Nishith Khandwala
A Generalizable Deep Learning System for Cardiac MRI
Dec 01, 2023



Abstract:Cardiac MRI allows for a comprehensive assessment of myocardial structure, function, and tissue characteristics. Here we describe a foundational vision system for cardiac MRI, capable of representing the breadth of human cardiovascular disease and health. Our deep learning model is trained via self-supervised contrastive learning, by which visual concepts in cine-sequence cardiac MRI scans are learned from the raw text of the accompanying radiology reports. We train and evaluate our model on data from four large academic clinical institutions in the United States. We additionally showcase the performance of our models on the UK BioBank, and two additional publicly available external datasets. We explore emergent zero-shot capabilities of our system, and demonstrate remarkable performance across a range of tasks; including the problem of left ventricular ejection fraction regression, and the diagnosis of 35 different conditions such as cardiac amyloidosis and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. We show that our deep learning system is capable of not only understanding the staggering complexity of human cardiovascular disease, but can be directed towards clinical problems of interest yielding impressive, clinical grade diagnostic accuracy with a fraction of the training data typically required for such tasks.
Cross-Modal Data Programming Enables Rapid Medical Machine Learning
Mar 26, 2019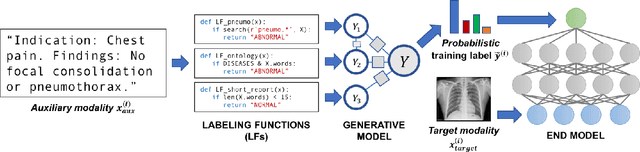
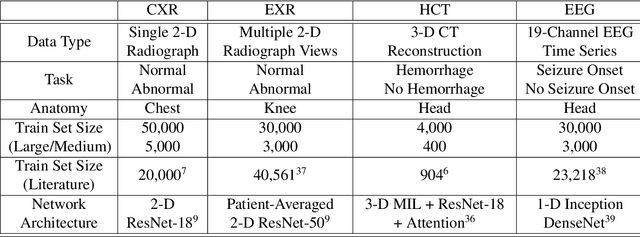
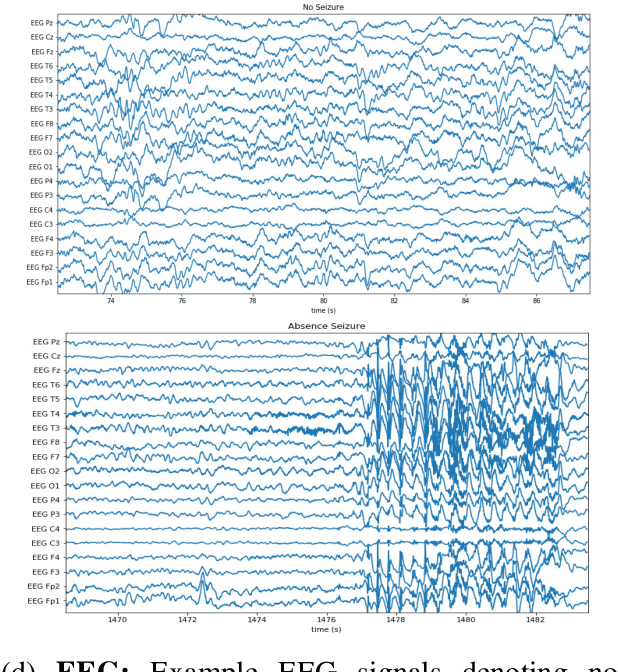
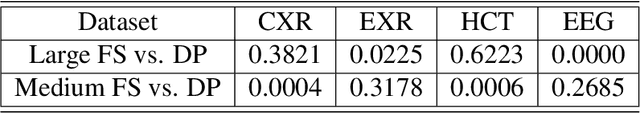
Abstract:Labeling training datasets has become a key barrier to building medical machine learning models. One strategy is to generate training labels programmatically, for example by applying natural language processing pipelines to text reports associated with imaging studies. We propose cross-modal data programming, which generalizes this intuitive strategy in a theoretically-grounded way that enables simpler, clinician-driven input, reduces required labeling time, and improves with additional unlabeled data. In this approach, clinicians generate training labels for models defined over a target modality (e.g. images or time series) by writing rules over an auxiliary modality (e.g. text reports). The resulting technical challenge consists of estimating the accuracies and correlations of these rules; we extend a recent unsupervised generative modeling technique to handle this cross-modal setting in a provably consistent way. Across four applications in radiography, computed tomography, and electroencephalography, and using only several hours of clinician time, our approach matches or exceeds the efficacy of physician-months of hand-labeling with statistical significance, demonstrating a fundamentally faster and more flexible way of building machine learning models in medicine.
Inferring Generative Model Structure with Static Analysis
Sep 07, 2017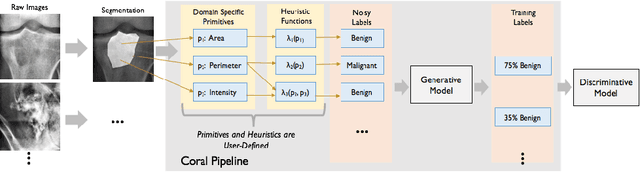

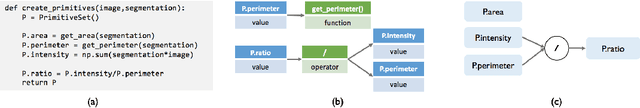
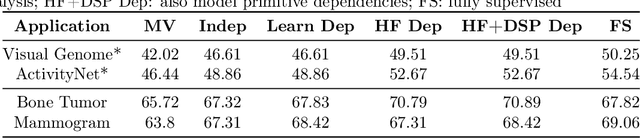
Abstract:Obtaining enough labeled data to robustly train complex discriminative models is a major bottleneck in the machine learning pipeline. A popular solution is combining multiple sources of weak supervision using generative models. The structure of these models affects training label quality, but is difficult to learn without any ground truth labels. We instead rely on these weak supervision sources having some structure by virtue of being encoded programmatically. We present Coral, a paradigm that infers generative model structure by statically analyzing the code for these heuristics, thus reducing the data required to learn structure significantly. We prove that Coral's sample complexity scales quasilinearly with the number of heuristics and number of relations found, improving over the standard sample complexity, which is exponential in $n$ for identifying $n^{\textrm{th}}$ degree relations. Experimentally, Coral matches or outperforms traditional structure learning approaches by up to 3.81 F1 points. Using Coral to model dependencies instead of assuming independence results in better performance than a fully supervised model by 3.07 accuracy points when heuristics are used to label radiology data without ground truth labels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge