Paul Jaeger
Touchstone Benchmark: Are We on the Right Way for Evaluating AI Algorithms for Medical Segmentation?
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:How can we test AI performance? This question seems trivial, but it isn't. Standard benchmarks often have problems such as in-distribution and small-size test sets, oversimplified metrics, unfair comparisons, and short-term outcome pressure. As a consequence, good performance on standard benchmarks does not guarantee success in real-world scenarios. To address these problems, we present Touchstone, a large-scale collaborative segmentation benchmark of 9 types of abdominal organs. This benchmark is based on 5,195 training CT scans from 76 hospitals around the world and 5,903 testing CT scans from 11 additional hospitals. This diverse test set enhances the statistical significance of benchmark results and rigorously evaluates AI algorithms across various out-of-distribution scenarios. We invited 14 inventors of 19 AI algorithms to train their algorithms, while our team, as a third party, independently evaluated these algorithms on three test sets. In addition, we also evaluated pre-existing AI frameworks--which, differing from algorithms, are more flexible and can support different algorithms--including MONAI from NVIDIA, nnU-Net from DKFZ, and numerous other open-source frameworks. We are committed to expanding this benchmark to encourage more innovation of AI algorithms for the medical domain.
Automatic Cardiac Disease Assessment on cine-MRI via Time-Series Segmentation and Domain Specific Features
Jan 25, 2018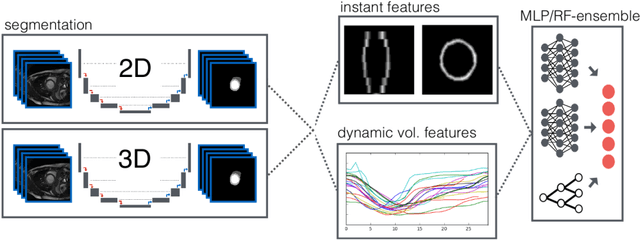
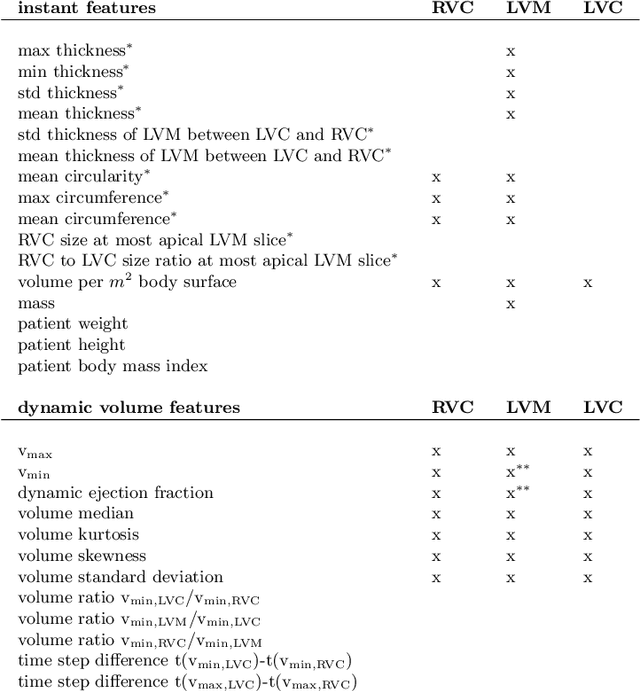
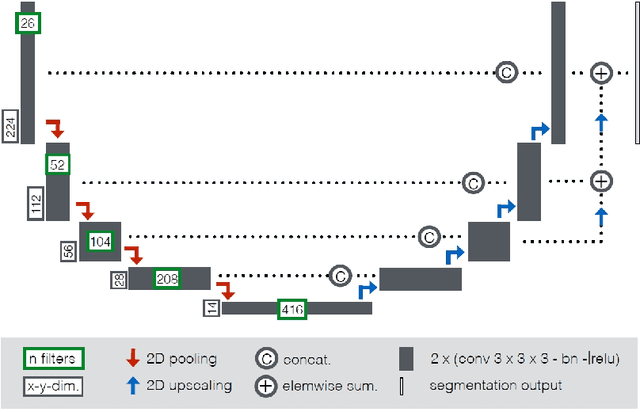
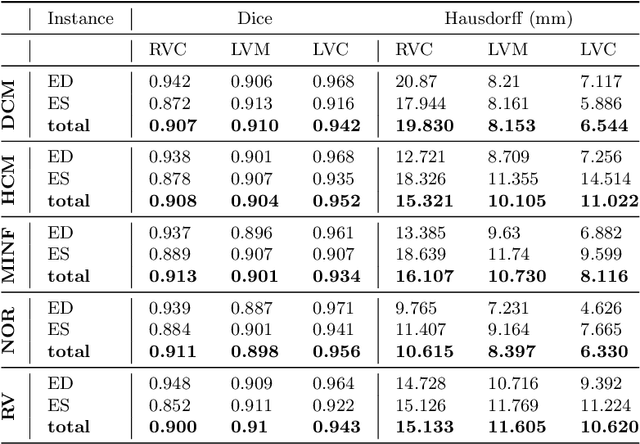
Abstract:Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging improves on diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases by providing images at high spatiotemporal resolution. Manual evaluation of these time-series, however, is expensive and prone to biased and non-reproducible outcomes. In this paper, we present a method that addresses named limitations by integrating segmentation and disease classification into a fully automatic processing pipeline. We use an ensemble of UNet inspired architectures for segmentation of cardiac structures such as the left and right ventricular cavity (LVC, RVC) and the left ventricular myocardium (LVM) on each time instance of the cardiac cycle. For the classification task, information is extracted from the segmented time-series in form of comprehensive features handcrafted to reflect diagnostic clinical procedures. Based on these features we train an ensemble of heavily regularized multilayer perceptrons (MLP) and a random forest classifier to predict the pathologic target class. We evaluated our method on the ACDC dataset (4 pathology groups, 1 healthy group) and achieve dice scores of 0.945 (LVC), 0.908 (RVC) and 0.905 (LVM) in a cross-validation over the training set (100 cases) and 0.950 (LVC), 0.923 (RVC) and 0.911 (LVM) on the test set (50 cases). We report a classification accuracy of 94% on a training set cross-validation and 92% on the test set. Our results underpin the potential of machine learning methods for accurate, fast and reproducible segmentation and computer-assisted diagnosis (CAD).
Revealing Hidden Potentials of the q-Space Signal in Breast Cancer
May 22, 2017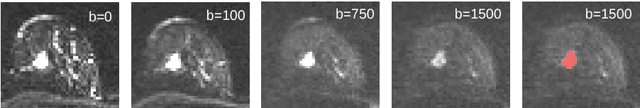
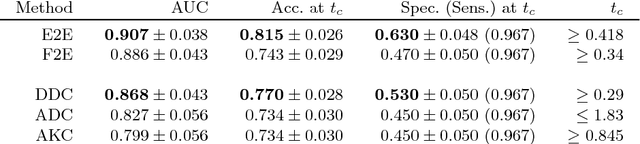
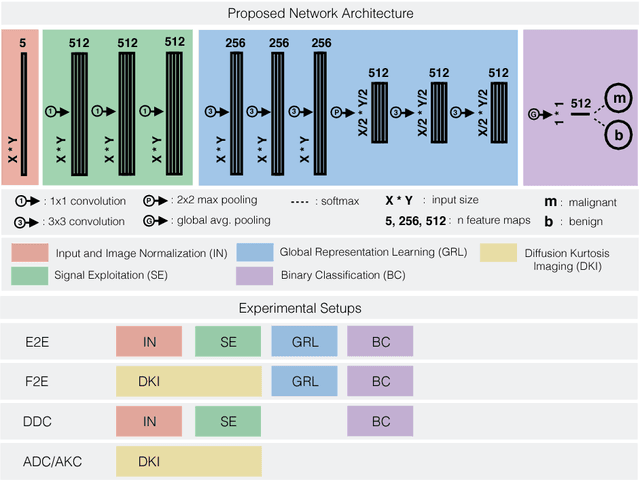
Abstract:Mammography screening for early detection of breast lesions currently suffers from high amounts of false positive findings, which result in unnecessary invasive biopsies. Diffusion-weighted MR images (DWI) can help to reduce many of these false-positive findings prior to biopsy. Current approaches estimate tissue properties by means of quantitative parameters taken from generative, biophysical models fit to the q-space encoded signal under certain assumptions regarding noise and spatial homogeneity. This process is prone to fitting instability and partial information loss due to model simplicity. We reveal unexplored potentials of the signal by integrating all data processing components into a convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture that is designed to propagate clinical target information down to the raw input images. This approach enables simultaneous and target-specific optimization of image normalization, signal exploitation, global representation learning and classification. Using a multicentric data set of 222 patients, we demonstrate that our approach significantly improves clinical decision making with respect to the current state of the art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge