Mitch Pryor
Limited Linguistic Diversity in Embodied AI Datasets
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Language plays a critical role in Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, yet the linguistic characteristics of the datasets used to train and evaluate these systems remain poorly documented. In this work, we present a systematic dataset audit of several widely used VLA corpora, aiming to characterize what kinds of instructions these datasets actually contain and how much linguistic variety they provide. We quantify instruction language along complementary dimensions-including lexical variety, duplication and overlap, semantic similarity, and syntactic complexity. Our analysis shows that many datasets rely on highly repetitive, template-like commands with limited structural variation, yielding a narrow distribution of instruction forms. We position these findings as descriptive documentation of the language signal available in current VLA training and evaluation data, intended to support more detailed dataset reporting, more principled dataset selection, and targeted curation or augmentation strategies that broaden language coverage.
Beyond Shortsighted Navigation: Merging Best View Trajectory Planning with Robot Navigation
Aug 22, 2024



Abstract:Gathering visual information effectively to monitor known environments is a key challenge in robotics. To be as efficient as human surveyors, robotic systems must continuously collect observational data required to complete their survey task. Inspection personnel instinctively know to look at relevant equipment that happens to be ``along the way.'' In this paper, we introduce a novel framework for continuous long-horizon viewpoint planning, for ground robots, applied to tasks involving patrolling, monitoring or visual data gathering in known environments. Our approach to Long Horizon Viewpoint Planning (LHVP), enables the robot to autonomously navigate and collect environmental data optimizing for coverage over the horizon of the patrol. Leveraging a quadruped's mobility and sensory capabilities, our LHVP framework plans patrol paths that account for coupling the viewpoint planner for the arm camera with the mobile base's navigation planner. The viewpath optimization algorithm seeks a balance between comprehensive environmental coverage and dynamically feasible movements, thus ensuring prolonged and effective operation in scenarios including monitoring, security surveillance, and disaster response. We validate our approach through simulations and in the real world and show that our LHVP significantly outperforms naive patrolling methods in terms of area coverage generating information-gathering trajectories for the robot arm. Our results indicate a promising direction for the deployment of mobile robots in long-term, autonomous surveying, and environmental data collection tasks, highlighting the potential of intelligent robotic systems in challenging real-world applications.
The Collection of a Human Robot Collaboration Dataset for Cooperative Assembly in Glovebox Environments
Jul 19, 2024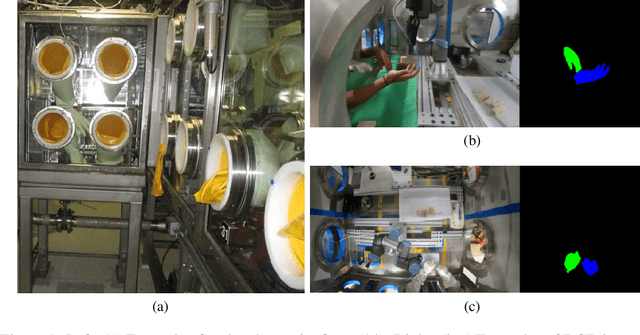
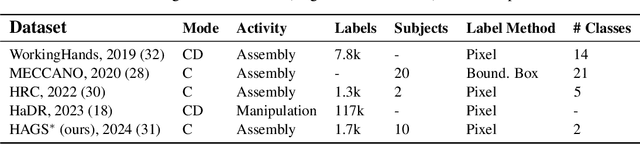
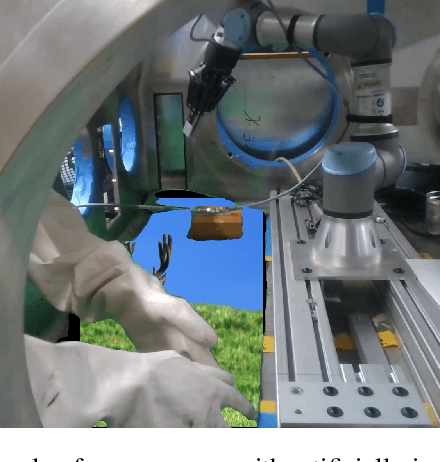
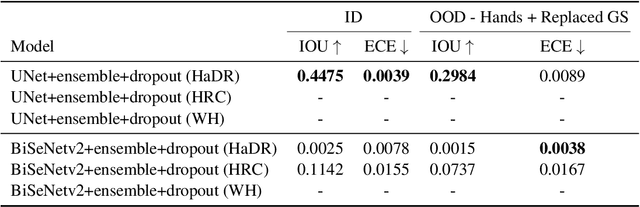
Abstract:Industry 4.0 introduced AI as a transformative solution for modernizing manufacturing processes. Its successor, Industry 5.0, envisions humans as collaborators and experts guiding these AI-driven manufacturing solutions. Developing these techniques necessitates algorithms capable of safe, real-time identification of human positions in a scene, particularly their hands, during collaborative assembly. Although substantial efforts have curated datasets for hand segmentation, most focus on residential or commercial domains. Existing datasets targeting industrial settings predominantly rely on synthetic data, which we demonstrate does not effectively transfer to real-world operations. Moreover, these datasets lack uncertainty estimations critical for safe collaboration. Addressing these gaps, we present HAGS: Hand and Glove Segmentation Dataset. This dataset provides 1200 challenging examples to build applications toward hand and glove segmentation in industrial human-robot collaboration scenarios as well as assess out-of-distribution images, constructed via green screen augmentations, to determine ML-classifier robustness. We study state-of-the-art, real-time segmentation models to evaluate existing methods. Our dataset and baselines are publicly available: https://dataverse.tdl.org/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.18738/T8/85R7KQ and https://github.com/UTNuclearRoboticsPublic/assembly_glovebox_dataset.
Temporal and Semantic Evaluation Metrics for Foundation Models in Post-Hoc Analysis of Robotic Sub-tasks
Mar 25, 2024Abstract:Recent works in Task and Motion Planning (TAMP) show that training control policies on language-supervised robot trajectories with quality labeled data markedly improves agent task success rates. However, the scarcity of such data presents a significant hurdle to extending these methods to general use cases. To address this concern, we present an automated framework to decompose trajectory data into temporally bounded and natural language-based descriptive sub-tasks by leveraging recent prompting strategies for Foundation Models (FMs) including both Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision Language Models (VLMs). Our framework provides both time-based and language-based descriptions for lower-level sub-tasks that comprise full trajectories. To rigorously evaluate the quality of our automatic labeling framework, we contribute an algorithm SIMILARITY to produce two novel metrics, temporal similarity and semantic similarity. The metrics measure the temporal alignment and semantic fidelity of language descriptions between two sub-task decompositions, namely an FM sub-task decomposition prediction and a ground-truth sub-task decomposition. We present scores for temporal similarity and semantic similarity above 90%, compared to 30% of a randomized baseline, for multiple robotic environments, demonstrating the effectiveness of our proposed framework. Our results enable building diverse, large-scale, language-supervised datasets for improved robotic TAMP.
Augmented Reality User Interface for Command, Control, and Supervision of Large Multi-Agent Teams
Jan 11, 2024Abstract:Multi-agent human-robot teaming allows for the potential to gather information about various environments more efficiently by exploiting and combining the strengths of humans and robots. In industries like defense, search and rescue, first-response, and others alike, heterogeneous human-robot teams show promise to accelerate data collection and improve team safety by removing humans from unknown and potentially hazardous situations. This work builds upon AugRE, an Augmented Reality (AR) based scalable human-robot teaming framework. It enables users to localize and communicate with 50+ autonomous agents. Through our efforts, users are able to command, control, and supervise agents in large teams, both line-of-sight and non-line-of-sight, without the need to modify the environment prior and without requiring users to use typical hardware (i.e. joysticks, keyboards, laptops, tablets, etc.) in the field. The demonstrated work shows early indications that combining these AR-HMD-based user interaction modalities for command, control, and supervision will help improve human-robot team collaboration, robustness, and trust.
Using Augmented Reality to Assess and Modify Mobile Manipulator Surface Repair Plans
Nov 02, 2023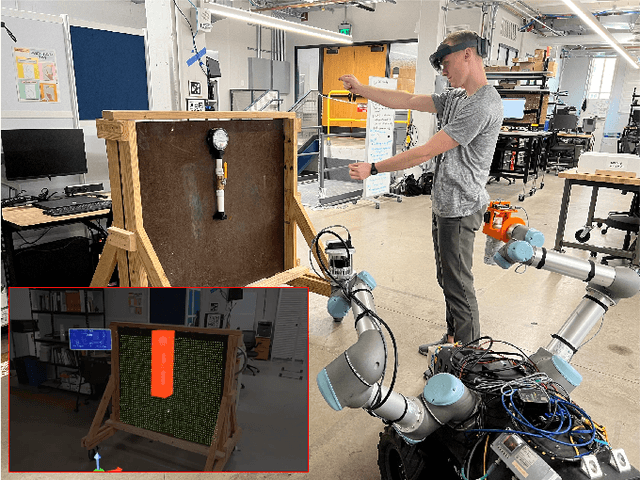
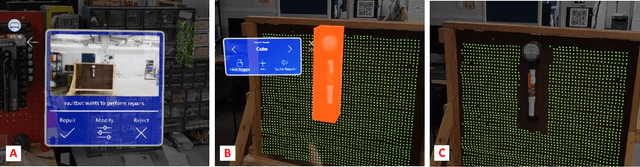
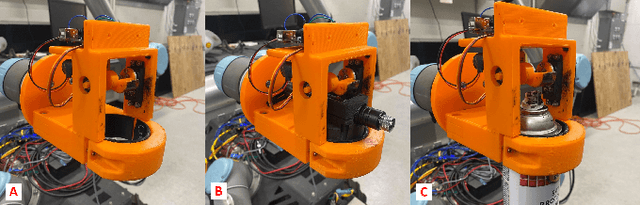
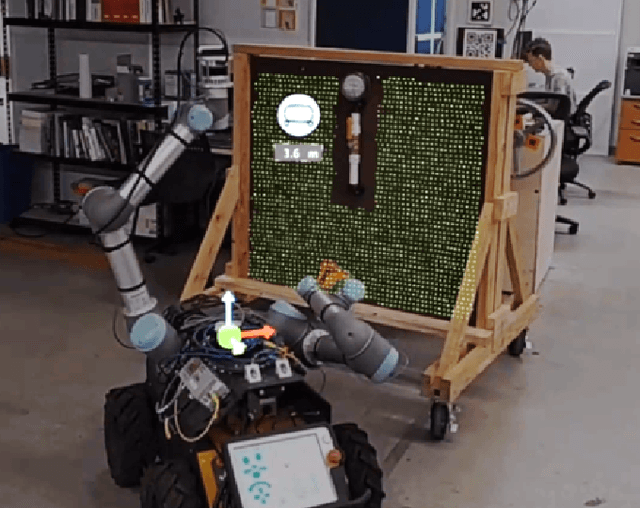
Abstract:Industrial robotics are redefining inspection and maintenance routines across multiple sectors, enhancing safety, efficiency, and environmental sustainability. In outdoor industrial facilities, it is crucial to inspect and repair complex surfaces affected by corrosion. To address this challenge, mobile manipulators have been developed to navigate these facilities, identify corroded areas, and apply protective coatings. However, given that this technology is still in its infancy and the consequences of improperly coating essential equipment can be significant, human oversight is necessary to review the robot's corrosion identification and repair plan. We present a practical and scalable Augmented Reality (AR)-based system designed to empower non-experts to visualize, modify, and approve robot-generated surface corrosion repair plans in real-time. Built upon an AR-based human-robot interaction framework, Augmented Robot Environment (AugRE), we developed a comprehensive AR application module called Situational Task Accept and Repair (STAR). STAR allows users to examine identified corrosion images, point cloud data, and robot navigation objectives overlaid on the physical environment within these industrial environments. Users are able to additionally make adjustments to the robot repair plan in real-time using interactive holographic volumes, excluding critical nearby equipment that might be at risk of coating overspray. We demonstrate the entire system using a Microsoft HoloLens 2 and a dual-arm mobile manipulator. Our future research will focus on evaluating user experience, system robustness, and real-world validation.
Multimodal Grounding for Embodied AI via Augmented Reality Headsets for Natural Language Driven Task Planning
Apr 26, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in generative modeling have spurred a resurgence in the field of Embodied Artificial Intelligence (EAI). EAI systems typically deploy large language models to physical systems capable of interacting with their environment. In our exploration of EAI for industrial domains, we successfully demonstrate the feasibility of co-located, human-robot teaming. Specifically, we construct an experiment where an Augmented Reality (AR) headset mediates information exchange between an EAI agent and human operator for a variety of inspection tasks. To our knowledge the use of an AR headset for multimodal grounding and the application of EAI to industrial tasks are novel contributions within Embodied AI research. In addition, we highlight potential pitfalls in EAI's construction by providing quantitative and qualitative analysis on prompt robustness.
Augmented Reality Remote Operation of Dual Arm Manipulators in Hot Boxes
Mar 28, 2023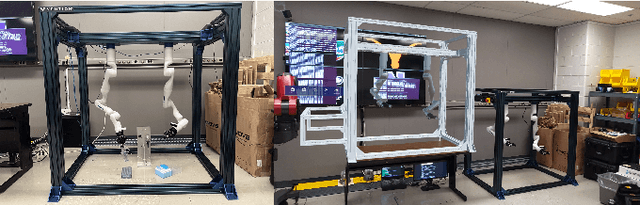
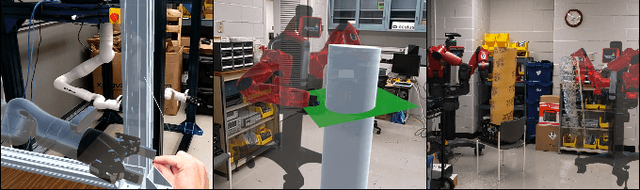
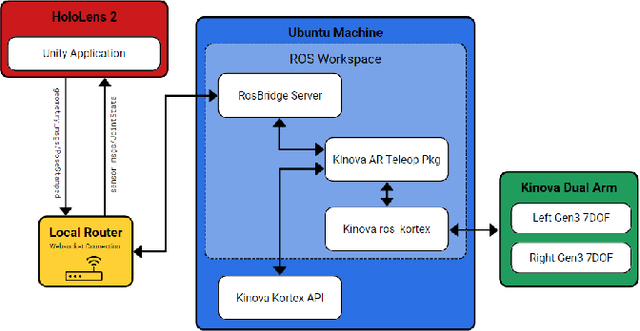
Abstract:In nuclear isotope and chemistry laboratories, hot cells and gloveboxes provide scientists with a controlled and safe environment to perform experiments. Working on experiments in these isolated containment cells requires scientists to be physically present. For hot cell work today, scientists manipulate equipment and radioactive material inside through a bilateral mechanical control mechanism. Motions produced outside the cell with the master control levers are mechanically transferred to the internal grippers inside the shielded containment cell. There is a growing need to have the capability to conduct experiments within these cells remotely. A simple method to enable remote manipulations within hot cell and glovebox cells is to mount two robotic arms inside a box to mimic the motions of human hands. An AR application was built in this work to allow a user wearing a Microsoft HoloLens 2 headset to teleoperate dual arm manipulators by grasping robotic end-effector digital replicas in AR from a remote location. In addition to the real-time replica of the physical robotic arms in AR, the application enables users to view a live video stream attached to the robotic arms and parse a 3D point cloud of 3D objects in their remote AR environment for better situational awareness. This work also provides users with virtual fixture to assist in manipulation and other teleoperation tasks.
Accelerating Trajectory Generation for Quadrotors Using Transformers
Mar 27, 2023
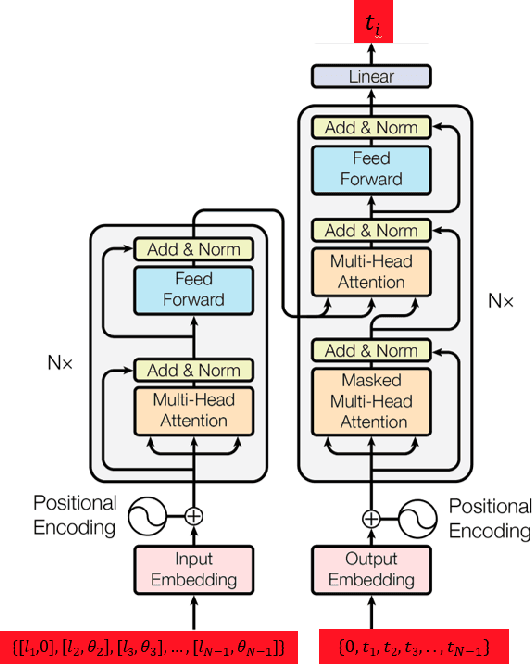
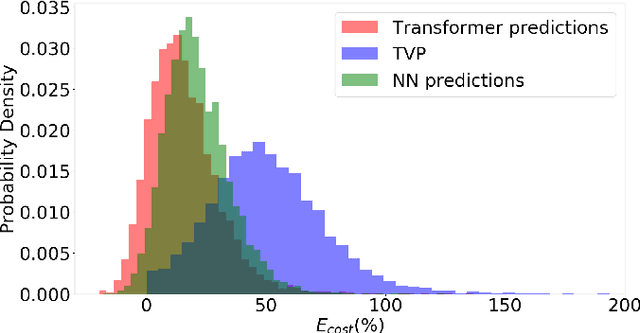
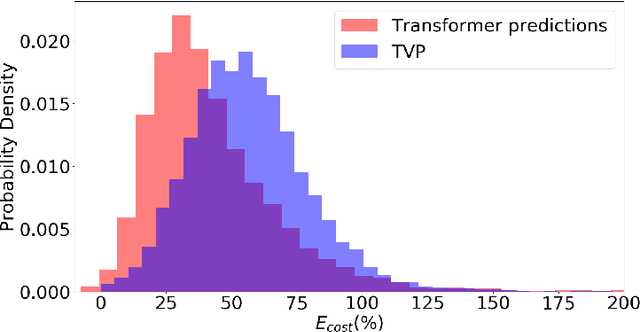
Abstract:In this work, we address the problem of computation time for trajectory generation in quadrotors. Most trajectory generation methods for waypoint navigation of quadrotors, for example minimum snap/jerk and minimum-time, are structured as bi-level optimizations. The first level involves allocating time across all input waypoints and the second step is to minimize the snap/jerk of the trajectory under that time allocation. Such an optimization can be computationally expensive to solve. In our approach we treat trajectory generation as a supervised learning problem between a sequential set of inputs and outputs. We adapt a transformer model to learn the optimal time allocations for a given set of input waypoints, thus making it into a single step optimization. We demonstrate the performance of the transformer model by training it to predict the time allocations for a minimum snap trajectory generator. The trained transformer model is able to predict accurate time allocations with fewer data samples and smaller model size, compared to a feedforward network (FFN), demonstrating that it is able to model the sequential nature of the waypoint navigation problem.
Smooth time optimal trajectory generation for drones
Feb 18, 2022

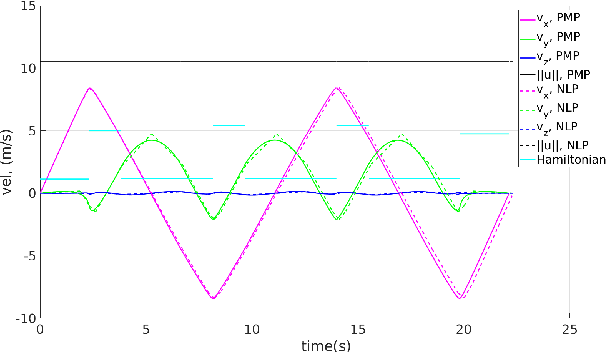
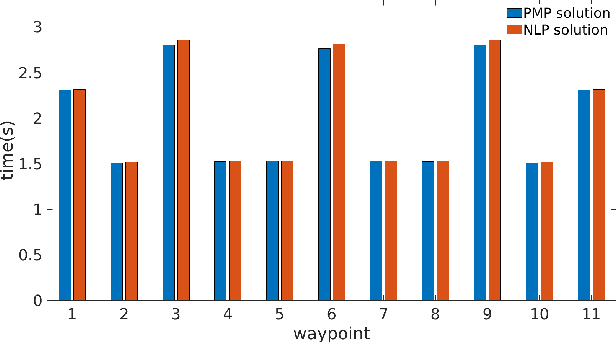
Abstract:In this paper, we address a minimum-time steering problem for a drone modeled as point mass with bounded acceleration, across a set of desired waypoints in the presence of gravity. We first provide a method to solve for the minimum-time control input that will steer the point mass between two waypoints based on a continuous-time problem formulation which we address by using Pontryagin's Minimum Principle. Subsequently, we solve for the time-optimal trajectory across the given set of waypoints by discretizing in the time domain and formulating the minimum-time problem as a nonlinear program (NLP). The velocities at each waypoint obtained from solving the NLP in the discretized domain are then used as boundary conditions to extend our two-point solution across those multiple waypoints. We apply this planning methodology to execute a surveying task that minimizes the time taken to completely explore a target area or volume. Numerical simulations and theoretical analyses of this new planning methodology are presented. The results from our approach are also compared to traditional polynomial trajectories like minimum snap planning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge