Fabian Parra
Augmented Reality User Interface for Command, Control, and Supervision of Large Multi-Agent Teams
Jan 11, 2024Abstract:Multi-agent human-robot teaming allows for the potential to gather information about various environments more efficiently by exploiting and combining the strengths of humans and robots. In industries like defense, search and rescue, first-response, and others alike, heterogeneous human-robot teams show promise to accelerate data collection and improve team safety by removing humans from unknown and potentially hazardous situations. This work builds upon AugRE, an Augmented Reality (AR) based scalable human-robot teaming framework. It enables users to localize and communicate with 50+ autonomous agents. Through our efforts, users are able to command, control, and supervise agents in large teams, both line-of-sight and non-line-of-sight, without the need to modify the environment prior and without requiring users to use typical hardware (i.e. joysticks, keyboards, laptops, tablets, etc.) in the field. The demonstrated work shows early indications that combining these AR-HMD-based user interaction modalities for command, control, and supervision will help improve human-robot team collaboration, robustness, and trust.
Using Augmented Reality to Assess and Modify Mobile Manipulator Surface Repair Plans
Nov 02, 2023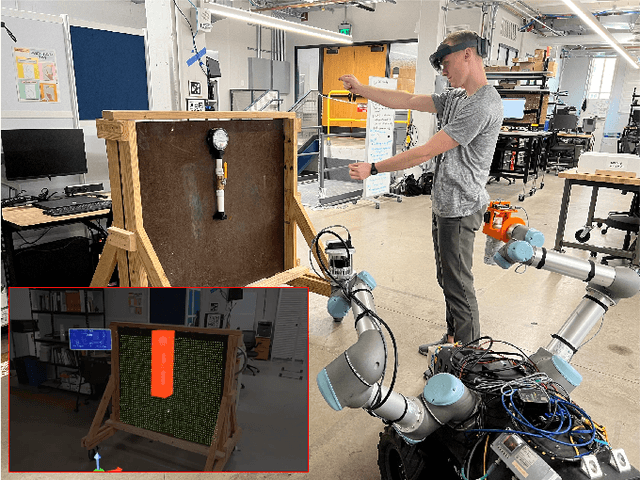
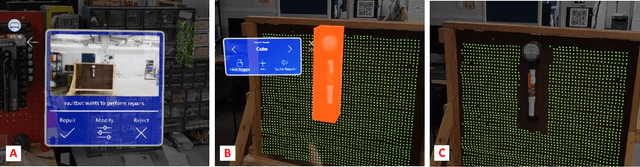
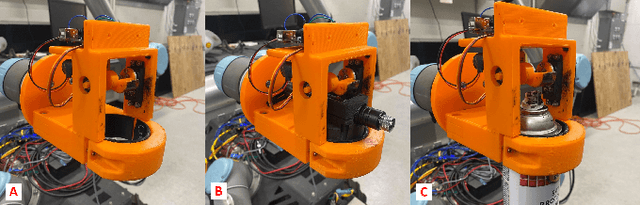
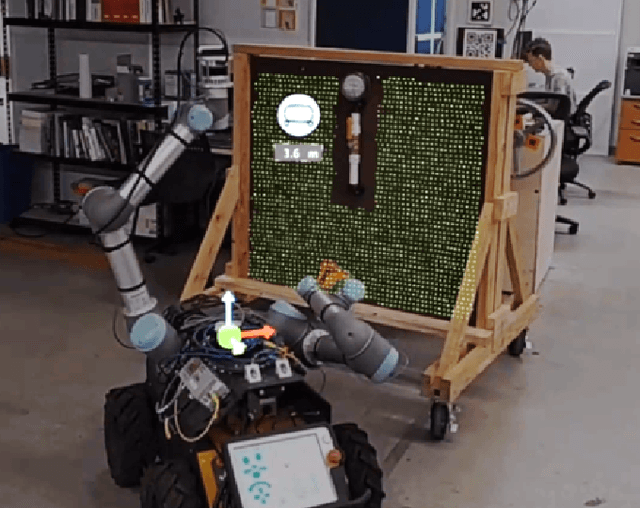
Abstract:Industrial robotics are redefining inspection and maintenance routines across multiple sectors, enhancing safety, efficiency, and environmental sustainability. In outdoor industrial facilities, it is crucial to inspect and repair complex surfaces affected by corrosion. To address this challenge, mobile manipulators have been developed to navigate these facilities, identify corroded areas, and apply protective coatings. However, given that this technology is still in its infancy and the consequences of improperly coating essential equipment can be significant, human oversight is necessary to review the robot's corrosion identification and repair plan. We present a practical and scalable Augmented Reality (AR)-based system designed to empower non-experts to visualize, modify, and approve robot-generated surface corrosion repair plans in real-time. Built upon an AR-based human-robot interaction framework, Augmented Robot Environment (AugRE), we developed a comprehensive AR application module called Situational Task Accept and Repair (STAR). STAR allows users to examine identified corrosion images, point cloud data, and robot navigation objectives overlaid on the physical environment within these industrial environments. Users are able to additionally make adjustments to the robot repair plan in real-time using interactive holographic volumes, excluding critical nearby equipment that might be at risk of coating overspray. We demonstrate the entire system using a Microsoft HoloLens 2 and a dual-arm mobile manipulator. Our future research will focus on evaluating user experience, system robustness, and real-world validation.
Multimodal Grounding for Embodied AI via Augmented Reality Headsets for Natural Language Driven Task Planning
Apr 26, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in generative modeling have spurred a resurgence in the field of Embodied Artificial Intelligence (EAI). EAI systems typically deploy large language models to physical systems capable of interacting with their environment. In our exploration of EAI for industrial domains, we successfully demonstrate the feasibility of co-located, human-robot teaming. Specifically, we construct an experiment where an Augmented Reality (AR) headset mediates information exchange between an EAI agent and human operator for a variety of inspection tasks. To our knowledge the use of an AR headset for multimodal grounding and the application of EAI to industrial tasks are novel contributions within Embodied AI research. In addition, we highlight potential pitfalls in EAI's construction by providing quantitative and qualitative analysis on prompt robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge