Peizhen Bai
Towards deployment-centric multimodal AI beyond vision and language
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Multimodal artificial intelligence (AI) integrates diverse types of data via machine learning to improve understanding, prediction, and decision-making across disciplines such as healthcare, science, and engineering. However, most multimodal AI advances focus on models for vision and language data, while their deployability remains a key challenge. We advocate a deployment-centric workflow that incorporates deployment constraints early to reduce the likelihood of undeployable solutions, complementing data-centric and model-centric approaches. We also emphasise deeper integration across multiple levels of multimodality and multidisciplinary collaboration to significantly broaden the research scope beyond vision and language. To facilitate this approach, we identify common multimodal-AI-specific challenges shared across disciplines and examine three real-world use cases: pandemic response, self-driving car design, and climate change adaptation, drawing expertise from healthcare, social science, engineering, science, sustainability, and finance. By fostering multidisciplinary dialogue and open research practices, our community can accelerate deployment-centric development for broad societal impact.
Mask prior-guided denoising diffusion improves inverse protein folding
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Inverse protein folding generates valid amino acid sequences that can fold into a desired protein structure, with recent deep-learning advances showing significant potential and competitive performance. However, challenges remain in predicting highly uncertain regions, such as those with loops and disorders. To tackle such low-confidence residue prediction, we propose a \textbf{Ma}sk \textbf{p}rior-guided denoising \textbf{Diff}usion (\textbf{MapDiff}) framework that accurately captures both structural and residue interactions for inverse protein folding. MapDiff is a discrete diffusion probabilistic model that iteratively generates amino acid sequences with reduced noise, conditioned on a given protein backbone. To incorporate structural and residue interactions, we develop a graph-based denoising network with a mask prior pre-training strategy. Moreover, in the generative process, we combine the denoising diffusion implicit model with Monte-Carlo dropout to improve uncertainty estimation. Evaluation on four challenging sequence design benchmarks shows that MapDiff significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, the in-silico sequences generated by MapDiff closely resemble the physico-chemical and structural characteristics of native proteins across different protein families and architectures.
Addressing Topic Granularity and Hallucination in Large Language Models for Topic Modelling
May 01, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) with their strong zero-shot topic extraction capabilities offer an alternative to probabilistic topic modelling and closed-set topic classification approaches. As zero-shot topic extractors, LLMs are expected to understand human instructions to generate relevant and non-hallucinated topics based on the given documents. However, LLM-based topic modelling approaches often face difficulties in generating topics with adherence to granularity as specified in human instructions, often resulting in many near-duplicate topics. Furthermore, methods for addressing hallucinated topics generated by LLMs have not yet been investigated. In this paper, we focus on addressing the issues of topic granularity and hallucinations for better LLM-based topic modelling. To this end, we introduce a novel approach that leverages Direct Preference Optimisation (DPO) to fine-tune open-source LLMs, such as Mistral-7B. Our approach does not rely on traditional human annotation to rank preferred answers but employs a reconstruction pipeline to modify raw topics generated by LLMs, thus enabling a fast and efficient training and inference framework. Comparative experiments show that our fine-tuning approach not only significantly improves the LLM's capability to produce more coherent, relevant, and precise topics, but also reduces the number of hallucinated topics.
Geometry-aware Line Graph Transformer Pre-training for Molecular Property Prediction
Sep 01, 2023



Abstract:Molecular property prediction with deep learning has gained much attention over the past years. Owing to the scarcity of labeled molecules, there has been growing interest in self-supervised learning methods that learn generalizable molecular representations from unlabeled data. Molecules are typically treated as 2D topological graphs in modeling, but it has been discovered that their 3D geometry is of great importance in determining molecular functionalities. In this paper, we propose the Geometry-aware line graph transformer (Galformer) pre-training, a novel self-supervised learning framework that aims to enhance molecular representation learning with 2D and 3D modalities. Specifically, we first design a dual-modality line graph transformer backbone to encode the topological and geometric information of a molecule. The designed backbone incorporates effective structural encodings to capture graph structures from both modalities. Then we devise two complementary pre-training tasks at the inter and intra-modality levels. These tasks provide properly supervised information and extract discriminative 2D and 3D knowledge from unlabeled molecules. Finally, we evaluate Galformer against six state-of-the-art baselines on twelve property prediction benchmarks via downstream fine-tuning. Experimental results show that Galformer consistently outperforms all baselines on both classification and regression tasks, demonstrating its effectiveness.
Interpretable bilinear attention network with domain adaptation improves drug-target prediction
Aug 03, 2022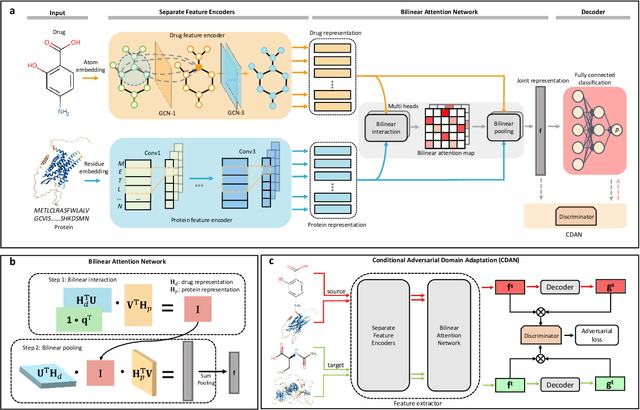
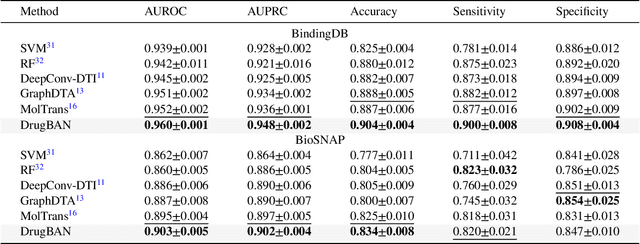


Abstract:Predicting drug-target interaction is key for drug discovery. Recent deep learning-based methods show promising performance but two challenges remain: (i) how to explicitly model and learn local interactions between drugs and targets for better prediction and interpretation; (ii) how to generalize prediction performance on novel drug-target pairs from different distribution. In this work, we propose DrugBAN, a deep bilinear attention network (BAN) framework with domain adaptation to explicitly learn pair-wise local interactions between drugs and targets, and adapt on out-of-distribution data. DrugBAN works on drug molecular graphs and target protein sequences to perform prediction, with conditional domain adversarial learning to align learned interaction representations across different distributions for better generalization on novel drug-target pairs. Experiments on three benchmark datasets under both in-domain and cross-domain settings show that DrugBAN achieves the best overall performance against five state-of-the-art baselines. Moreover, visualizing the learned bilinear attention map provides interpretable insights from prediction results.
PyKale: Knowledge-Aware Machine Learning from Multiple Sources in Python
Jun 17, 2021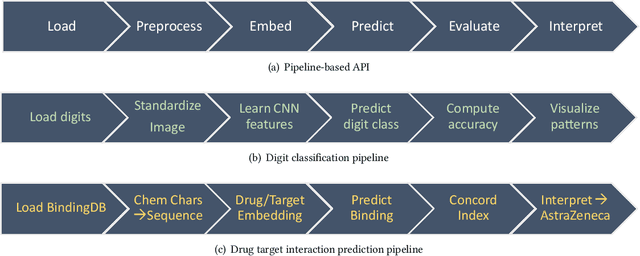
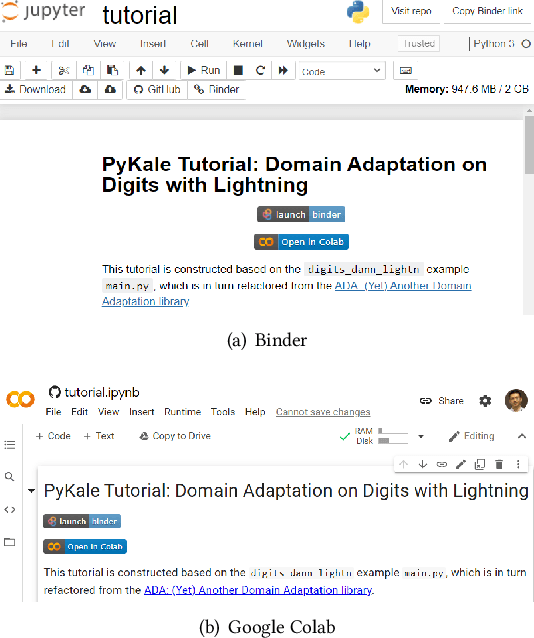
Abstract:Machine learning is a general-purpose technology holding promises for many interdisciplinary research problems. However, significant barriers exist in crossing disciplinary boundaries when most machine learning tools are developed in different areas separately. We present Pykale - a Python library for knowledge-aware machine learning on graphs, images, texts, and videos to enable and accelerate interdisciplinary research. We formulate new green machine learning guidelines based on standard software engineering practices and propose a novel pipeline-based application programming interface (API). PyKale focuses on leveraging knowledge from multiple sources for accurate and interpretable prediction, thus supporting multimodal learning and transfer learning (particularly domain adaptation) with latest deep learning and dimensionality reduction models. We build PyKale on PyTorch and leverage the rich PyTorch ecosystem. Our pipeline-based API design enforces standardization and minimalism, embracing green machine learning concepts via reducing repetitions and redundancy, reusing existing resources, and recycling learning models across areas. We demonstrate its interdisciplinary nature via examples in bioinformatics, knowledge graph, image/video recognition, and medical imaging.
GripNet: Graph Information Propagation on Supergraph for Heterogeneous Graphs
Oct 29, 2020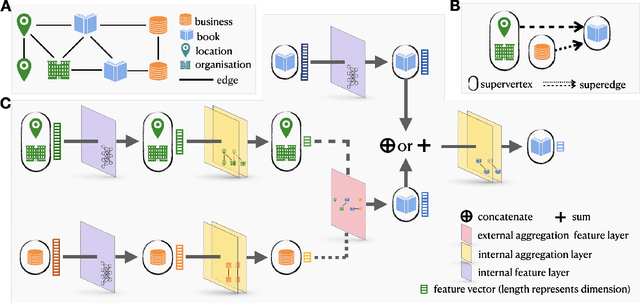



Abstract:Heterogeneous graph representation learning aims to learn low-dimensional vector representations of different types of entities and relations to empower downstream tasks. Existing methods either capture semantic relationships but indirectly leverage node/edge attributes in a complex way, or leverage node/edge attributes directly without taking semantic relationships into account. When involving multiple convolution operations, they also have poor scalability. To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes a flexible and efficient Graph information propagation Network (GripNet) framework. Specifically, we introduce a new supergraph data structure consisting of supervertices and superedges. A supervertex is a semantically-coherent subgraph. A superedge defines an information propagation path between two supervertices. GripNet learns new representations for the supervertex of interest by propagating information along the defined path using multiple layers. We construct multiple large-scale graphs and evaluate GripNet against competing methods to show its superiority in link prediction, node classification, and data integration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge