Nikhil Patel
RealMedQA: A pilot biomedical question answering dataset containing realistic clinical questions
Aug 16, 2024Abstract:Clinical question answering systems have the potential to provide clinicians with relevant and timely answers to their questions. Nonetheless, despite the advances that have been made, adoption of these systems in clinical settings has been slow. One issue is a lack of question-answering datasets which reflect the real-world needs of health professionals. In this work, we present RealMedQA, a dataset of realistic clinical questions generated by humans and an LLM. We describe the process for generating and verifying the QA pairs and assess several QA models on BioASQ and RealMedQA to assess the relative difficulty of matching answers to questions. We show that the LLM is more cost-efficient for generating "ideal" QA pairs. Additionally, we achieve a lower lexical similarity between questions and answers than BioASQ which provides an additional challenge to the top two QA models, as per the results. We release our code and our dataset publicly to encourage further research.
MRAnnotator: A Multi-Anatomy Deep Learning Model for MRI Segmentation
Feb 01, 2024



Abstract:Purpose To develop a deep learning model for multi-anatomy and many-class segmentation of diverse anatomic structures on MRI imaging. Materials and Methods In this retrospective study, two datasets were curated and annotated for model development and evaluation. An internal dataset of 1022 MRI sequences from various clinical sites within a health system and an external dataset of 264 MRI sequences from an independent imaging center were collected. In both datasets, 49 anatomic structures were annotated as the ground truth. The internal dataset was divided into training, validation, and test sets and used to train and evaluate an nnU-Net model. The external dataset was used to evaluate nnU-Net model generalizability and performance in all classes on independent imaging data. Dice scores were calculated to evaluate model segmentation performance. Results The model achieved an average Dice score of 0.801 on the internal test set, and an average score of 0.814 on the complete external dataset across 49 classes. Conclusion The developed model achieves robust and generalizable segmentation of 49 anatomic structures on MRI imaging. A future direction is focused on the incorporation of additional anatomic regions and structures into the datasets and model.
VISION-MAE: A Foundation Model for Medical Image Segmentation and Classification
Feb 01, 2024Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize diagnosis and segmentation in medical imaging. However, development and clinical implementation face multiple challenges including limited data availability, lack of generalizability, and the necessity to incorporate multi-modal data effectively. A foundation model, which is a large-scale pre-trained AI model, offers a versatile base that can be adapted to a variety of specific tasks and contexts. Here, we present a novel foundation model, VISION-MAE, specifically designed for medical imaging. Specifically, VISION-MAE is trained on a dataset of 2.5 million unlabeled images from various modalities (CT, MR, PET, X-rays, and ultrasound), using self-supervised learning techniques. It is then adapted to classification and segmentation tasks using explicit labels. VISION-MAE has high label efficiency, outperforming several benchmark models in both in-domain and out-of-domain applications, and achieves high performance even with reduced availability of labeled data. This model represents a significant advancement in medical imaging AI, offering a generalizable and robust solution for improving segmentation and classification tasks while reducing the data annotation workload.
Question answering systems for health professionals at the point of care -- a systematic review
Jan 24, 2024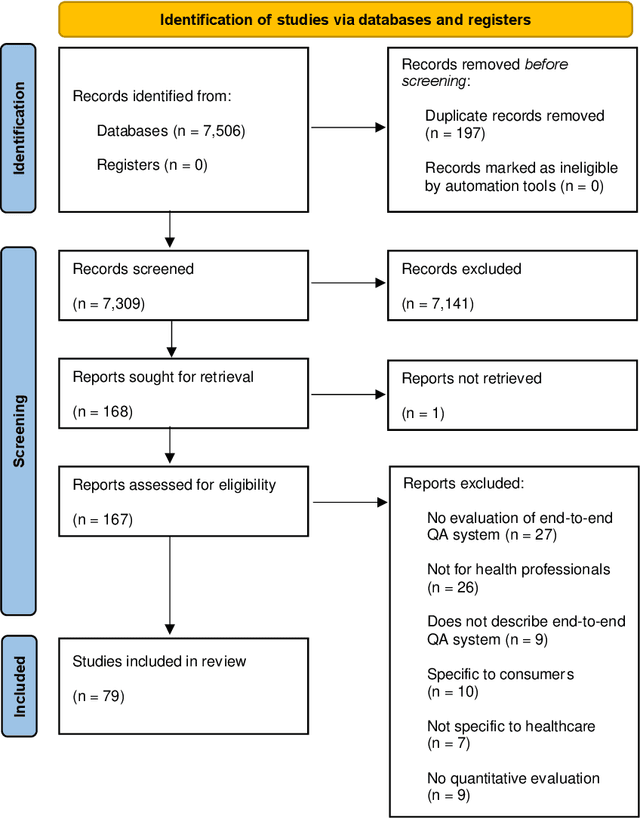
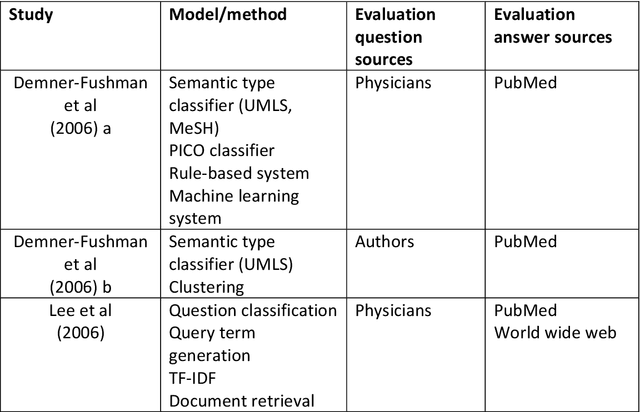
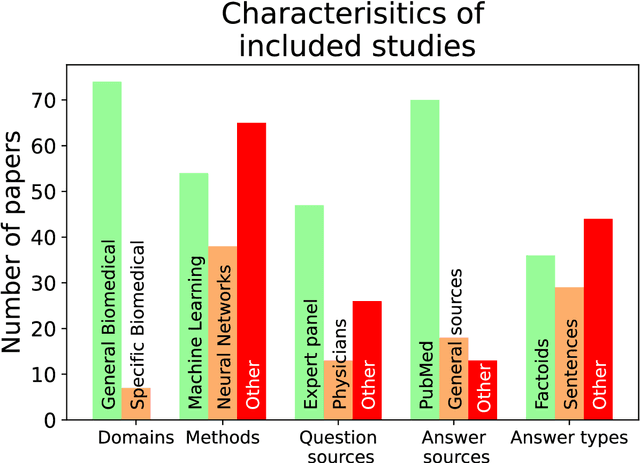

Abstract:Objective: Question answering (QA) systems have the potential to improve the quality of clinical care by providing health professionals with the latest and most relevant evidence. However, QA systems have not been widely adopted. This systematic review aims to characterize current medical QA systems, assess their suitability for healthcare, and identify areas of improvement. Materials and methods: We searched PubMed, IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library, ACL Anthology and forward and backward citations on 7th February 2023. We included peer-reviewed journal and conference papers describing the design and evaluation of biomedical QA systems. Two reviewers screened titles, abstracts, and full-text articles. We conducted a narrative synthesis and risk of bias assessment for each study. We assessed the utility of biomedical QA systems. Results: We included 79 studies and identified themes, including question realism, answer reliability, answer utility, clinical specialism, systems, usability, and evaluation methods. Clinicians' questions used to train and evaluate QA systems were restricted to certain sources, types and complexity levels. No system communicated confidence levels in the answers or sources. Many studies suffered from high risks of bias and applicability concerns. Only 8 studies completely satisfied any criterion for clinical utility, and only 7 reported user evaluations. Most systems were built with limited input from clinicians. Discussion: While machine learning methods have led to increased accuracy, most studies imperfectly reflected real-world healthcare information needs. Key research priorities include developing more realistic healthcare QA datasets and considering the reliability of answer sources, rather than merely focusing on accuracy.
Building on Huang et al. GlossBERT for Word Sense Disambiguation
Dec 14, 2021



Abstract:We propose to take on the problem ofWord Sense Disambiguation (WSD). In language, words of the same form can take different meanings depending on context. While humans easily infer the meaning or gloss of such words by their context, machines stumble on this task.As such, we intend to replicated and expand upon the results of Huang et al.GlossBERT, a model which they design to disambiguate these words (Huang et al.,2019). Specifically, we propose the following augmentations: data-set tweaking(alpha hyper-parameter), ensemble methods, and replacement of BERT with BART andALBERT. The following GitHub repository contains all code used in this report, which extends on the code made available by Huang et al.
Viola: A Topic Agnostic Generate-and-Rank Dialogue System
Aug 25, 2021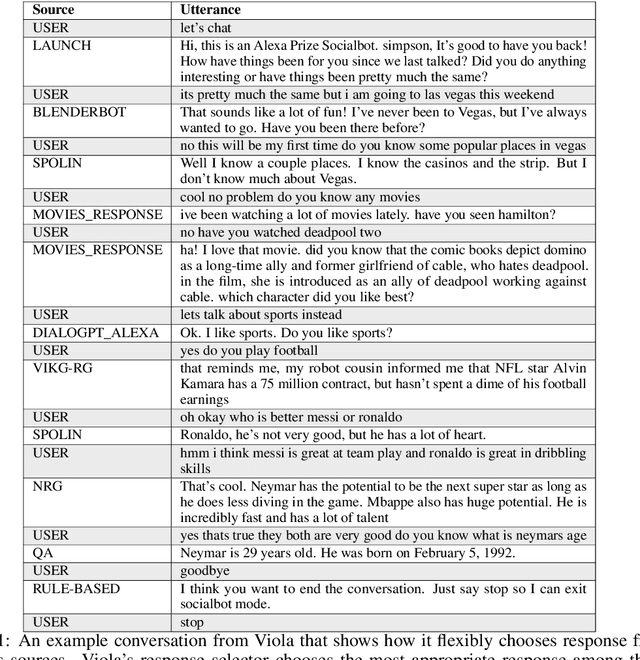
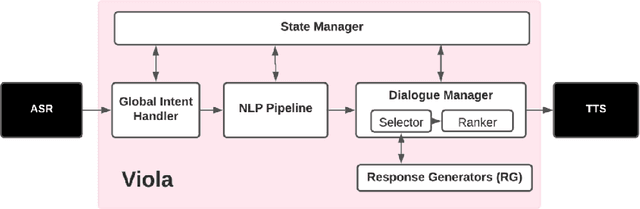
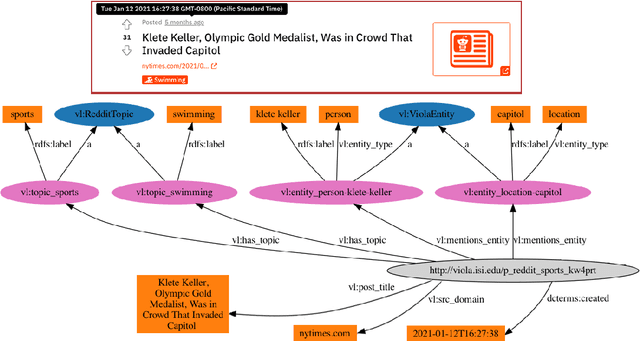
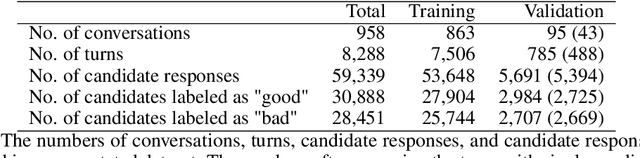
Abstract:We present Viola, an open-domain dialogue system for spoken conversation that uses a topic-agnostic dialogue manager based on a simple generate-and-rank approach. Leveraging recent advances of generative dialogue systems powered by large language models, Viola fetches a batch of response candidates from various neural dialogue models trained with different datasets and knowledge-grounding inputs. Additional responses originating from template-based generators are also considered, depending on the user's input and detected entities. The hand-crafted generators build on a dynamic knowledge graph injected with rich content that is crawled from the web and automatically processed on a daily basis. Viola's response ranker is a fine-tuned polyencoder that chooses the best response given the dialogue history. While dedicated annotations for the polyencoder alone can indirectly steer it away from choosing problematic responses, we add rule-based safety nets to detect neural degeneration and a dedicated classifier to filter out offensive content. We analyze conversations that Viola took part in for the Alexa Prize Socialbot Grand Challenge 4 and discuss the strengths and weaknesses of our approach. Lastly, we suggest future work with a focus on curating conversation data specifcially for socialbots that will contribute towards a more robust data-driven socialbot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge