Nicola Dall'Asen
MAMBO: High-Resolution Generative Approach for Mammography Images
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Mammography is the gold standard for the detection and diagnosis of breast cancer. This procedure can be significantly enhanced with Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based software, which assists radiologists in identifying abnormalities. However, training AI systems requires large and diverse datasets, which are often difficult to obtain due to privacy and ethical constraints. To address this issue, the paper introduces MAMmography ensemBle mOdel (MAMBO), a novel patch-based diffusion approach designed to generate full-resolution mammograms. Diffusion models have shown breakthrough results in realistic image generation, yet few studies have focused on mammograms, and none have successfully generated high-resolution outputs required to capture fine-grained features of small lesions. To achieve this, MAMBO integrates separate diffusion models to capture both local and global (image-level) contexts. The contextual information is then fed into the final patch-based model, significantly aiding the noise removal process. This thoughtful design enables MAMBO to generate highly realistic mammograms of up to 3840x3840 pixels. Importantly, this approach can be used to enhance the training of classification models and extended to anomaly detection. Experiments, both numerical and radiologist validation, assess MAMBO's capabilities in image generation, super-resolution, and anomaly detection, highlighting its potential to enhance mammography analysis for more accurate diagnoses and earlier lesion detection.
Retrieval-enriched zero-shot image classification in low-resource domains
Nov 01, 2024



Abstract:Low-resource domains, characterized by scarce data and annotations, present significant challenges for language and visual understanding tasks, with the latter much under-explored in the literature. Recent advancements in Vision-Language Models (VLM) have shown promising results in high-resource domains but fall short in low-resource concepts that are under-represented (e.g. only a handful of images per category) in the pre-training set. We tackle the challenging task of zero-shot low-resource image classification from a novel perspective. By leveraging a retrieval-based strategy, we achieve this in a training-free fashion. Specifically, our method, named CoRE (Combination of Retrieval Enrichment), enriches the representation of both query images and class prototypes by retrieving relevant textual information from large web-crawled databases. This retrieval-based enrichment significantly boosts classification performance by incorporating the broader contextual information relevant to the specific class. We validate our method on a newly established benchmark covering diverse low-resource domains, including medical imaging, rare plants, and circuits. Our experiments demonstrate that CORE outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods that rely on synthetic data generation and model fine-tuning.
AL-GTD: Deep Active Learning for Gaze Target Detection
Sep 27, 2024



Abstract:Gaze target detection aims at determining the image location where a person is looking. While existing studies have made significant progress in this area by regressing accurate gaze heatmaps, these achievements have largely relied on access to extensive labeled datasets, which demands substantial human labor. In this paper, our goal is to reduce the reliance on the size of labeled training data for gaze target detection. To achieve this, we propose AL-GTD, an innovative approach that integrates supervised and self-supervised losses within a novel sample acquisition function to perform active learning (AL). Additionally, it utilizes pseudo-labeling to mitigate distribution shifts during the training phase. AL-GTD achieves the best of all AUC results by utilizing only 40-50% of the training data, in contrast to state-of-the-art (SOTA) gaze target detectors requiring the entire training dataset to achieve the same performance. Importantly, AL-GTD quickly reaches satisfactory performance with 10-20% of the training data, showing the effectiveness of our acquisition function, which is able to acquire the most informative samples. We provide a comprehensive experimental analysis by adapting several AL methods for the task. AL-GTD outperforms AL competitors, simultaneously exhibiting superior performance compared to SOTA gaze target detectors when all are trained within a low-data regime. Code is available at https://github.com/francescotonini/al-gtd.
Adv-KD: Adversarial Knowledge Distillation for Faster Diffusion Sampling
May 31, 2024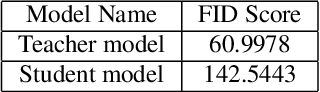
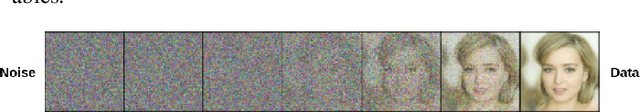
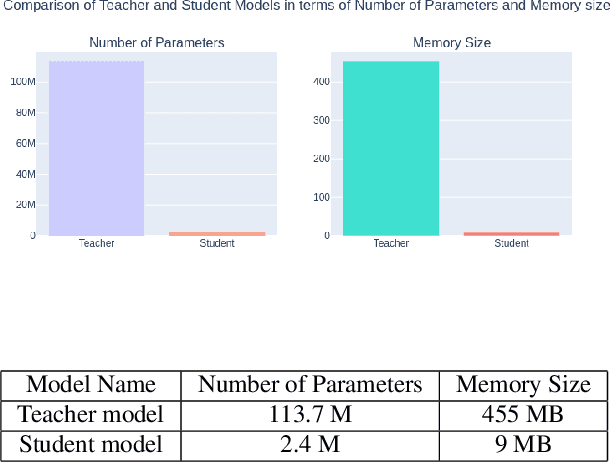
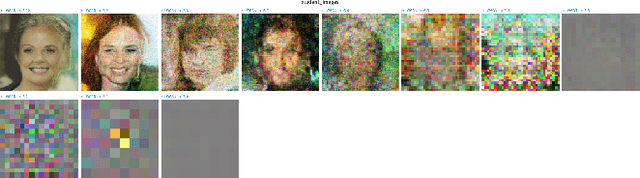
Abstract:Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DPMs) have emerged as a powerful class of deep generative models, achieving remarkable performance in image synthesis tasks. However, these models face challenges in terms of widespread adoption due to their reliance on sequential denoising steps during sample generation. This dependence leads to substantial computational requirements, making them unsuitable for resource-constrained or real-time processing systems. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method that integrates denoising phases directly into the model's architecture, thereby reducing the need for resource-intensive computations. Our approach combines diffusion models with generative adversarial networks (GANs) through knowledge distillation, enabling more efficient training and evaluation. By utilizing a pre-trained diffusion model as a teacher model, we train a student model through adversarial learning, employing layerwise transformations for denoising and submodules for predicting the teacher model's output at various points in time. This integration significantly reduces the number of parameters and denoising steps required, leading to improved sampling speed at test time. We validate our method with extensive experiments, demonstrating comparable performance with reduced computational requirements compared to existing approaches. By enabling the deployment of diffusion models on resource-constrained devices, our research mitigates their computational burden and paves the way for wider accessibility and practical use across the research community and end-users. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/kidist-amde/Adv-KD
Diversified in-domain synthesis with efficient fine-tuning for few-shot classification
Dec 07, 2023Abstract:Few-shot image classification aims to learn an image classifier using only a small set of labeled examples per class. A recent research direction for improving few-shot classifiers involves augmenting the labelled samples with synthetic images created by state-of-the-art text-to-image generation models. Following this trend, we propose Diversified In-domain Synthesis with Efficient Fine-tuning (DISEF), a novel approach which addresses the generalization challenge in few-shot learning using synthetic data. DISEF consists of two main components. First, we propose a novel text-to-image augmentation pipeline that, by leveraging the real samples and their rich semantics coming from an advanced captioning model, promotes in-domain sample diversity for better generalization. Second, we emphasize the importance of effective model fine-tuning in few-shot recognition, proposing to use Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for joint adaptation of the text and image encoders in a Vision Language Model. We validate our method in ten different benchmarks, consistently outperforming baselines and establishing a new state-of-the-art for few-shot classification. Code is available at https://github.com/vturrisi/disef.
Collaborative Neural Painting
Dec 04, 2023Abstract:The process of painting fosters creativity and rational planning. However, existing generative AI mostly focuses on producing visually pleasant artworks, without emphasizing the painting process. We introduce a novel task, Collaborative Neural Painting (CNP), to facilitate collaborative art painting generation between humans and machines. Given any number of user-input brushstrokes as the context or just the desired object class, CNP should produce a sequence of strokes supporting the completion of a coherent painting. Importantly, the process can be gradual and iterative, so allowing users' modifications at any phase until the completion. Moreover, we propose to solve this task using a painting representation based on a sequence of parametrized strokes, which makes it easy both editing and composition operations. These parametrized strokes are processed by a Transformer-based architecture with a novel attention mechanism to model the relationship between the input strokes and the strokes to complete. We also propose a new masking scheme to reflect the interactive nature of CNP and adopt diffusion models as the basic learning process for its effectiveness and diversity in the generative field. Finally, to develop and validate methods on the novel task, we introduce a new dataset of painted objects and an evaluation protocol to benchmark CNP both quantitatively and qualitatively. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach and the potential of the CNP task as a promising avenue for future research.
Unsupervised Video Anomaly Detection with Diffusion Models Conditioned on Compact Motion Representations
Jul 19, 2023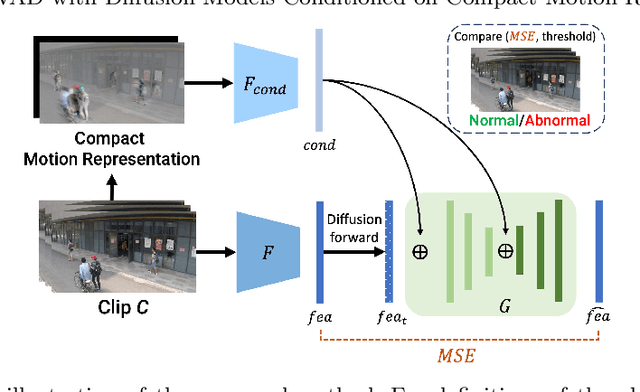
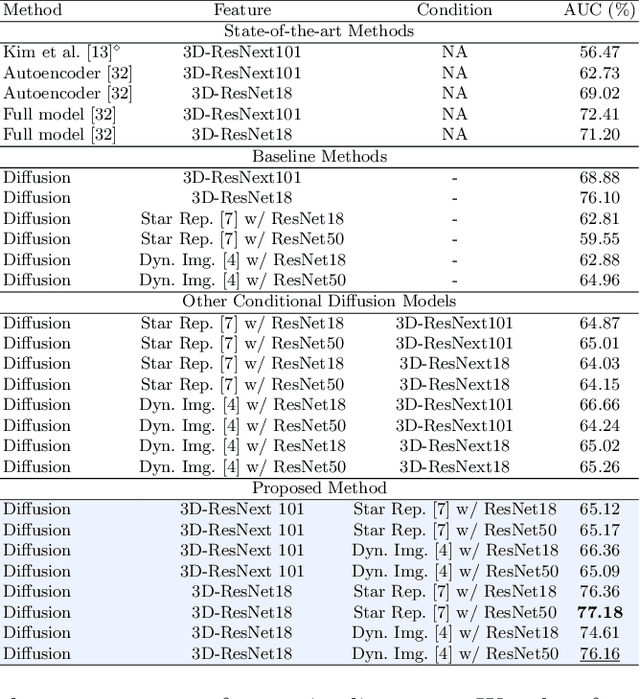
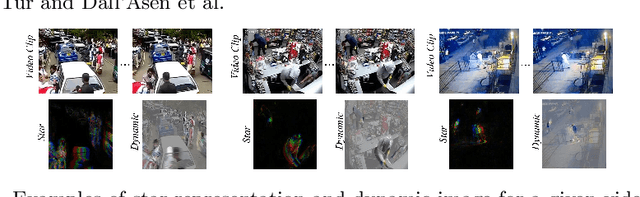

Abstract:This paper aims to address the unsupervised video anomaly detection (VAD) problem, which involves classifying each frame in a video as normal or abnormal, without any access to labels. To accomplish this, the proposed method employs conditional diffusion models, where the input data is the spatiotemporal features extracted from a pre-trained network, and the condition is the features extracted from compact motion representations that summarize a given video segment in terms of its motion and appearance. Our method utilizes a data-driven threshold and considers a high reconstruction error as an indicator of anomalous events. This study is the first to utilize compact motion representations for VAD and the experiments conducted on two large-scale VAD benchmarks demonstrate that they supply relevant information to the diffusion model, and consequently improve VAD performances w.r.t the prior art. Importantly, our method exhibits better generalization performance across different datasets, notably outperforming both the state-of-the-art and baseline methods. The code of our method is available at https://github.com/AnilOsmanTur/conditioned_video_anomaly_diffusion
Object-aware Gaze Target Detection
Jul 18, 2023Abstract:Gaze target detection aims to predict the image location where the person is looking and the probability that a gaze is out of the scene. Several works have tackled this task by regressing a gaze heatmap centered on the gaze location, however, they overlooked decoding the relationship between the people and the gazed objects. This paper proposes a Transformer-based architecture that automatically detects objects (including heads) in the scene to build associations between every head and the gazed-head/object, resulting in a comprehensive, explainable gaze analysis composed of: gaze target area, gaze pixel point, the class and the image location of the gazed-object. Upon evaluation of the in-the-wild benchmarks, our method achieves state-of-the-art results on all metrics (up to 2.91% gain in AUC, 50% reduction in gaze distance, and 9% gain in out-of-frame average precision) for gaze target detection and 11-13% improvement in average precision for the classification and the localization of the gazed-objects. The code of the proposed method is available https://github.com/francescotonini/object-aware-gaze-target-detection
Exploring Diffusion Models for Unsupervised Video Anomaly Detection
Apr 12, 2023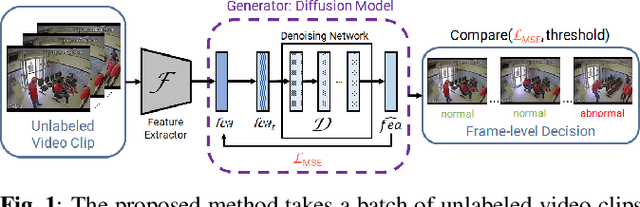
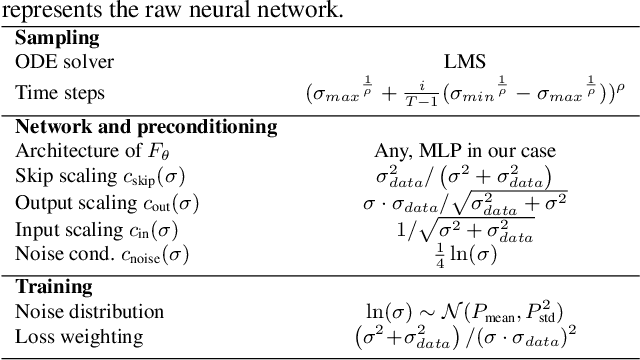
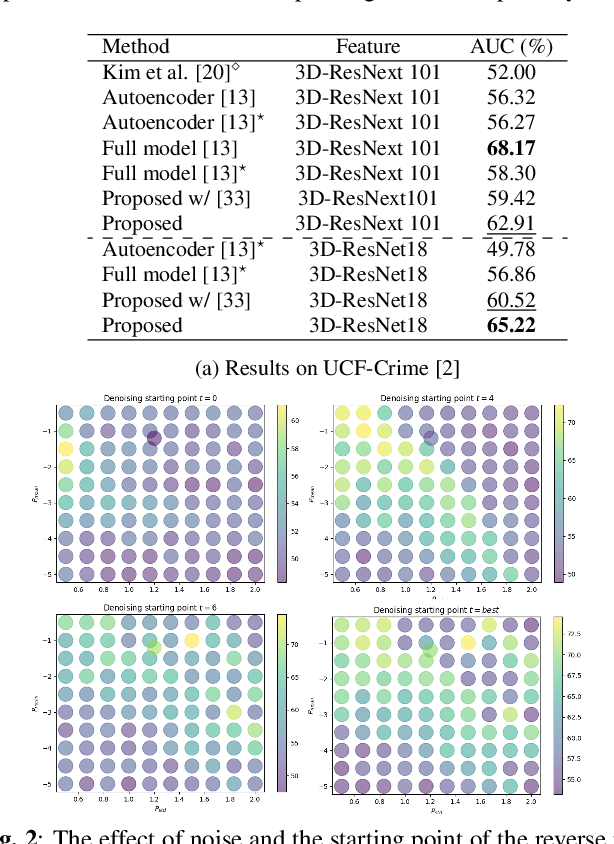
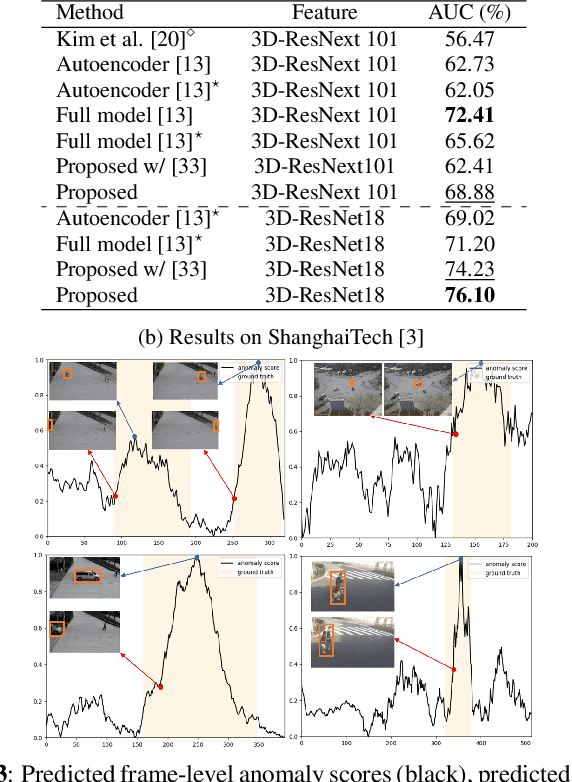
Abstract:This paper investigates the performance of diffusion models for video anomaly detection (VAD) within the most challenging but also the most operational scenario in which the data annotations are not used. As being sparse, diverse, contextual, and often ambiguous, detecting abnormal events precisely is a very ambitious task. To this end, we rely only on the information-rich spatio-temporal data, and the reconstruction power of the diffusion models such that a high reconstruction error is utilized to decide the abnormality. Experiments performed on two large-scale video anomaly detection datasets demonstrate the consistent improvement of the proposed method over the state-of-the-art generative models while in some cases our method achieves better scores than the more complex models. This is the first study using a diffusion model and examining its parameters' influence to present guidance for VAD in surveillance scenarios.
Graph-based Generative Face Anonymisation with Pose Preservation
Dec 10, 2021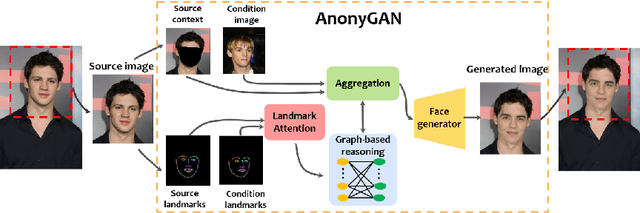
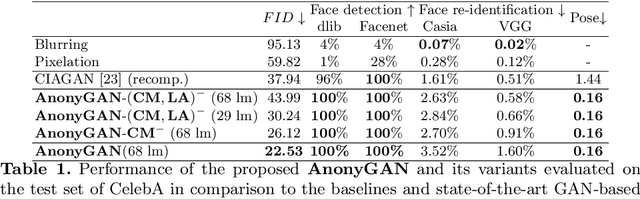
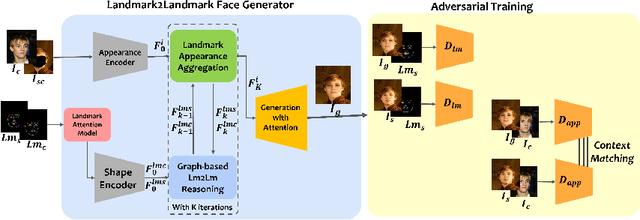
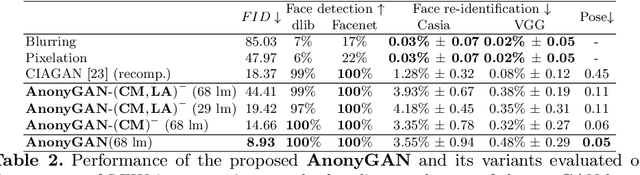
Abstract:We propose AnonyGAN, a GAN-based solution for face anonymisation which replaces the visual information corresponding to a source identity with a condition identity provided as any single image. With the goal to maintain the geometric attributes of the source face, i.e., the facial pose and expression, and to promote more natural face generation, we propose to exploit a Bipartite Graph to explicitly model the relations between the facial landmarks of the source identity and the ones of the condition identity through a deep model. We further propose a landmark attention model to relax the manual selection of facial landmarks, allowing the network to weight the landmarks for the best visual naturalness and pose preservation. Finally, to facilitate the appearance learning, we propose a hybrid training strategy to address the challenge caused by the lack of direct pixel-level supervision. We evaluate our method and its variants on two public datasets, CelebA and LFW, in terms of visual naturalness, facial pose preservation and of its impacts on face detection and re-identification. We prove that AnonyGAN significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of visual naturalness, face detection and pose preservation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge