Samuele Garda
HunFlair2 in a cross-corpus evaluation of biomedical named entity recognition and normalization tools
Feb 20, 2024Abstract:With the exponential growth of the life science literature, biomedical text mining (BTM) has become an essential technology for accelerating the extraction of insights from publications. Identifying named entities (e.g., diseases, drugs, or genes) in texts and their linkage to reference knowledge bases are crucial steps in BTM pipelines to enable information aggregation from different documents. However, tools for these two steps are rarely applied in the same context in which they were developed. Instead, they are applied in the wild, i.e., on application-dependent text collections different from those used for the tools' training, varying, e.g., in focus, genre, style, and text type. This raises the question of whether the reported performance of BTM tools can be trusted for downstream applications. Here, we report on the results of a carefully designed cross-corpus benchmark for named entity extraction, where tools were applied systematically to corpora not used during their training. Based on a survey of 28 published systems, we selected five for an in-depth analysis on three publicly available corpora encompassing four different entity types. Comparison between tools results in a mixed picture and shows that, in a cross-corpus setting, the performance is significantly lower than the one reported in an in-corpus setting. HunFlair2 showed the best performance on average, being closely followed by PubTator. Our results indicate that users of BTM tools should expect diminishing performances when applying them in the wild compared to original publications and show that further research is necessary to make BTM tools more robust.
BELHD: Improving Biomedical Entity Linking with Homonoym Disambiguation
Jan 10, 2024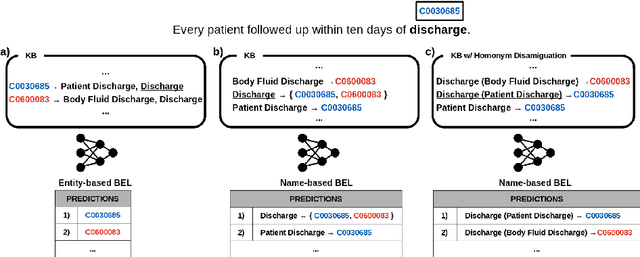
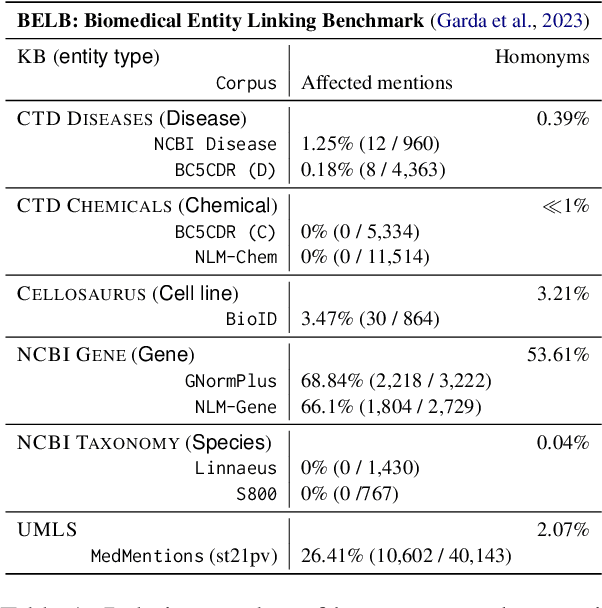
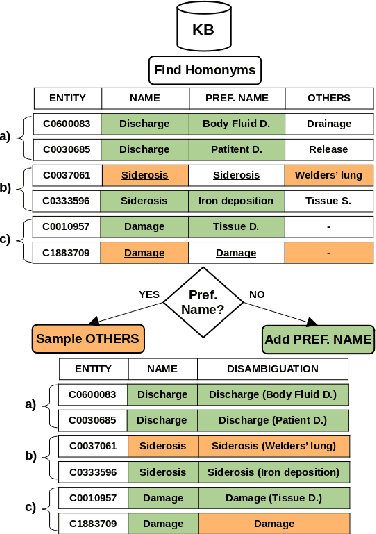
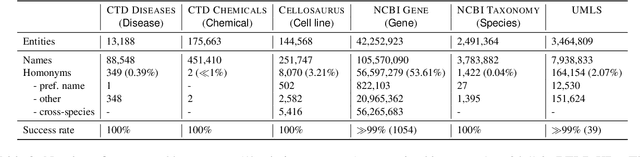
Abstract:Biomedical entity linking (BEL) is the task of grounding entity mentions to a knowledge base (KB). A popular approach to the task are name-based methods, i.e. those identifying the most appropriate name in the KB for a given mention, either via dense retrieval or autoregressive modeling. However, as these methods directly return KB names, they cannot cope with homonyms, i.e. different KB entities sharing the exact same name. This significantly affects their performance, especially for KBs where homonyms account for a large amount of entity mentions (e.g. UMLS and NCBI Gene). We therefore present BELHD (Biomedical Entity Linking with Homonym Disambiguation), a new name-based method that copes with this challenge. Specifically, BELHD builds upon the BioSyn (Sung et al.,2020) model introducing two crucial extensions. First, it performs a preprocessing of the KB in which it expands homonyms with an automatically chosen disambiguating string, thus enforcing unique linking decisions. Second, we introduce candidate sharing, a novel strategy to select candidates for contrastive learning that enhances the overall training signal. Experiments with 10 corpora and five entity types show that BELHD improves upon state-of-the-art approaches, achieving the best results in 6 out 10 corpora with an average improvement of 4.55pp recall@1. Furthermore, the KB preprocessing is orthogonal to the core prediction model and thus can also improve other methods, which we exemplify for GenBioEL (Yuan et al, 2022), a generative name-based BEL approach. Code is available at: link added upon publication.
BELB: a Biomedical Entity Linking Benchmark
Aug 22, 2023



Abstract:Biomedical entity linking (BEL) is the task of grounding entity mentions to a knowledge base. It plays a vital role in information extraction pipelines for the life sciences literature. We review recent work in the field and find that, as the task is absent from existing benchmarks for biomedical text mining, different studies adopt different experimental setups making comparisons based on published numbers problematic. Furthermore, neural systems are tested primarily on instances linked to the broad coverage knowledge base UMLS, leaving their performance to more specialized ones, e.g. genes or variants, understudied. We therefore developed BELB, a Biomedical Entity Linking Benchmark, providing access in a unified format to 11 corpora linked to 7 knowledge bases and spanning six entity types: gene, disease, chemical, species, cell line and variant. BELB greatly reduces preprocessing overhead in testing BEL systems on multiple corpora offering a standardized testbed for reproducible experiments. Using BELB we perform an extensive evaluation of six rule-based entity-specific systems and three recent neural approaches leveraging pre-trained language models. Our results reveal a mixed picture showing that neural approaches fail to perform consistently across entity types, highlighting the need of further studies towards entity-agnostic models.
BLOOM: A 176B-Parameter Open-Access Multilingual Language Model
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to be able to perform new tasks based on a few demonstrations or natural language instructions. While these capabilities have led to widespread adoption, most LLMs are developed by resource-rich organizations and are frequently kept from the public. As a step towards democratizing this powerful technology, we present BLOOM, a 176B-parameter open-access language model designed and built thanks to a collaboration of hundreds of researchers. BLOOM is a decoder-only Transformer language model that was trained on the ROOTS corpus, a dataset comprising hundreds of sources in 46 natural and 13 programming languages (59 in total). We find that BLOOM achieves competitive performance on a wide variety of benchmarks, with stronger results after undergoing multitask prompted finetuning. To facilitate future research and applications using LLMs, we publicly release our models and code under the Responsible AI License.
BigBIO: A Framework for Data-Centric Biomedical Natural Language Processing
Jun 30, 2022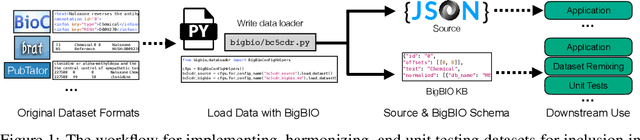
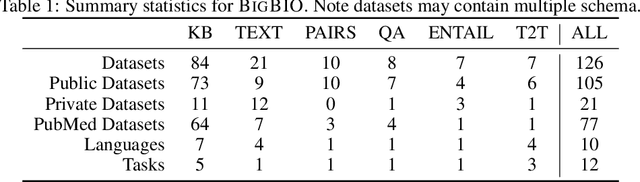
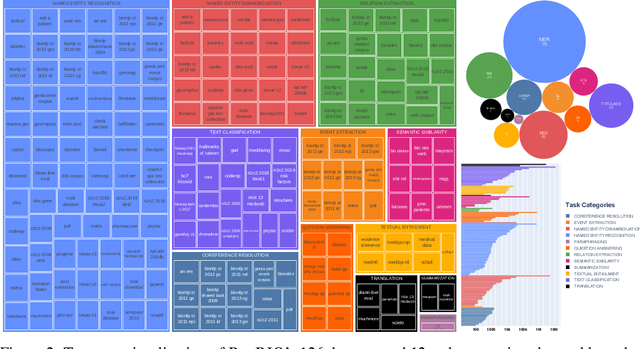
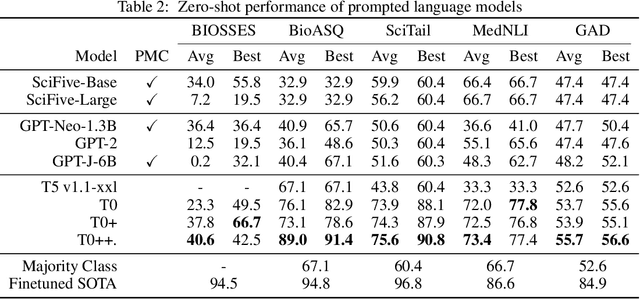
Abstract:Training and evaluating language models increasingly requires the construction of meta-datasets --diverse collections of curated data with clear provenance. Natural language prompting has recently lead to improved zero-shot generalization by transforming existing, supervised datasets into a diversity of novel pretraining tasks, highlighting the benefits of meta-dataset curation. While successful in general-domain text, translating these data-centric approaches to biomedical language modeling remains challenging, as labeled biomedical datasets are significantly underrepresented in popular data hubs. To address this challenge, we introduce BigBIO a community library of 126+ biomedical NLP datasets, currently covering 12 task categories and 10+ languages. BigBIO facilitates reproducible meta-dataset curation via programmatic access to datasets and their metadata, and is compatible with current platforms for prompt engineering and end-to-end few/zero shot language model evaluation. We discuss our process for task schema harmonization, data auditing, contribution guidelines, and outline two illustrative use cases: zero-shot evaluation of biomedical prompts and large-scale, multi-task learning. BigBIO is an ongoing community effort and is available at https://github.com/bigscience-workshop/biomedical
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge