Naili Xing
NeurDB: On the Design and Implementation of an AI-powered Autonomous Database
Aug 06, 2024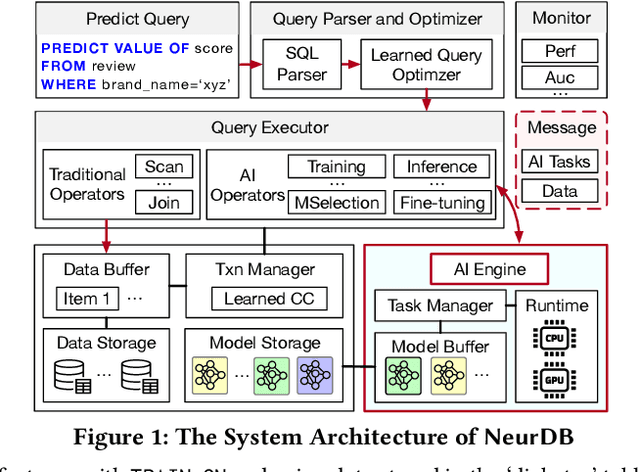
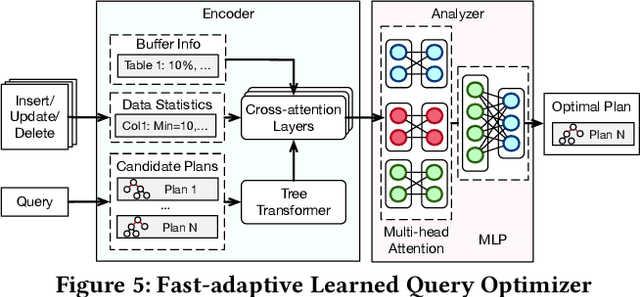
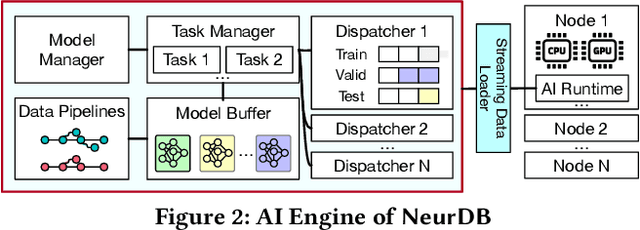
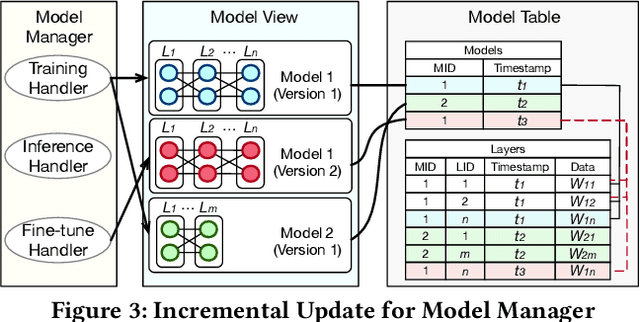
Abstract:Databases are increasingly embracing AI to provide autonomous system optimization and intelligent in-database analytics, aiming to relieve end-user burdens across various industry sectors. Nonetheless, most existing approaches fail to account for the dynamic nature of databases, which renders them ineffective for real-world applications characterized by evolving data and workloads. This paper introduces NeurDB, an AI-powered autonomous database that deepens the fusion of AI and databases with adaptability to data and workload drift. NeurDB establishes a new in-database AI ecosystem that seamlessly integrates AI workflows within the database. This integration enables efficient and effective in-database AI analytics and fast-adaptive learned system components. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that NeurDB substantially outperforms existing solutions in managing AI analytics tasks, with the proposed learned components more effectively handling environmental dynamism than state-of-the-art approaches.
NeurDB: An AI-powered Autonomous Data System
May 07, 2024Abstract:In the wake of rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), we stand on the brink of a transformative leap in data systems. The imminent fusion of AI and DB (AIxDB) promises a new generation of data systems, which will relieve the burden on end-users across all industry sectors by featuring AI-enhanced functionalities, such as personalized and automated in-database AI-powered analytics, self-driving capabilities for improved system performance, etc. In this paper, we explore the evolution of data systems with a focus on deepening the fusion of AI and DB. We present NeurDB, our next-generation data system designed to fully embrace AI design in each major system component and provide in-database AI-powered analytics. We outline the conceptual and architectural overview of NeurDB, discuss its design choices and key components, and report its current development and future plan.
Powering In-Database Dynamic Model Slicing for Structured Data Analytics
May 01, 2024



Abstract:Relational database management systems (RDBMS) are widely used for the storage and retrieval of structured data. To derive insights beyond statistical aggregation, we typically have to extract specific subdatasets from the database using conventional database operations, and then apply deep neural networks (DNN) training and inference on these respective subdatasets in a separate machine learning system. The process can be prohibitively expensive, especially when there are a combinatorial number of subdatasets extracted for different analytical purposes. This calls for efficient in-database support of advanced analytical methods In this paper, we introduce LEADS, a novel SQL-aware dynamic model slicing technique to customize models for subdatasets specified by SQL queries. LEADS improves the predictive modeling of structured data via the mixture of experts (MoE) technique and maintains inference efficiency by a SQL-aware gating network. At the core of LEADS is the construction of a general model with multiple expert sub-models via MoE trained over the entire database. This SQL-aware MoE technique scales up the modeling capacity, enhances effectiveness, and preserves efficiency by activating only necessary experts via the gating network during inference. Additionally, we introduce two regularization terms during the training process of LEADS to strike a balance between effectiveness and efficiency. We also design and build an in-database inference system, called INDICES, to support end-to-end advanced structured data analytics by non-intrusively incorporating LEADS onto PostgreSQL. Our extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that LEADS consistently outperforms baseline models, and INDICES delivers effective in-database analytics with a considerable reduction in inference latency compared to traditional solutions.
Anytime Neural Architecture Search on Tabular Data
Mar 15, 2024



Abstract:The increasing demand for tabular data analysis calls for transitioning from manual architecture design to Neural Architecture Search (NAS). This transition demands an efficient and responsive anytime NAS approach that is capable of returning current optimal architectures within any given time budget while progressively enhancing architecture quality with increased budget allocation. However, the area of research on Anytime NAS for tabular data remains unexplored. To this end, we introduce ATLAS, the first anytime NAS approach tailored for tabular data. ATLAS introduces a novel two-phase filtering-and-refinement optimization scheme with joint optimization, combining the strengths of both paradigms of training-free and training-based architecture evaluation. Specifically, in the filtering phase, ATLAS employs a new zero-cost proxy specifically designed for tabular data to efficiently estimate the performance of candidate architectures, thereby obtaining a set of promising architectures. Subsequently, in the refinement phase, ATLAS leverages a fixed-budget search algorithm to schedule the training of the promising candidates, so as to accurately identify the optimal architecture. To jointly optimize the two phases for anytime NAS, we also devise a budget-aware coordinator that delivers high NAS performance within constraints. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that our ATLAS can obtain a good-performing architecture within any predefined time budget and return better architectures as and when a new time budget is made available. Overall, it reduces the search time on tabular data by up to 82.75x compared to existing NAS approaches.
SINGA-Easy: An Easy-to-Use Framework for MultiModal Analysis
Aug 03, 2021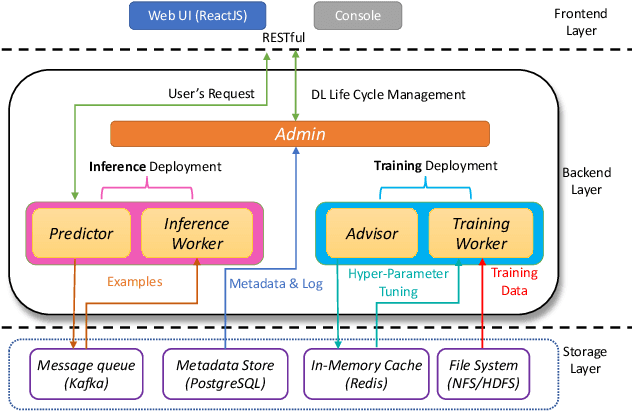
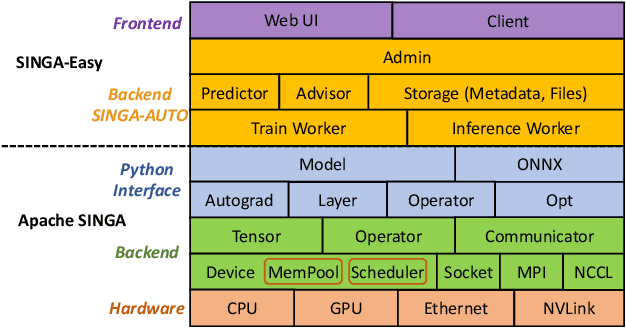
Abstract:Deep learning has achieved great success in a wide spectrum of multimedia applications such as image classification, natural language processing and multimodal data analysis. Recent years have seen the development of many deep learning frameworks that provide a high-level programming interface for users to design models, conduct training and deploy inference. However, it remains challenging to build an efficient end-to-end multimedia application with most existing frameworks. Specifically, in terms of usability, it is demanding for non-experts to implement deep learning models, obtain the right settings for the entire machine learning pipeline, manage models and datasets, and exploit external data sources all together. Further, in terms of adaptability, elastic computation solutions are much needed as the actual serving workload fluctuates constantly, and scaling the hardware resources to handle the fluctuating workload is typically infeasible. To address these challenges, we introduce SINGA-Easy, a new deep learning framework that provides distributed hyper-parameter tuning at the training stage, dynamic computational cost control at the inference stage, and intuitive user interactions with multimedia contents facilitated by model explanation. Our experiments on the training and deployment of multi-modality data analysis applications show that the framework is both usable and adaptable to dynamic inference loads. We implement SINGA-Easy on top of Apache SINGA and demonstrate our system with the entire machine learning life cycle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge