Renhong Cheng
Simple but Effective Compound Geometric Operations for Temporal Knowledge Graph Completion
Aug 13, 2024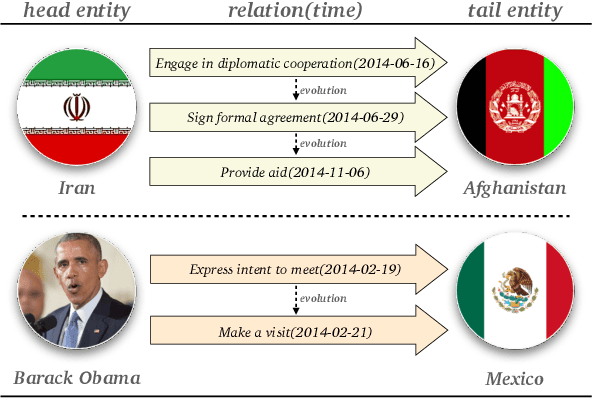
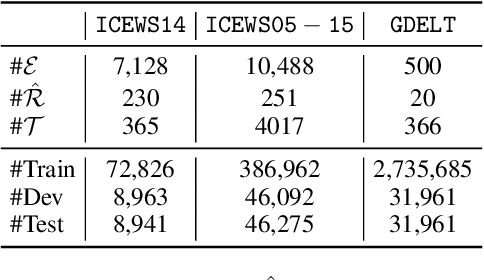
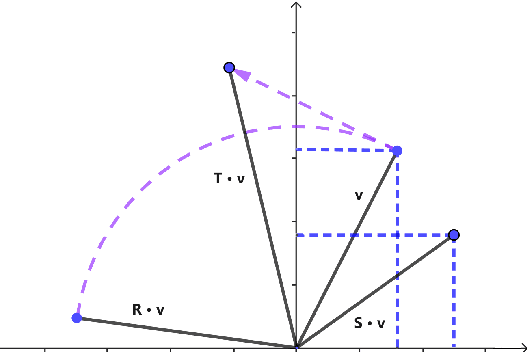
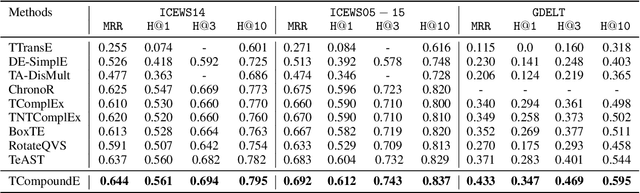
Abstract:Temporal knowledge graph completion aims to infer the missing facts in temporal knowledge graphs. Current approaches usually embed factual knowledge into continuous vector space and apply geometric operations to learn potential patterns in temporal knowledge graphs. However, these methods only adopt a single operation, which may have limitations in capturing the complex temporal dynamics present in temporal knowledge graphs. Therefore, we propose a simple but effective method, i.e. TCompoundE, which is specially designed with two geometric operations, including time-specific and relation-specific operations. We provide mathematical proofs to demonstrate the ability of TCompoundE to encode various relation patterns. Experimental results show that our proposed model significantly outperforms existing temporal knowledge graph embedding models. Our code is available at https://github.com/nk-ruiying/TCompoundE.
BvSP: Broad-view Soft Prompting for Few-Shot Aspect Sentiment Quad Prediction
Jun 11, 2024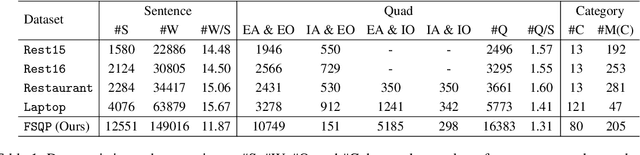


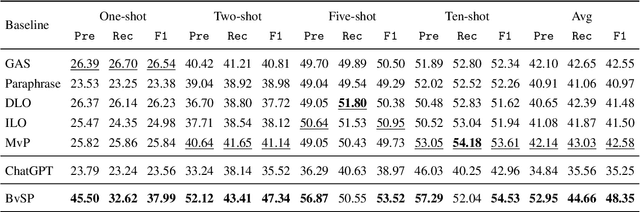
Abstract:Aspect sentiment quad prediction (ASQP) aims to predict four aspect-based elements, including aspect term, opinion term, aspect category, and sentiment polarity. In practice, unseen aspects, due to distinct data distribution, impose many challenges for a trained neural model. Motivated by this, this work formulates ASQP into the few-shot scenario, which aims for fast adaptation in real applications. Therefore, we first construct a few-shot ASQP dataset (FSQP) that contains richer categories and is more balanced for the few-shot study. Moreover, recent methods extract quads through a generation paradigm, which involves converting the input sentence into a templated target sequence. However, they primarily focus on the utilization of a single template or the consideration of different template orders, thereby overlooking the correlations among various templates. To tackle this issue, we further propose a Broadview Soft Prompting (BvSP) method that aggregates multiple templates with a broader view by taking into account the correlation between the different templates. Specifically, BvSP uses the pre-trained language model to select the most relevant k templates with Jensen-Shannon divergence. BvSP further introduces soft prompts to guide the pre-trained language model using the selected templates. Then, we aggregate the results of multi-templates by voting mechanism. Empirical results demonstrate that BvSP significantly outperforms the stateof-the-art methods under four few-shot settings and other public datasets. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/byinhao/BvSP.
Multi-Label Few-Shot Learning for Aspect Category Detection
May 29, 2021

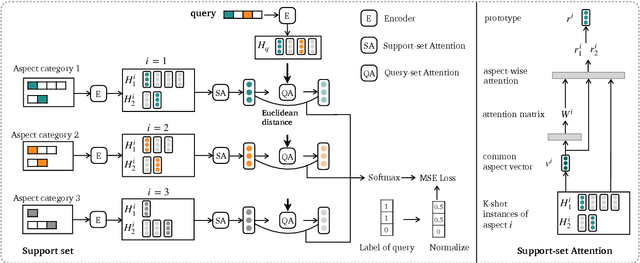
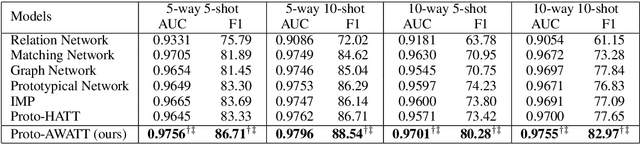
Abstract:Aspect category detection (ACD) in sentiment analysis aims to identify the aspect categories mentioned in a sentence. In this paper, we formulate ACD in the few-shot learning scenario. However, existing few-shot learning approaches mainly focus on single-label predictions. These methods can not work well for the ACD task since a sentence may contain multiple aspect categories. Therefore, we propose a multi-label few-shot learning method based on the prototypical network. To alleviate the noise, we design two effective attention mechanisms. The support-set attention aims to extract better prototypes by removing irrelevant aspects. The query-set attention computes multiple prototype-specific representations for each query instance, which are then used to compute accurate distances with the corresponding prototypes. To achieve multi-label inference, we further learn a dynamic threshold per instance by a policy network. Extensive experimental results on three datasets demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms strong baselines.
Hierarchical Ranking for Answer Selection
Feb 01, 2021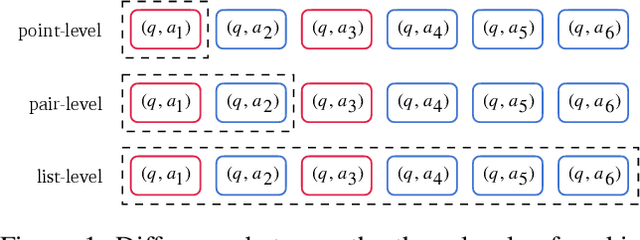
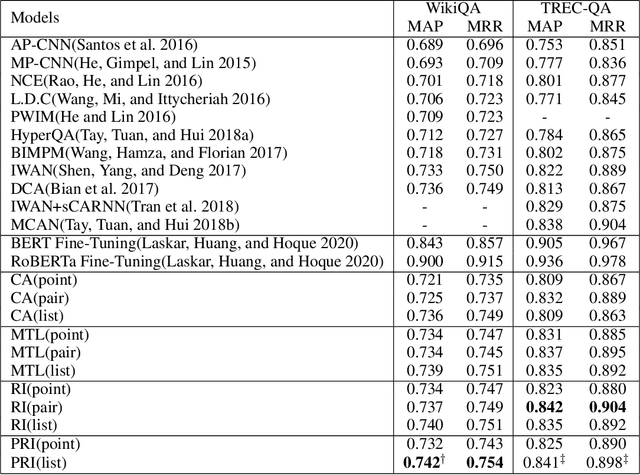
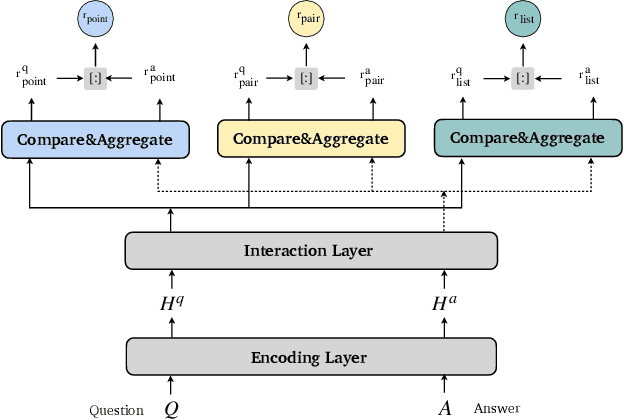
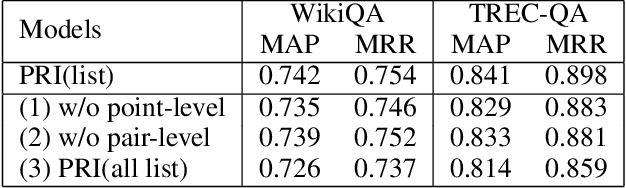
Abstract:Answer selection is a task to choose the positive answers from a pool of candidate answers for a given question. In this paper, we propose a novel strategy for answer selection, called hierarchical ranking. We introduce three levels of ranking: point-level ranking, pair-level ranking, and list-level ranking. They formulate their optimization objectives by employing supervisory information from different perspectives to achieve the same goal of ranking candidate answers. Therefore, the three levels of ranking are related and they can promote each other. We take the well-performed compare-aggregate model as the backbone and explore three schemes to implement the idea of applying the hierarchical rankings jointly: the scheme under the Multi-Task Learning (MTL) strategy, the Ranking Integration (RI) scheme, and the Progressive Ranking Integration (PRI) scheme. Experimental results on two public datasets, WikiQA and TREC-QA, demonstrate that the proposed hierarchical ranking is effective. Our method achieves state-of-the-art (non-BERT) performance on both TREC-QA and WikiQA.
Learning to Detect Opinion Snippet for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis
Sep 25, 2019



Abstract:Aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) is to predict the sentiment polarity towards a particular aspect in a sentence. Recently, this task has been widely addressed by the neural attention mechanism, which computes attention weights to softly select words for generating aspect-specific sentence representations. The attention is expected to concentrate on opinion words for accurate sentiment prediction. However, attention is prone to be distracted by noisy or misleading words, or opinion words from other aspects. In this paper, we propose an alternative hard-selection approach, which determines the start and end positions of the opinion snippet, and selects the words between these two positions for sentiment prediction. Specifically, we learn deep associations between the sentence and aspect, and the long-term dependencies within the sentence by leveraging the pre-trained BERT model. We further detect the opinion snippet by self-critical reinforcement learning. Especially, experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method and prove that our hard-selection approach outperforms soft-selection approaches when handling multi-aspect sentences.
Domain-Invariant Feature Distillation for Cross-Domain Sentiment Classification
Aug 24, 2019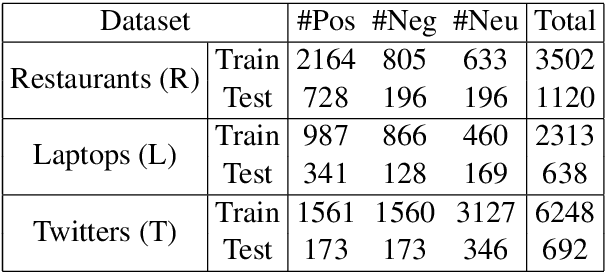
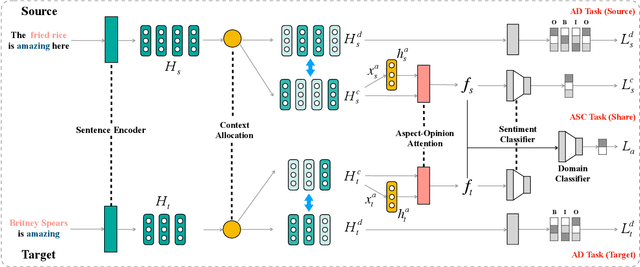
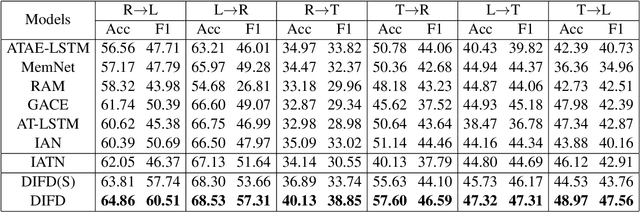
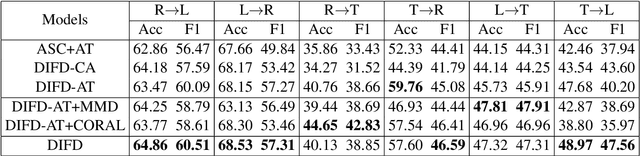
Abstract:Cross-domain sentiment classification has drawn much attention in recent years. Most existing approaches focus on learning domain-invariant representations in both the source and target domains, while few of them pay attention to the domain-specific information. Despite the non-transferability of the domain-specific information, simultaneously learning domain-dependent representations can facilitate the learning of domain-invariant representations. In this paper, we focus on aspect-level cross-domain sentiment classification, and propose to distill the domain-invariant sentiment features with the help of an orthogonal domain-dependent task, i.e. aspect detection, which is built on the aspects varying widely in different domains. We conduct extensive experiments on three public datasets and the experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
CAN: Constrained Attention Networks for Multi-Aspect Sentiment Analysis
Dec 27, 2018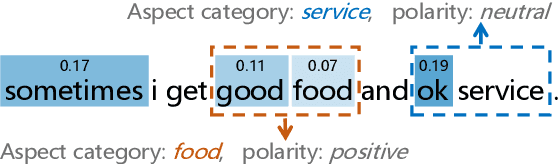
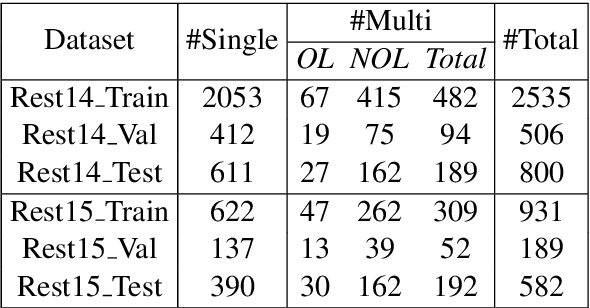
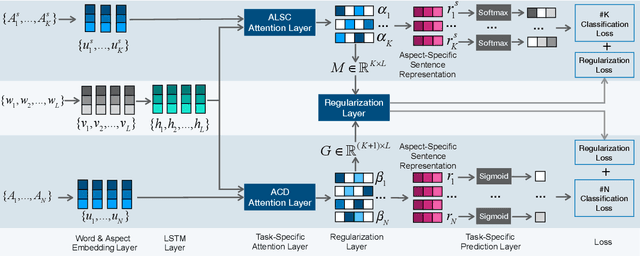
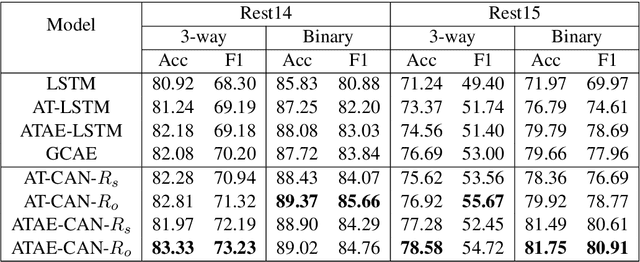
Abstract:Aspect level sentiment classification is a fine-grained sentiment analysis task, compared to the sentence level classification. A sentence usually contains one or more aspects. To detect the sentiment towards a particular aspect in a sentence, previous studies have developed various methods for generating aspect-specific sentence representations. However, these studies handle each aspect of a sentence separately. In this paper, we argue that multiple aspects of a sentence are usually orthogonal based on the observation that different aspects concentrate on different parts of the sentence. To force the orthogonality among aspects, we propose constrained attention networks (CAN) for multi-aspect sentiment analysis, which handles multiple aspects of a sentence simultaneously. Experimental results on two public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. We also extend our approach to multi-task settings, outperforming the state-of-the-arts significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge