Ruizhi Qiao
When should I search more: Adaptive Complex Query Optimization with Reinforcement Learning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Query optimization is a crucial component for the efficacy of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. While reinforcement learning (RL)-based agentic and reasoning methods have recently emerged as a promising direction on query optimization, most existing approaches focus on the expansion and abstraction of a single query. However, complex user queries are prevalent in real-world scenarios, often requiring multiple parallel and sequential search strategies to handle disambiguation and decomposition. Directly applying RL to these complex cases introduces significant hurdles. Determining the optimal number of sub-queries and effectively re-ranking and merging retrieved documents vastly expands the search space and complicates reward design, frequently leading to training instability. To address these challenges, we propose a novel RL framework called Adaptive Complex Query Optimization (ACQO). Our framework is designed to adaptively determine when and how to expand the search process. It features two core components: an Adaptive Query Reformulation (AQR) module that dynamically decides when to decompose a query into multiple sub-queries, and a Rank-Score Fusion (RSF) module that ensures robust result aggregation and provides stable reward signals for the learning agent. To mitigate training instabilities, we adopt a Curriculum Reinforcement Learning (CRL) approach, which stabilizes the training process by progressively introducing more challenging queries through a two-stage strategy. Our comprehensive experiments demonstrate that ACQO achieves state-of-the-art performance on three complex query benchmarks, significantly outperforming established baselines. The framework also showcases improved computational efficiency and broad compatibility with different retrieval architectures, establishing it as a powerful and generalizable solution for next-generation RAG systems.
Youtu-VL: Unleashing Visual Potential via Unified Vision-Language Supervision
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Despite the significant advancements represented by Vision-Language Models (VLMs), current architectures often exhibit limitations in retaining fine-grained visual information, leading to coarse-grained multimodal comprehension. We attribute this deficiency to a suboptimal training paradigm inherent in prevailing VLMs, which exhibits a text-dominant optimization bias by conceptualizing visual signals merely as passive conditional inputs rather than supervisory targets. To mitigate this, we introduce Youtu-VL, a framework leveraging the Vision-Language Unified Autoregressive Supervision (VLUAS) paradigm, which fundamentally shifts the optimization objective from ``vision-as-input'' to ``vision-as-target.'' By integrating visual tokens directly into the prediction stream, Youtu-VL applies unified autoregressive supervision to both visual details and linguistic content. Furthermore, we extend this paradigm to encompass vision-centric tasks, enabling a standard VLM to perform vision-centric tasks without task-specific additions. Extensive empirical evaluations demonstrate that Youtu-VL achieves competitive performance on both general multimodal tasks and vision-centric tasks, establishing a robust foundation for the development of comprehensive generalist visual agents.
Youtu-LLM: Unlocking the Native Agentic Potential for Lightweight Large Language Models
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:We introduce Youtu-LLM, a lightweight yet powerful language model that harmonizes high computational efficiency with native agentic intelligence. Unlike typical small models that rely on distillation, Youtu-LLM (1.96B) is pre-trained from scratch to systematically cultivate reasoning and planning capabilities. The key technical advancements are as follows: (1) Compact Architecture with Long-Context Support: Built on a dense Multi-Latent Attention (MLA) architecture with a novel STEM-oriented vocabulary, Youtu-LLM supports a 128k context window. This design enables robust long-context reasoning and state tracking within a minimal memory footprint, making it ideal for long-horizon agent and reasoning tasks. (2) Principled "Commonsense-STEM-Agent" Curriculum: We curated a massive corpus of approximately 11T tokens and implemented a multi-stage training strategy. By progressively shifting the pre-training data distribution from general commonsense to complex STEM and agentic tasks, we ensure the model acquires deep cognitive abilities rather than superficial alignment. (3) Scalable Agentic Mid-training: Specifically for the agentic mid-training, we employ diverse data construction schemes to synthesize rich and varied trajectories across math, coding, and tool-use domains. This high-quality data enables the model to internalize planning and reflection behaviors effectively. Extensive evaluations show that Youtu-LLM sets a new state-of-the-art for sub-2B LLMs. On general benchmarks, it achieves competitive performance against larger models, while on agent-specific tasks, it significantly surpasses existing SOTA baselines, demonstrating that lightweight models can possess strong intrinsic agentic capabilities.
ASPD: Unlocking Adaptive Serial-Parallel Decoding by Exploring Intrinsic Parallelism in LLMs
Aug 12, 2025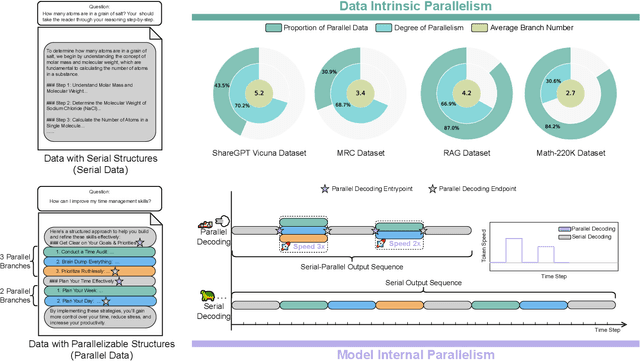
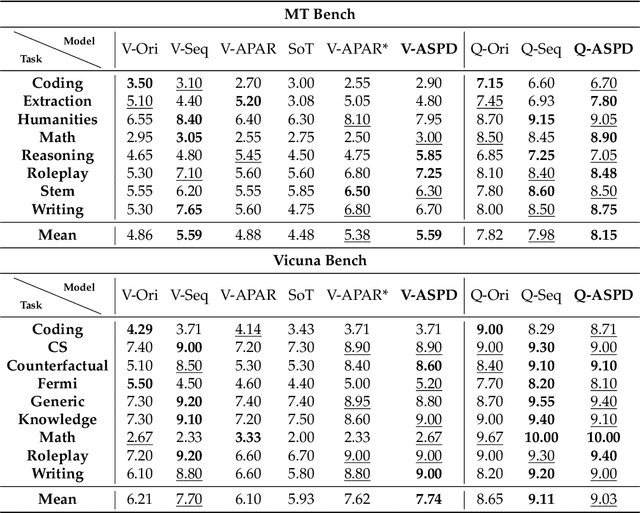
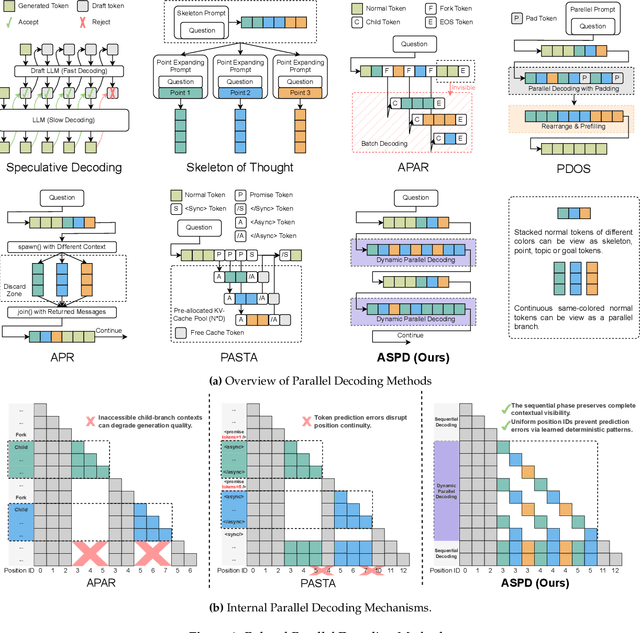
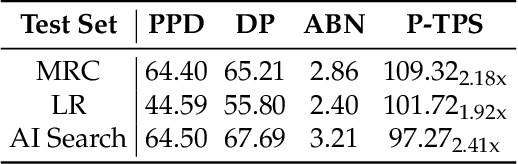
Abstract:The increasing scale and complexity of large language models (LLMs) pose significant inference latency challenges, primarily due to their autoregressive decoding paradigm characterized by the sequential nature of next-token prediction. By re-examining the outputs of autoregressive models, we observed that some segments exhibit parallelizable structures, which we term intrinsic parallelism. Decoding each parallelizable branch simultaneously (i.e. parallel decoding) can significantly improve the overall inference speed of LLMs. In this paper, we propose an Adaptive Serial-Parallel Decoding (ASPD), which addresses two core challenges: automated construction of parallelizable data and efficient parallel decoding mechanism. More specifically, we introduce a non-invasive pipeline that automatically extracts and validates parallelizable structures from the responses of autoregressive models. To empower efficient adaptive serial-parallel decoding, we implement a Hybrid Decoding Engine which enables seamless transitions between serial and parallel decoding modes while maintaining a reusable KV cache, maximizing computational efficiency. Extensive evaluations across General Tasks, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, Mathematical Reasoning, demonstrate that ASPD achieves unprecedented performance in both effectiveness and efficiency. Notably, on Vicuna Bench, our method achieves up to 3.19x speedup (1.85x on average) while maintaining response quality within 1% difference compared to autoregressive models, realizing significant acceleration without compromising generation quality. Our framework sets a groundbreaking benchmark for efficient LLM parallel inference, paving the way for its deployment in latency-sensitive applications such as AI-powered customer service bots and answer retrieval engines.
RocketEval: Efficient Automated LLM Evaluation via Grading Checklist
Mar 07, 2025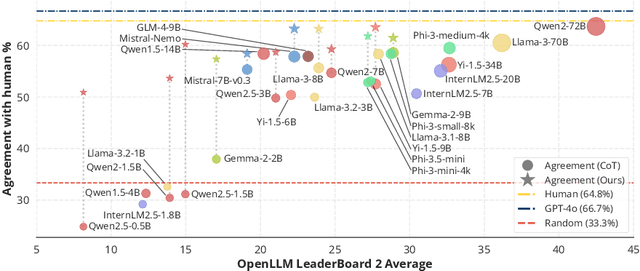
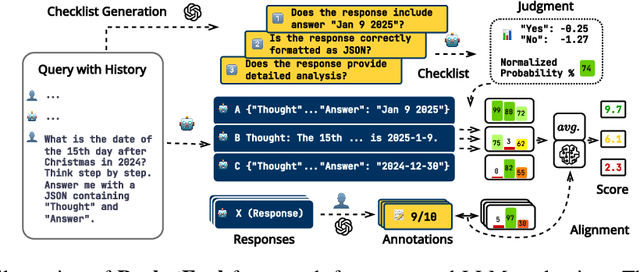
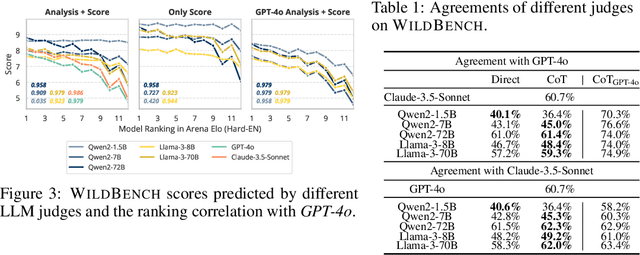
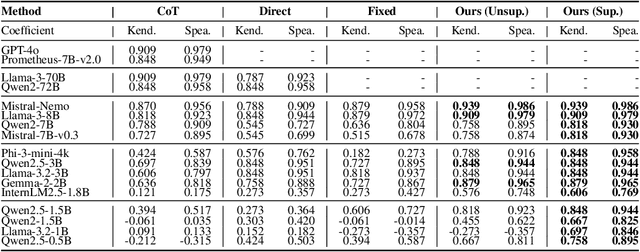
Abstract:Evaluating large language models (LLMs) in diverse and challenging scenarios is essential to align them with human preferences. To mitigate the prohibitive costs associated with human evaluations, utilizing a powerful LLM as a judge has emerged as a favored approach. Nevertheless, this methodology encounters several challenges, including substantial expenses, concerns regarding privacy and security, and reproducibility. In this paper, we propose a straightforward, replicable, and accurate automated evaluation method by leveraging a lightweight LLM as the judge, named RocketEval. Initially, we identify that the performance disparity between lightweight and powerful LLMs in evaluation tasks primarily stems from their ability to conduct comprehensive analyses, which is not easily enhanced through techniques such as chain-of-thought reasoning. By reframing the evaluation task as a multi-faceted Q&A using an instance-specific checklist, we demonstrate that the limited judgment accuracy of lightweight LLMs is largely attributes to high uncertainty and positional bias. To address these challenges, we introduce an automated evaluation process grounded in checklist grading, which is designed to accommodate a variety of scenarios and questions. This process encompasses the creation of checklists, the grading of these checklists by lightweight LLMs, and the reweighting of checklist items to align with the supervised annotations. Our experiments carried out on the automated evaluation benchmarks, MT-Bench and WildBench datasets, reveal that RocketEval, when using Gemma-2-2B as the judge, achieves a high correlation (0.965) with human preferences, which is comparable to GPT-4o. Moreover, RocketEval provides a cost reduction exceeding 50-fold for large-scale evaluation and comparison scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/Joinn99/RocketEval-ICLR .
Multimodal Label Relevance Ranking via Reinforcement Learning
Jul 18, 2024Abstract:Conventional multi-label recognition methods often focus on label confidence, frequently overlooking the pivotal role of partial order relations consistent with human preference. To resolve these issues, we introduce a novel method for multimodal label relevance ranking, named Label Relevance Ranking with Proximal Policy Optimization (LR\textsuperscript{2}PPO), which effectively discerns partial order relations among labels. LR\textsuperscript{2}PPO first utilizes partial order pairs in the target domain to train a reward model, which aims to capture human preference intrinsic to the specific scenario. Furthermore, we meticulously design state representation and a policy loss tailored for ranking tasks, enabling LR\textsuperscript{2}PPO to boost the performance of label relevance ranking model and largely reduce the requirement of partial order annotation for transferring to new scenes. To assist in the evaluation of our approach and similar methods, we further propose a novel benchmark dataset, LRMovieNet, featuring multimodal labels and their corresponding partial order data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our LR\textsuperscript{2}PPO algorithm achieves state-of-the-art performance, proving its effectiveness in addressing the multimodal label relevance ranking problem. Codes and the proposed LRMovieNet dataset are publicly available at \url{https://github.com/ChazzyGordon/LR2PPO}.
Unified and Dynamic Graph for Temporal Character Grouping in Long Videos
Aug 29, 2023Abstract:Video temporal character grouping locates appearing moments of major characters within a video according to their identities. To this end, recent works have evolved from unsupervised clustering to graph-based supervised clustering. However, graph methods are built upon the premise of fixed affinity graphs, bringing many inexact connections. Besides, they extract multi-modal features with kinds of models, which are unfriendly to deployment. In this paper, we present a unified and dynamic graph (UniDG) framework for temporal character grouping. This is accomplished firstly by a unified representation network that learns representations of multiple modalities within the same space and still preserves the modality's uniqueness simultaneously. Secondly, we present a dynamic graph clustering where the neighbors of different quantities are dynamically constructed for each node via a cyclic matching strategy, leading to a more reliable affinity graph. Thirdly, a progressive association method is introduced to exploit spatial and temporal contexts among different modalities, allowing multi-modal clustering results to be well fused. As current datasets only provide pre-extracted features, we evaluate our UniDG method on a collected dataset named MTCG, which contains each character's appearing clips of face and body and speaking voice tracks. We also evaluate our key components on existing clustering and retrieval datasets to verify the generalization ability. Experimental results manifest that our method can achieve promising results and outperform several state-of-the-art approaches.
Coarse-to-Fine: Learning Compact Discriminative Representation for Single-Stage Image Retrieval
Aug 08, 2023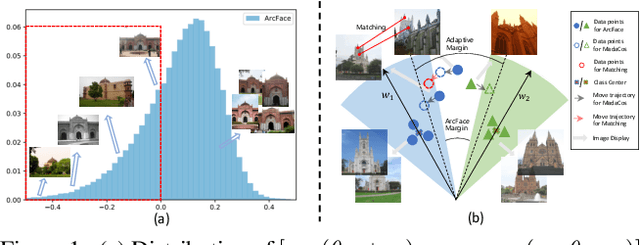
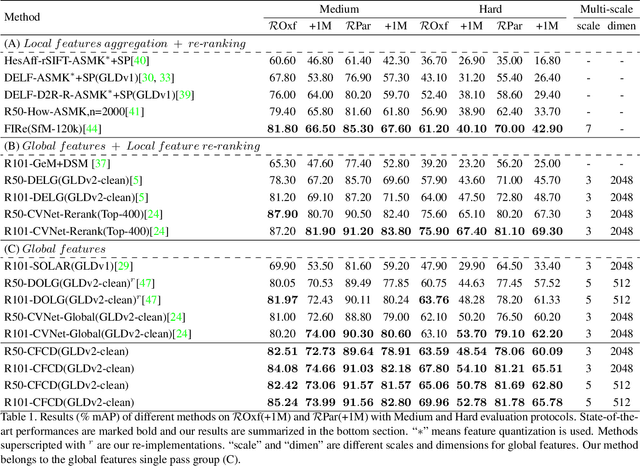
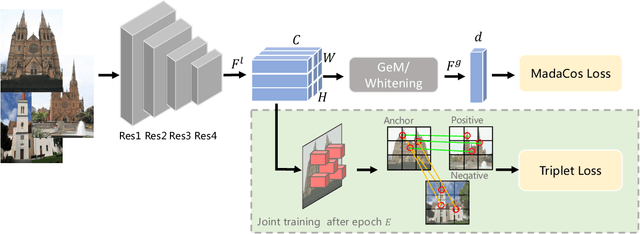
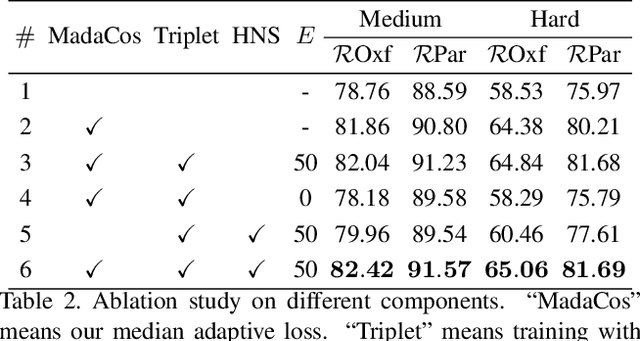
Abstract:Image retrieval targets to find images from a database that are visually similar to the query image. Two-stage methods following retrieve-and-rerank paradigm have achieved excellent performance, but their separate local and global modules are inefficient to real-world applications. To better trade-off retrieval efficiency and accuracy, some approaches fuse global and local feature into a joint representation to perform single-stage image retrieval. However, they are still challenging due to various situations to tackle, $e.g.$, background, occlusion and viewpoint. In this work, we design a Coarse-to-Fine framework to learn Compact Discriminative representation (CFCD) for end-to-end single-stage image retrieval-requiring only image-level labels. Specifically, we first design a novel adaptive softmax-based loss which dynamically tunes its scale and margin within each mini-batch and increases them progressively to strengthen supervision during training and intra-class compactness. Furthermore, we propose a mechanism which attentively selects prominent local descriptors and infuse fine-grained semantic relations into the global representation by a hard negative sampling strategy to optimize inter-class distinctiveness at a global scale. Extensive experimental results have demonstrated the effectiveness of our method, which achieves state-of-the-art single-stage image retrieval performance on benchmarks such as Revisited Oxford and Revisited Paris. Code is available at https://github.com/bassyess/CFCD.
D3G: Exploring Gaussian Prior for Temporal Sentence Grounding with Glance Annotation
Aug 08, 2023



Abstract:Temporal sentence grounding (TSG) aims to locate a specific moment from an untrimmed video with a given natural language query. Recently, weakly supervised methods still have a large performance gap compared to fully supervised ones, while the latter requires laborious timestamp annotations. In this study, we aim to reduce the annotation cost yet keep competitive performance for TSG task compared to fully supervised ones. To achieve this goal, we investigate a recently proposed glance-supervised temporal sentence grounding task, which requires only single frame annotation (referred to as glance annotation) for each query. Under this setup, we propose a Dynamic Gaussian prior based Grounding framework with Glance annotation (D3G), which consists of a Semantic Alignment Group Contrastive Learning module (SA-GCL) and a Dynamic Gaussian prior Adjustment module (DGA). Specifically, SA-GCL samples reliable positive moments from a 2D temporal map via jointly leveraging Gaussian prior and semantic consistency, which contributes to aligning the positive sentence-moment pairs in the joint embedding space. Moreover, to alleviate the annotation bias resulting from glance annotation and model complex queries consisting of multiple events, we propose the DGA module, which adjusts the distribution dynamically to approximate the ground truth of target moments. Extensive experiments on three challenging benchmarks verify the effectiveness of the proposed D3G. It outperforms the state-of-the-art weakly supervised methods by a large margin and narrows the performance gap compared to fully supervised methods. Code is available at https://github.com/solicucu/D3G.
Collaborative Noisy Label Cleaner: Learning Scene-aware Trailers for Multi-modal Highlight Detection in Movies
Mar 26, 2023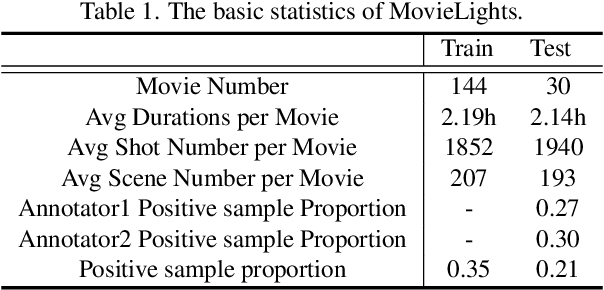
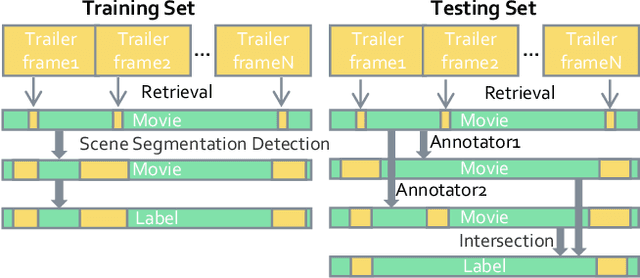
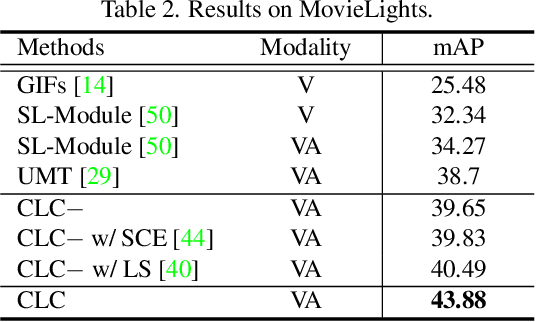
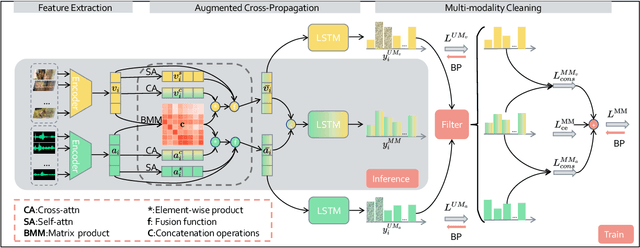
Abstract:Movie highlights stand out of the screenplay for efficient browsing and play a crucial role on social media platforms. Based on existing efforts, this work has two observations: (1) For different annotators, labeling highlight has uncertainty, which leads to inaccurate and time-consuming annotations. (2) Besides previous supervised or unsupervised settings, some existing video corpora can be useful, e.g., trailers, but they are often noisy and incomplete to cover the full highlights. In this work, we study a more practical and promising setting, i.e., reformulating highlight detection as "learning with noisy labels". This setting does not require time-consuming manual annotations and can fully utilize existing abundant video corpora. First, based on movie trailers, we leverage scene segmentation to obtain complete shots, which are regarded as noisy labels. Then, we propose a Collaborative noisy Label Cleaner (CLC) framework to learn from noisy highlight moments. CLC consists of two modules: augmented cross-propagation (ACP) and multi-modality cleaning (MMC). The former aims to exploit the closely related audio-visual signals and fuse them to learn unified multi-modal representations. The latter aims to achieve cleaner highlight labels by observing the changes in losses among different modalities. To verify the effectiveness of CLC, we further collect a large-scale highlight dataset named MovieLights. Comprehensive experiments on MovieLights and YouTube Highlights datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Code has been made available at: https://github.com/TencentYoutuResearch/HighlightDetection-CLC
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge