large number of training samples to achieve good results. Due to their sole dependence on image data, these methods tend to fail when confronted with new environments where even small deviations occur. Human perception, however, has proven to be significantly more robust to such distribution shifts. It is assumed that their ability to deal with unknown scenarios is based on extensive incorporation of contextual knowledge. Context can be based either on object co-occurrences in a scene or on memory of experience. In accordance with the human visual cortex which uses context to form different object representations for a seen image, we propose an approach that enhances deep learning methods by using external contextual knowledge encoded in a knowledge graph. Therefore, we extract different contextual views from a generic knowledge graph, transform the views into vector space and infuse it into a DNN. We conduct a series of experiments to investigate the impact of different contextual views on the learned object representations for the same image dataset. The experimental results provide evidence that the contextual views influence the image representations in the DNN differently and therefore lead to different predictions for the same images. We also show that context helps to strengthen the robustness of object recognition models for out-of-distribution images, usually occurring in transfer learning tasks or real-world scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge