Rahul Nadkarni
Rewriting History: A Recipe for Interventional Analyses to Study Data Effects on Model Behavior
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:We present an experimental recipe for studying the relationship between training data and language model (LM) behavior. We outline steps for intervening on data batches -- i.e., ``rewriting history'' -- and then retraining model checkpoints over that data to test hypotheses relating data to behavior. Our recipe breaks down such an intervention into stages that include selecting evaluation items from a benchmark that measures model behavior, matching relevant documents to those items, and modifying those documents before retraining and measuring the effects. We demonstrate the utility of our recipe through case studies on factual knowledge acquisition in LMs, using both cooccurrence statistics and information retrieval methods to identify documents that might contribute to knowledge learning. Our results supplement past observational analyses that link cooccurrence to model behavior, while demonstrating that extant methods for identifying relevant training documents do not fully explain an LM's ability to correctly answer knowledge questions. Overall, we outline a recipe that researchers can follow to test further hypotheses about how training data affects model behavior. Our code is made publicly available to promote future work.
AFEN: Respiratory Disease Classification using Ensemble Learning
May 08, 2024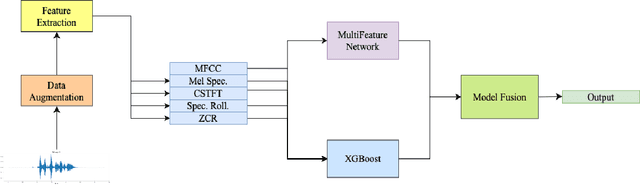
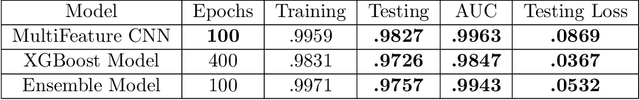
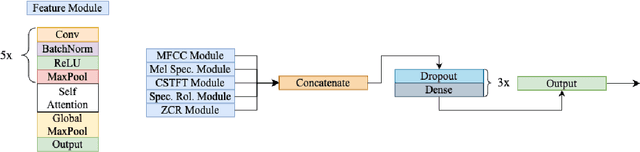
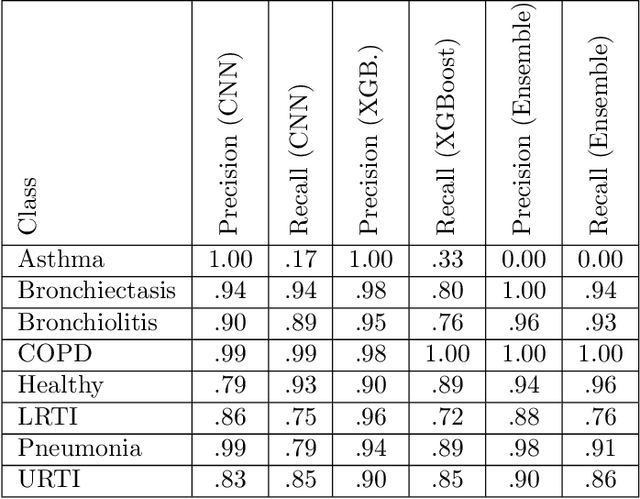
Abstract:We present AFEN (Audio Feature Ensemble Learning), a model that leverages Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and XGBoost in an ensemble learning fashion to perform state-of-the-art audio classification for a range of respiratory diseases. We use a meticulously selected mix of audio features which provide the salient attributes of the data and allow for accurate classification. The extracted features are then used as an input to two separate model classifiers 1) a multi-feature CNN classifier and 2) an XGBoost Classifier. The outputs of the two models are then fused with the use of soft voting. Thus, by exploiting ensemble learning, we achieve increased robustness and accuracy. We evaluate the performance of the model on a database of 920 respiratory sounds, which undergoes data augmentation techniques to increase the diversity of the data and generalizability of the model. We empirically verify that AFEN sets a new state-of-the-art using Precision and Recall as metrics, while decreasing training time by 60%.
Third-Party Language Model Performance Prediction from Instruction
Mar 19, 2024Abstract:Language model-based instruction-following systems have lately shown increasing performance on many benchmark tasks, demonstrating the capability of adapting to a broad variety of instructions. However, such systems are often not designed to be transparent about their limitations; a user may easily prompt a model with an instruction without any idea of whether the responses should be expected to be accurate, or if the system is even capable of performing the task. We propose a third party performance prediction framework, where a separate model is trained to predict the metric resulting from evaluating an instruction-following system on a task while assuming access only to its inputs and outputs at inference time. We perform this analysis with a variety of both open and closed instruction-following models as well as multiple performance predictors, and examine the effect of various factors such as model size, number of training tasks, and prompt format. Our findings indicate that third-party performance prediction is very challenging, and much work remains in developing predictors that can automatically reveal the limitations of modern instruction-following natural language processing systems.
Binding Language Models in Symbolic Languages
Oct 06, 2022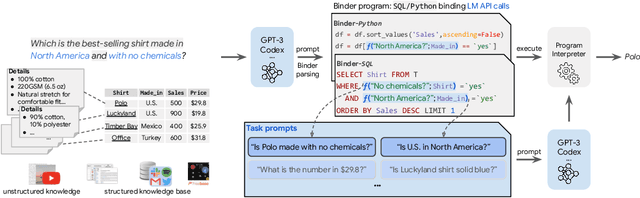
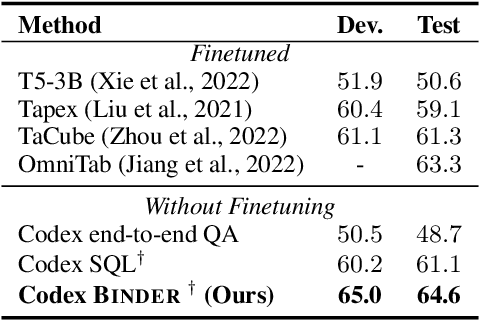

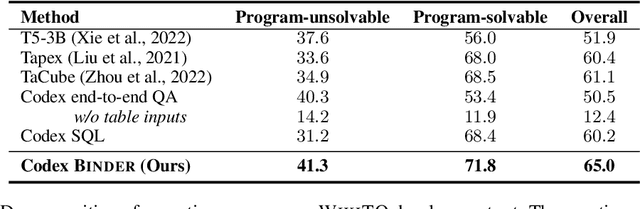
Abstract:Though end-to-end neural approaches have recently been dominating NLP tasks in both performance and ease-of-use, they lack interpretability and robustness. We propose Binder, a training-free neural-symbolic framework that maps the task input to a program, which (1) allows binding a unified API of language model (LM) functionalities to a programming language (e.g., SQL, Python) to extend its grammar coverage and thus tackle more diverse questions, (2) adopts an LM as both the program parser and the underlying model called by the API during execution, and (3) requires only a few in-context exemplar annotations. Specifically, we employ GPT-3 Codex as the LM. In the parsing stage, with only a few in-context exemplars, Codex is able to identify the part of the task input that cannot be answerable by the original programming language, correctly generate API calls to prompt Codex to solve the unanswerable part, and identify where to place the API calls while being compatible with the original grammar. In the execution stage, Codex can perform versatile functionalities (e.g., commonsense QA, information extraction) given proper prompts in the API calls. Binder achieves state-of-the-art results on WikiTableQuestions and TabFact datasets, with explicit output programs that benefit human debugging. Note that previous best systems are all finetuned on tens of thousands of task-specific samples, while Binder only uses dozens of annotations as in-context exemplars without any training. Our code is available at https://github.com/HKUNLP/Binder .
Scientific Language Models for Biomedical Knowledge Base Completion: An Empirical Study
Jun 17, 2021

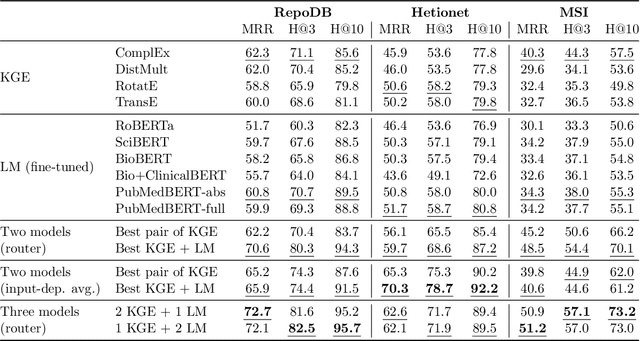

Abstract:Biomedical knowledge graphs (KGs) hold rich information on entities such as diseases, drugs, and genes. Predicting missing links in these graphs can boost many important applications, such as drug design and repurposing. Recent work has shown that general-domain language models (LMs) can serve as "soft" KGs, and that they can be fine-tuned for the task of KG completion. In this work, we study scientific LMs for KG completion, exploring whether we can tap into their latent knowledge to enhance biomedical link prediction. We evaluate several domain-specific LMs, fine-tuning them on datasets centered on drugs and diseases that we represent as KGs and enrich with textual entity descriptions. We integrate the LM-based models with KG embedding models, using a router method that learns to assign each input example to either type of model and provides a substantial boost in performance. Finally, we demonstrate the advantage of LM models in the inductive setting with novel scientific entities. Our datasets and code are made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge