Naoya Takeishi
A Temporal Difference Method for Stochastic Continuous Dynamics
May 21, 2025Abstract:For continuous systems modeled by dynamical equations such as ODEs and SDEs, Bellman's principle of optimality takes the form of the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) equation, which provides the theoretical target of reinforcement learning (RL). Although recent advances in RL successfully leverage this formulation, the existing methods typically assume the underlying dynamics are known a priori because they need explicit access to the coefficient functions of dynamical equations to update the value function following the HJB equation. We address this inherent limitation of HJB-based RL; we propose a model-free approach still targeting the HJB equation and propose the corresponding temporal difference method. We demonstrate its potential advantages over transition kernel-based formulations, both qualitatively and empirically. The proposed formulation paves the way toward bridging stochastic optimal control and model-free reinforcement learning.
Kolmogorov-Smirnov GAN
Jun 28, 2024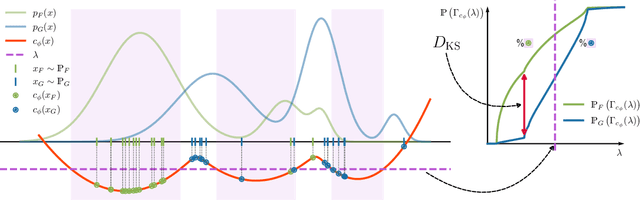
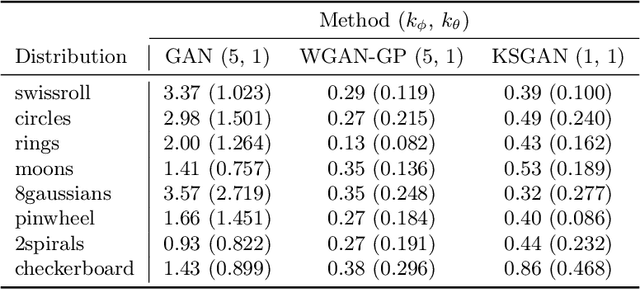
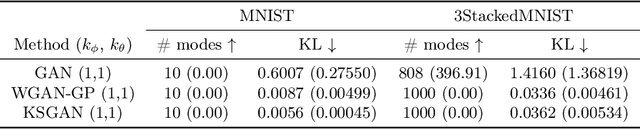
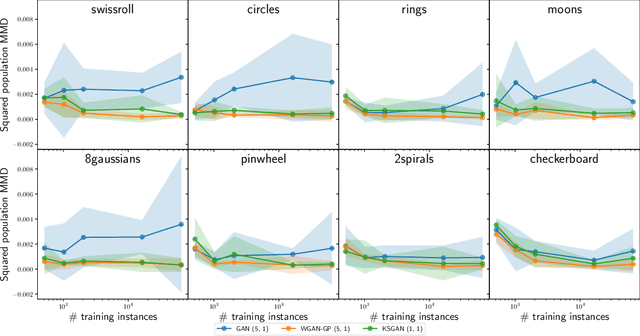
Abstract:We propose a novel deep generative model, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov Generative Adversarial Network (KSGAN). Unlike existing approaches, KSGAN formulates the learning process as a minimization of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) distance, generalized to handle multivariate distributions. This distance is calculated using the quantile function, which acts as the critic in the adversarial training process. We formally demonstrate that minimizing the KS distance leads to the trained approximate distribution aligning with the target distribution. We propose an efficient implementation and evaluate its effectiveness through experiments. The results show that KSGAN performs on par with existing adversarial methods, exhibiting stability during training, resistance to mode dropping and collapse, and tolerance to variations in hyperparameter settings. Additionally, we review the literature on the Generalized KS test and discuss the connections between KSGAN and existing adversarial generative models.
Calibrating Neural Simulation-Based Inference with Differentiable Coverage Probability
Oct 20, 2023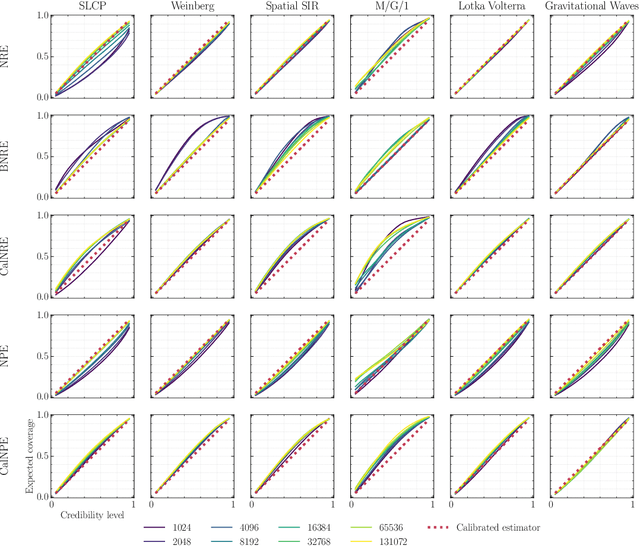
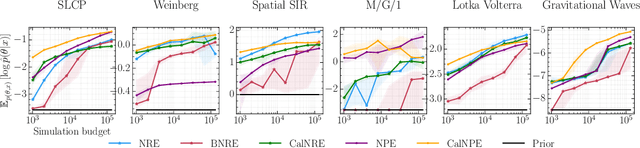
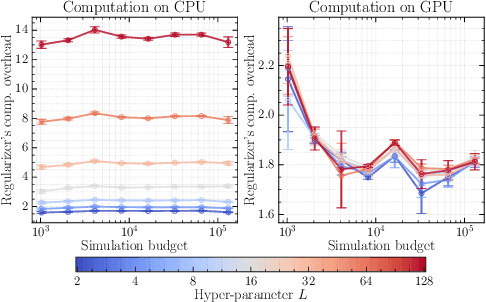
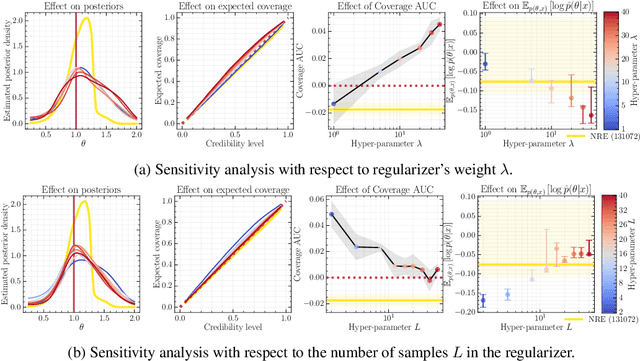
Abstract:Bayesian inference allows expressing the uncertainty of posterior belief under a probabilistic model given prior information and the likelihood of the evidence. Predominantly, the likelihood function is only implicitly established by a simulator posing the need for simulation-based inference (SBI). However, the existing algorithms can yield overconfident posteriors (Hermans *et al.*, 2022) defeating the whole purpose of credibility if the uncertainty quantification is inaccurate. We propose to include a calibration term directly into the training objective of the neural model in selected amortized SBI techniques. By introducing a relaxation of the classical formulation of calibration error we enable end-to-end backpropagation. The proposed method is not tied to any particular neural model and brings moderate computational overhead compared to the profits it introduces. It is directly applicable to existing computational pipelines allowing reliable black-box posterior inference. We empirically show on six benchmark problems that the proposed method achieves competitive or better results in terms of coverage and expected posterior density than the previously existing approaches.
Sample-Efficient On-Policy Imitation Learning from Observations
Jun 16, 2023Abstract:Imitation learning from demonstrations (ILD) aims to alleviate numerous shortcomings of reinforcement learning through the use of demonstrations. However, in most real-world applications, expert action guidance is absent, making the use of ILD impossible. Instead, we consider imitation learning from observations (ILO), where no expert actions are provided, making it a significantly more challenging problem to address. Existing methods often employ on-policy learning, which is known to be sample-costly. This paper presents SEILO, a novel sample-efficient on-policy algorithm for ILO, that combines standard adversarial imitation learning with inverse dynamics modeling. This approach enables the agent to receive feedback from both the adversarial procedure and a behavior cloning loss. We empirically demonstrate that our proposed algorithm requires fewer interactions with the environment to achieve expert performance compared to other state-of-the-art on-policy ILO and ILD methods.
Adaptive action supervision in reinforcement learning from real-world multi-agent demonstrations
May 22, 2023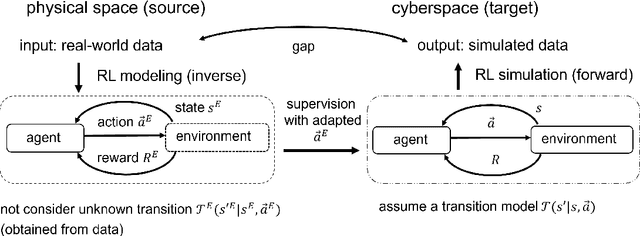
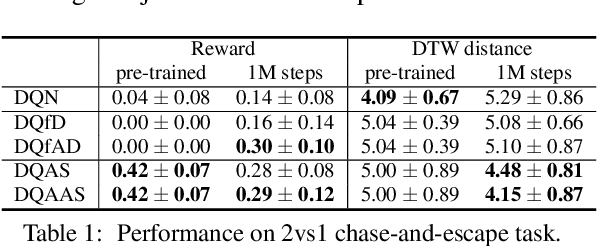
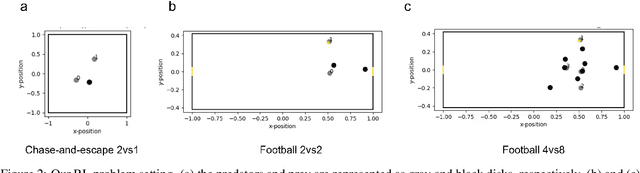

Abstract:Modeling of real-world biological multi-agents is a fundamental problem in various scientific and engineering fields. Reinforcement learning (RL) is a powerful framework to generate flexible and diverse behaviors in cyberspace; however, when modeling real-world biological multi-agents, there is a domain gap between behaviors in the source (i.e., real-world data) and the target (i.e., cyberspace for RL), and the source environment parameters are usually unknown. In this paper, we propose a method for adaptive action supervision in RL from real-world demonstrations in multi-agent scenarios. We adopt an approach that combines RL and supervised learning by selecting actions of demonstrations in RL based on the minimum distance of dynamic time warping for utilizing the information of the unknown source dynamics. This approach can be easily applied to many existing neural network architectures and provide us with an RL model balanced between reproducibility as imitation and generalization ability to obtain rewards in cyberspace. In the experiments, using chase-and-escape and football tasks with the different dynamics between the unknown source and target environments, we show that our approach achieved a balance between the reproducibility and the generalization ability compared with the baselines. In particular, we used the tracking data of professional football players as expert demonstrations in football and show successful performances despite the larger gap between behaviors in the source and target environments than the chase-and-escape task.
Deep Grey-Box Modeling With Adaptive Data-Driven Models Toward Trustworthy Estimation of Theory-Driven Models
Oct 24, 2022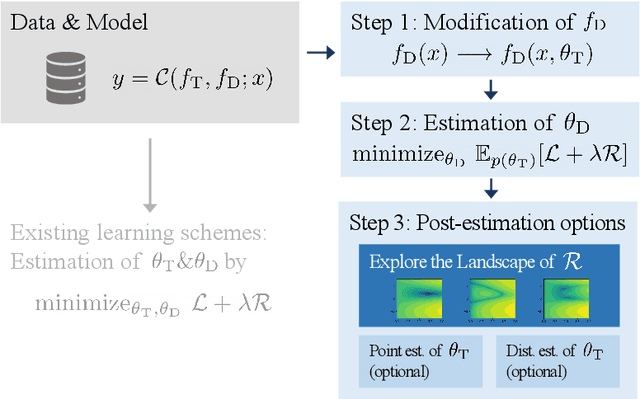
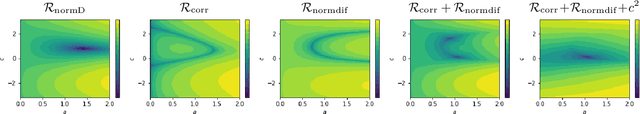
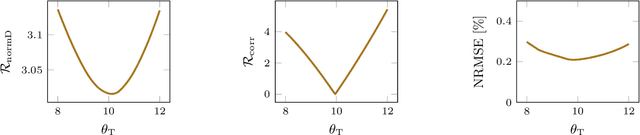
Abstract:The combination of deep neural nets and theory-driven models, which we call deep grey-box modeling, can be inherently interpretable to some extent thanks to the theory backbone. Deep grey-box models are usually learned with a regularized risk minimization to prevent a theory-driven part from being overwritten and ignored by a deep neural net. However, an estimation of the theory-driven part obtained by uncritically optimizing a regularizer can hardly be trustworthy when we are not sure what regularizer is suitable for the given data, which may harm the interpretability. Toward a trustworthy estimation of the theory-driven part, we should analyze regularizers' behavior to compare different candidates and to justify a specific choice. In this paper, we present a framework that enables us to analyze a regularizer's behavior empirically with a slight change in the neural net's architecture and the training objective.
Estimating counterfactual treatment outcomes over time in complex multi-agent scenarios
Jun 04, 2022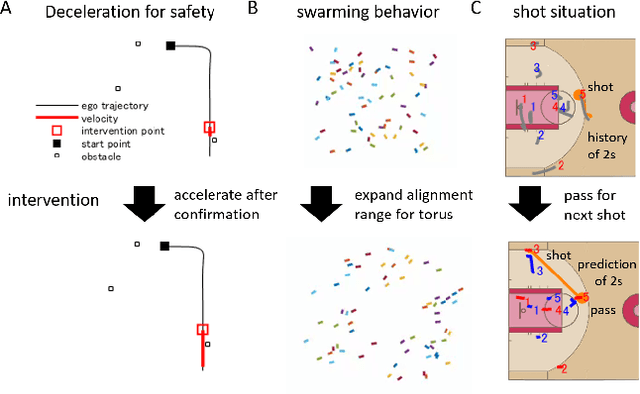
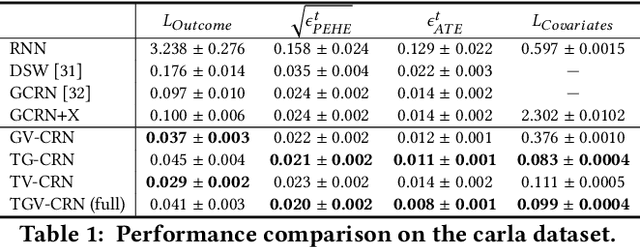
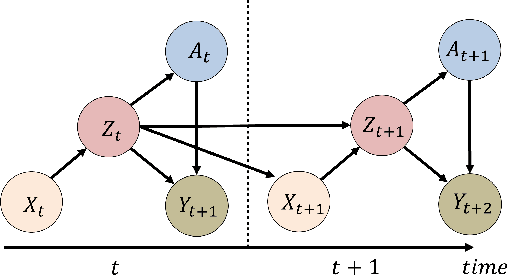
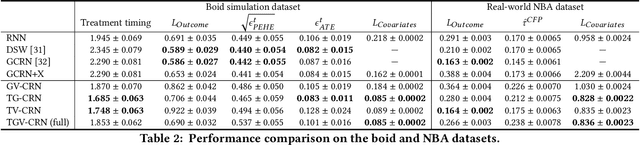
Abstract:Evaluation of intervention in a multi-agent system, e.g., when humans should intervene in autonomous driving systems and when a player should pass to teammates for a good shot, is challenging in various engineering and scientific fields. Estimating the individual treatment effect (ITE) using counterfactual long-term prediction is practical to evaluate such interventions. However, most of the conventional frameworks did not consider the time-varying complex structure of multi-agent relationships and covariate counterfactual prediction. This may sometimes lead to erroneous assessments of ITE and interpretation problems. Here we propose an interpretable, counterfactual recurrent network in multi-agent systems to estimate the effect of the intervention. Our model leverages graph variational recurrent neural networks and theory-based computation with domain knowledge for the ITE estimation framework based on long-term prediction of multi-agent covariates and outcomes, which can confirm under the circumstances under which the intervention is effective. On simulated models of an automated vehicle and biological agents with time-varying confounders, we show that our methods achieved lower estimation errors in counterfactual covariates and the most effective treatment timing than the baselines. Furthermore, using real basketball data, our methods performed realistic counterfactual predictions and evaluated the counterfactual passes in shot scenarios.
Asteroid Flyby Cycler Trajectory Design Using Deep Neural Networks
Nov 23, 2021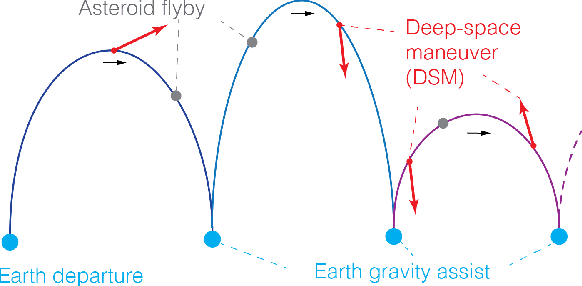
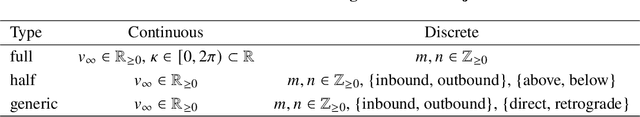
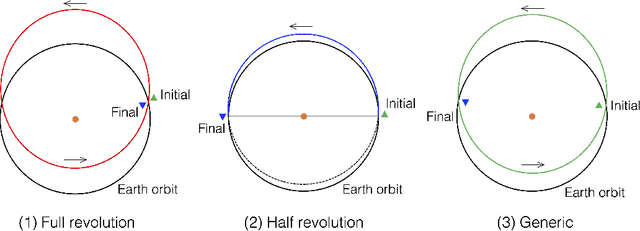

Abstract:Asteroid exploration has been attracting more attention in recent years. Nevertheless, we have just visited tens of asteroids while we have discovered more than one million bodies. As our current observation and knowledge should be biased, it is essential to explore multiple asteroids directly to better understand the remains of planetary building materials. One of the mission design solutions is utilizing asteroid flyby cycler trajectories with multiple Earth gravity assists. An asteroid flyby cycler trajectory design problem is a subclass of global trajectory optimization problems with multiple flybys, involving a trajectory optimization problem for a given flyby sequence and a combinatorial optimization problem to decide the sequence of the flybys. As the number of flyby bodies grows, the computation time of this optimization problem expands maliciously. This paper presents a new method to design asteroid flyby cycler trajectories utilizing a surrogate model constructed by deep neural networks approximating trajectory optimization results. Since one of the bottlenecks of machine learning approaches is to generate massive trajectory databases, we propose an efficient database generation strategy by introducing pseudo-asteroids satisfying the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker conditions. The numerical result applied to JAXA's DESTINY+ mission shows that the proposed method can significantly reduce the computational time for searching asteroid flyby sequences.
Learning interaction rules from multi-animal trajectories via augmented behavioral models
Jul 14, 2021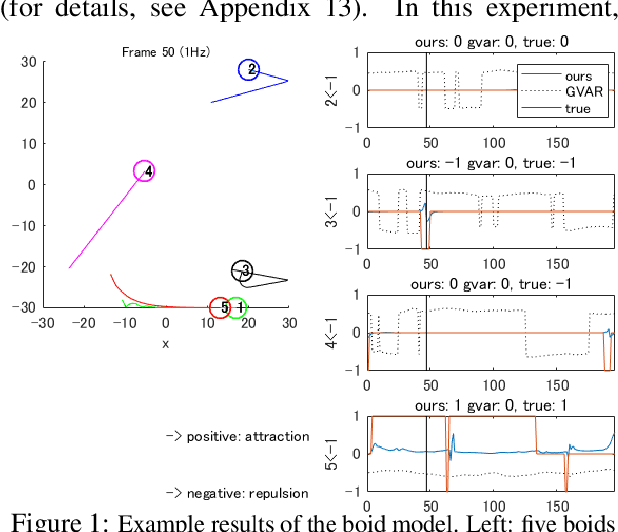
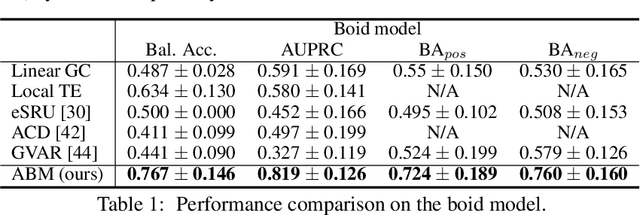
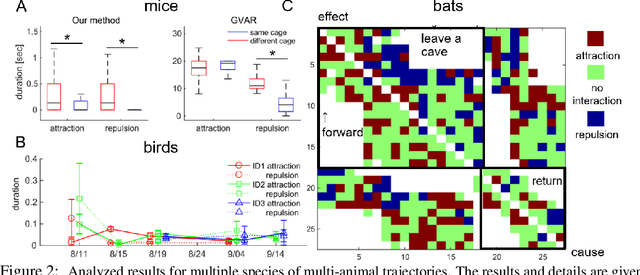
Abstract:Extracting the interaction rules of biological agents from moving sequences pose challenges in various domains. Granger causality is a practical framework for analyzing the interactions from observed time-series data; however, this framework ignores the structures of the generative process in animal behaviors, which may lead to interpretational problems and sometimes erroneous assessments of causality. In this paper, we propose a new framework for learning Granger causality from multi-animal trajectories via augmented theory-based behavioral models with interpretable data-driven models. We adopt an approach for augmenting incomplete multi-agent behavioral models described by time-varying dynamical systems with neural networks. For efficient and interpretable learning, our model leverages theory-based architectures separating navigation and motion processes, and the theory-guided regularization for reliable behavioral modeling. This can provide interpretable signs of Granger-causal effects over time, i.e., when specific others cause the approach or separation. In experiments using synthetic datasets, our method achieved better performance than various baselines. We then analyzed multi-animal datasets of mice, flies, birds, and bats, which verified our method and obtained novel biological insights.
Physics-Integrated Variational Autoencoders for Robust and Interpretable Generative Modeling
Feb 25, 2021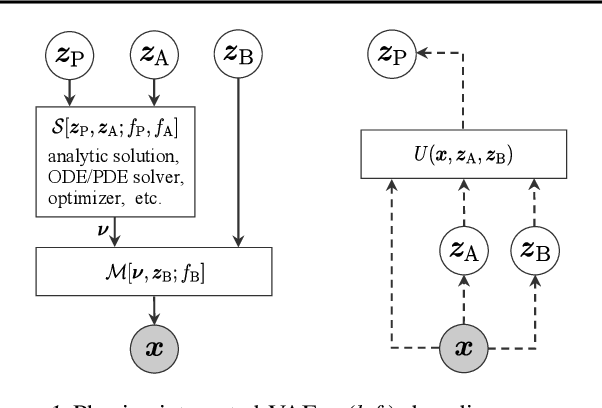
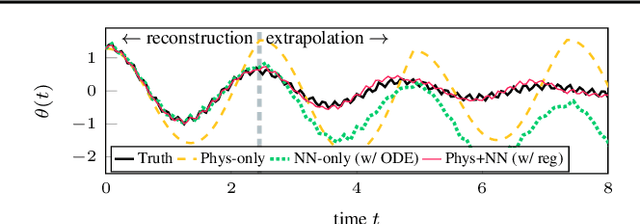
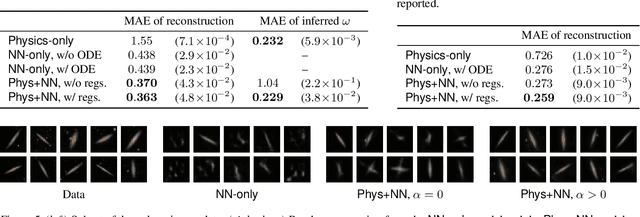
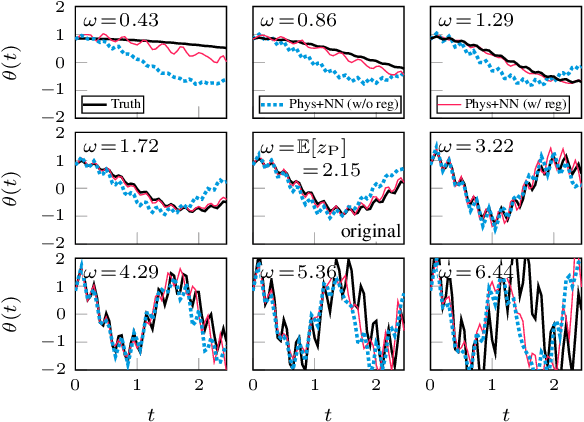
Abstract:Integrating physics models within machine learning holds considerable promise toward learning robust models with improved interpretability and abilities to extrapolate. In this work, we focus on the integration of incomplete physics models into deep generative models, variational autoencoders (VAEs) in particular. A key technical challenge is to strike a balance between the incomplete physics model and the learned components (i.e., neural nets) of the complete model, in order to ensure that the physics part is used in a meaningful manner. To this end, we propose a VAE architecture in which a part of the latent space is grounded by physics. We couple it with a set of regularizers that control the effect of the learned components and preserve the semantics of the physics-based latent variables as intended. We not only demonstrate generative performance improvements over a set of synthetic and real-world datasets, but we also show that we learn robust models that can consistently extrapolate beyond the training distribution in a meaningful manner. Moreover, we show that we can control the generative process in an interpretable manner.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge