Peter Bankhead
InstanSeg: an embedding-based instance segmentation algorithm optimized for accurate, efficient and portable cell segmentation
Aug 28, 2024
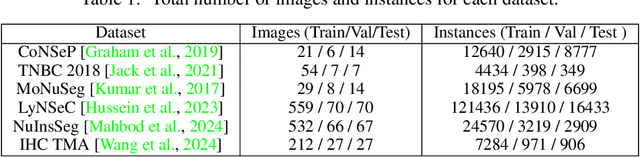

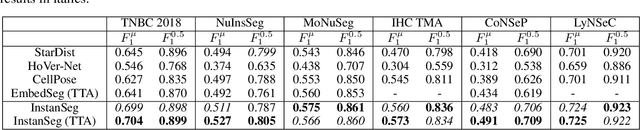
Abstract:Cell and nucleus segmentation are fundamental tasks for quantitative bioimage analysis. Despite progress in recent years, biologists and other domain experts still require novel algorithms to handle increasingly large and complex real-world datasets. These algorithms must not only achieve state-of-the-art accuracy, but also be optimized for efficiency, portability and user-friendliness. Here, we introduce InstanSeg: a novel embedding-based instance segmentation pipeline designed to identify cells and nuclei in microscopy images. Using six public cell segmentation datasets, we demonstrate that InstanSeg can significantly improve accuracy when compared to the most widely used alternative methods, while reducing the processing time by at least 60%. Furthermore, InstanSeg is designed to be fully serializable as TorchScript and supports GPU acceleration on a range of hardware. We provide an open-source implementation of InstanSeg in Python, in addition to a user-friendly, interactive QuPath extension for inference written in Java. Our code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/instanseg/instanseg .
Open and reusable deep learning for pathology with WSInfer and QuPath
Sep 08, 2023Abstract:The field of digital pathology has seen a proliferation of deep learning models in recent years. Despite substantial progress, it remains rare for other researchers and pathologists to be able to access models published in the literature and apply them to their own images. This is due to difficulties in both sharing and running models. To address these concerns, we introduce WSInfer: a new, open-source software ecosystem designed to make deep learning for pathology more streamlined and accessible. WSInfer comprises three main elements: 1) a Python package and command line tool to efficiently apply patch-based deep learning inference to whole slide images; 2) a QuPath extension that provides an alternative inference engine through user-friendly and interactive software, and 3) a model zoo, which enables pathology models and metadata to be easily shared in a standardized form. Together, these contributions aim to encourage wider reuse, exploration, and interrogation of deep learning models for research purposes, by putting them into the hands of pathologists and eliminating a need for coding experience when accessed through QuPath. The WSInfer source code is hosted on GitHub and documentation is available at https://wsinfer.readthedocs.io.
Metrics reloaded: Pitfalls and recommendations for image analysis validation
Jun 03, 2022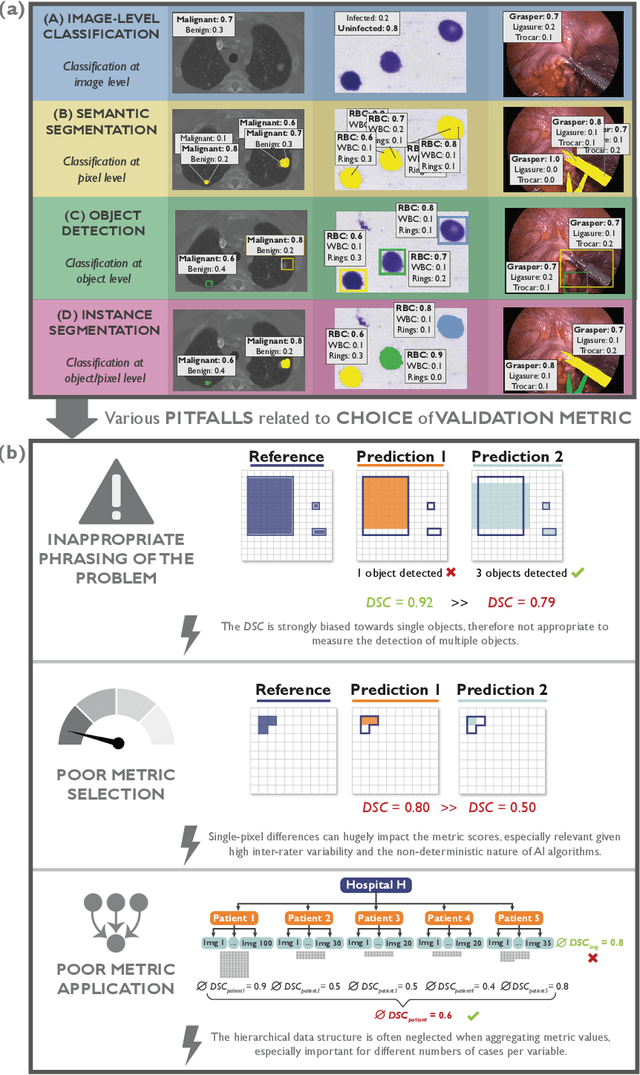
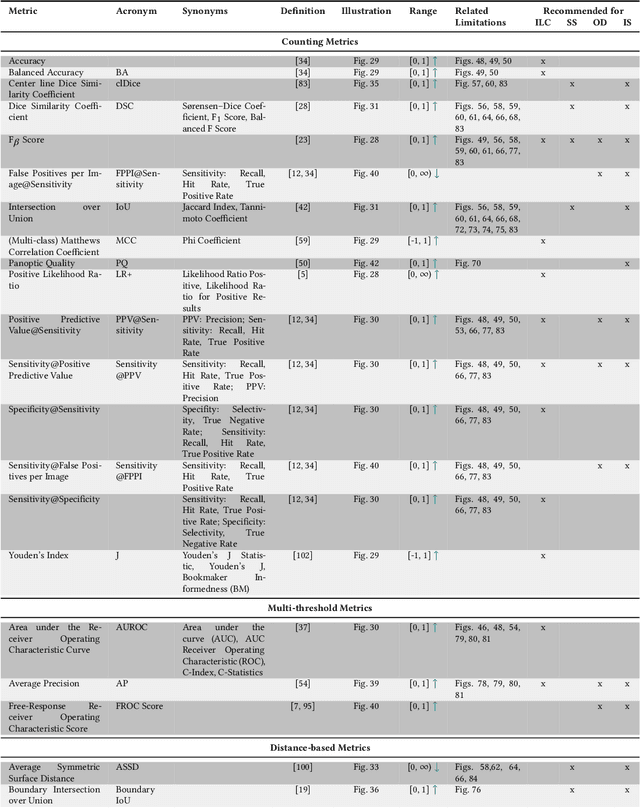
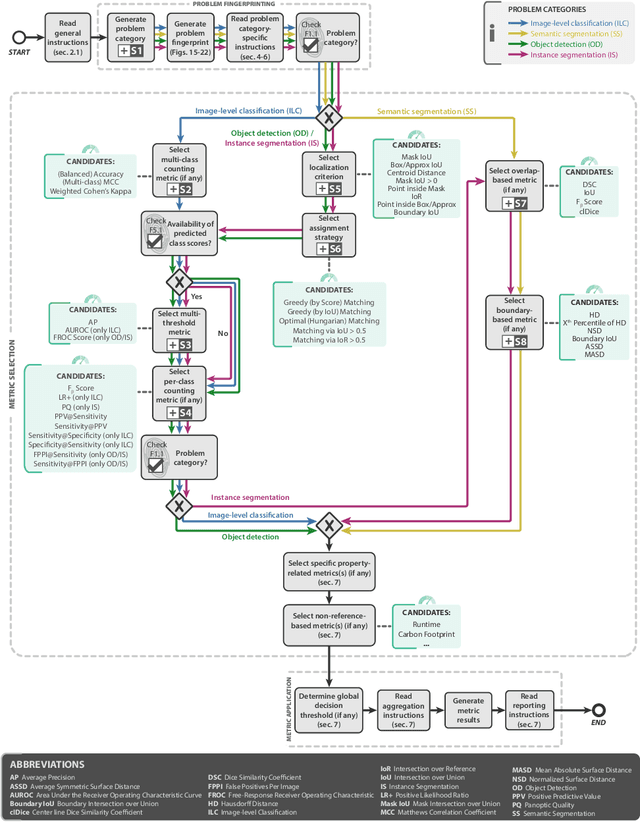
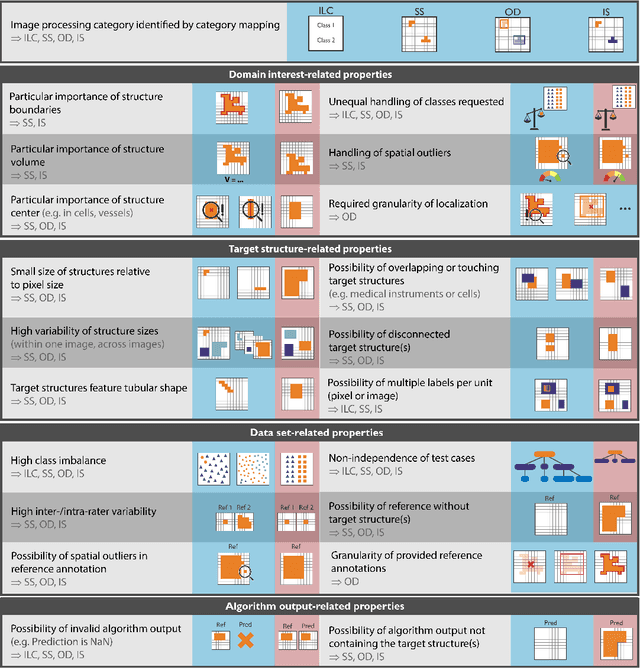
Abstract:The field of automatic biomedical image analysis crucially depends on robust and meaningful performance metrics for algorithm validation. Current metric usage, however, is often ill-informed and does not reflect the underlying domain interest. Here, we present a comprehensive framework that guides researchers towards choosing performance metrics in a problem-aware manner. Specifically, we focus on biomedical image analysis problems that can be interpreted as a classification task at image, object or pixel level. The framework first compiles domain interest-, target structure-, data set- and algorithm output-related properties of a given problem into a problem fingerprint, while also mapping it to the appropriate problem category, namely image-level classification, semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, or object detection. It then guides users through the process of selecting and applying a set of appropriate validation metrics while making them aware of potential pitfalls related to individual choices. In this paper, we describe the current status of the Metrics Reloaded recommendation framework, with the goal of obtaining constructive feedback from the image analysis community. The current version has been developed within an international consortium of more than 60 image analysis experts and will be made openly available as a user-friendly toolkit after community-driven optimization.
MITI Minimum Information guidelines for highly multiplexed tissue images
Aug 21, 2021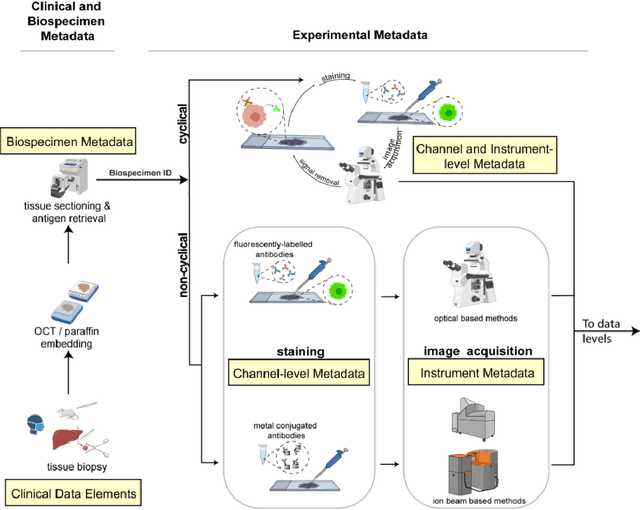
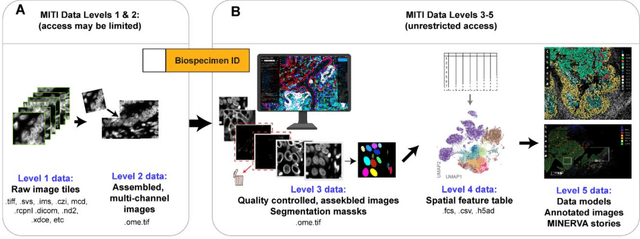
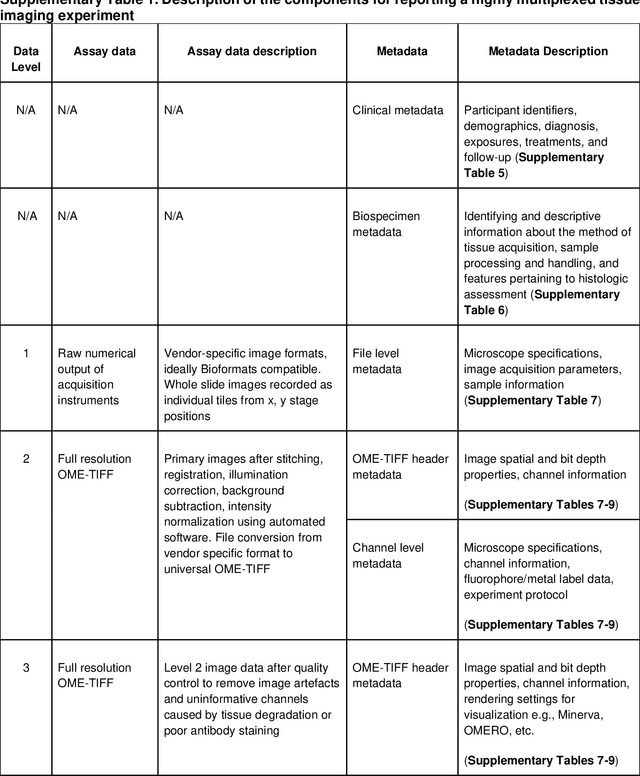
Abstract:The imminent release of atlases combining highly multiplexed tissue imaging with single cell sequencing and other omics data from human tissues and tumors creates an urgent need for data and metadata standards compliant with emerging and traditional approaches to histology. We describe the development of a Minimum Information about highly multiplexed Tissue Imaging (MITI) standard that draws on best practices from genomics and microscopy of cultured cells and model organisms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge