Minh Hieu Nguyen
Model-Free Counterfactual Subset Selection at Scale
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Ensuring transparency in AI decision-making requires interpretable explanations, particularly at the instance level. Counterfactual explanations are a powerful tool for this purpose, but existing techniques frequently depend on synthetic examples, introducing biases from unrealistic assumptions, flawed models, or skewed data. Many methods also assume full dataset availability, an impractical constraint in real-time environments where data flows continuously. In contrast, streaming explanations offer adaptive, real-time insights without requiring persistent storage of the entire dataset. This work introduces a scalable, model-free approach to selecting diverse and relevant counterfactual examples directly from observed data. Our algorithm operates efficiently in streaming settings, maintaining $O(\log k)$ update complexity per item while ensuring high-quality counterfactual selection. Empirical evaluations on both real-world and synthetic datasets demonstrate superior performance over baseline methods, with robust behavior even under adversarial conditions.
Technology Mapping with Large Language Models
Jan 25, 2025


Abstract:In today's fast-evolving business landscape, having insight into the technology stacks that organizations use is crucial for forging partnerships, uncovering market openings, and informing strategic choices. However, conventional technology mapping, which typically hinges on keyword searches, struggles with the sheer scale and variety of data available, often failing to capture nascent technologies. To overcome these hurdles, we present STARS (Semantic Technology and Retrieval System), a novel framework that harnesses Large Language Models (LLMs) and Sentence-BERT to pinpoint relevant technologies within unstructured content, build comprehensive company profiles, and rank each firm's technologies according to their operational importance. By integrating entity extraction with Chain-of-Thought prompting and employing semantic ranking, STARS provides a precise method for mapping corporate technology portfolios. Experimental results show that STARS markedly boosts retrieval accuracy, offering a versatile and high-performance solution for cross-industry technology mapping.
FedCert: Federated Accuracy Certification
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for training machine learning models in a decentralized manner, preserving data privacy by keeping local data on clients. However, evaluating the robustness of these models against data perturbations on clients remains a significant challenge. Previous studies have assessed the effectiveness of models in centralized training based on certified accuracy, which guarantees that a certain percentage of the model's predictions will remain correct even if the input data is perturbed. However, the challenge of extending these evaluations to FL remains unresolved due to the unknown client's local data. To tackle this challenge, this study proposed a method named FedCert to take the first step toward evaluating the robustness of FL systems. The proposed method is designed to approximate the certified accuracy of a global model based on the certified accuracy and class distribution of each client. Additionally, considering the Non-Independent and Identically Distributed (Non-IID) nature of data in real-world scenarios, we introduce the client grouping algorithm to ensure reliable certified accuracy during the aggregation step of the approximation algorithm. Through theoretical analysis, we demonstrate the effectiveness of FedCert in assessing the robustness and reliability of FL systems. Moreover, experimental results on the CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets under various scenarios show that FedCert consistently reduces the estimation error compared to baseline methods. This study offers a solution for evaluating the robustness of FL systems and lays the groundwork for future research to enhance the dependability of decentralized learning. The source code is available at https://github.com/thanhhff/FedCert/.
MV2Cyl: Reconstructing 3D Extrusion Cylinders from Multi-View Images
Jun 16, 2024Abstract:We present MV2Cyl, a novel method for reconstructing 3D from 2D multi-view images, not merely as a field or raw geometry but as a sketch-extrude CAD model. Extracting extrusion cylinders from raw 3D geometry has been extensively researched in computer vision, while the processing of 3D data through neural networks has remained a bottleneck. Since 3D scans are generally accompanied by multi-view images, leveraging 2D convolutional neural networks allows these images to be exploited as a rich source for extracting extrusion cylinder information. However, we observe that extracting only the surface information of the extrudes and utilizing it results in suboptimal outcomes due to the challenges in the occlusion and surface segmentation. By synergizing with the extracted base curve information, we achieve the optimal reconstruction result with the best accuracy in 2D sketch and extrude parameter estimation. Our experiments, comparing our method with previous work that takes a raw 3D point cloud as input, demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach by taking advantage of multi-view images.
SALAD: Part-Level Latent Diffusion for 3D Shape Generation and Manipulation
Mar 21, 2023Abstract:We present a cascaded diffusion model based on a part-level implicit 3D representation. Our model achieves state-of-the-art generation quality and also enables part-level shape editing and manipulation without any additional training in conditional setup. Diffusion models have demonstrated impressive capabilities in data generation as well as zero-shot completion and editing via a guided reverse process. Recent research on 3D diffusion models has focused on improving their generation capabilities with various data representations, while the absence of structural information has limited their capability in completion and editing tasks. We thus propose our novel diffusion model using a part-level implicit representation. To effectively learn diffusion with high-dimensional embedding vectors of parts, we propose a cascaded framework, learning diffusion first on a low-dimensional subspace encoding extrinsic parameters of parts and then on the other high-dimensional subspace encoding intrinsic attributes. In the experiments, we demonstrate the outperformance of our method compared with the previous ones both in generation and part-level completion and manipulation tasks.
Efficient Integration of Multi-Order Dynamics and Internal Dynamics in Stock Movement Prediction
Nov 11, 2022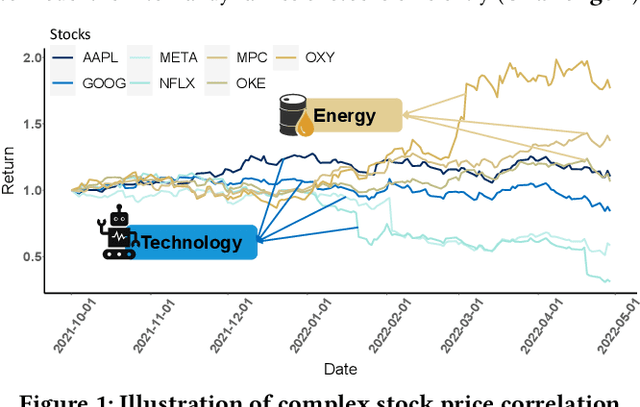
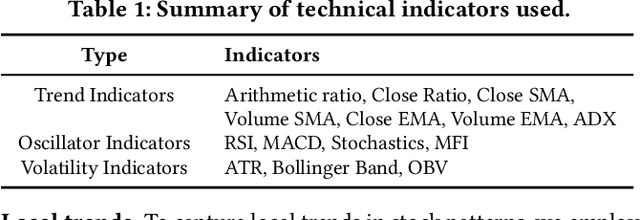
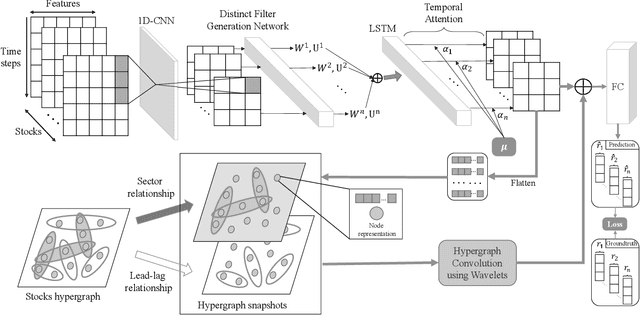
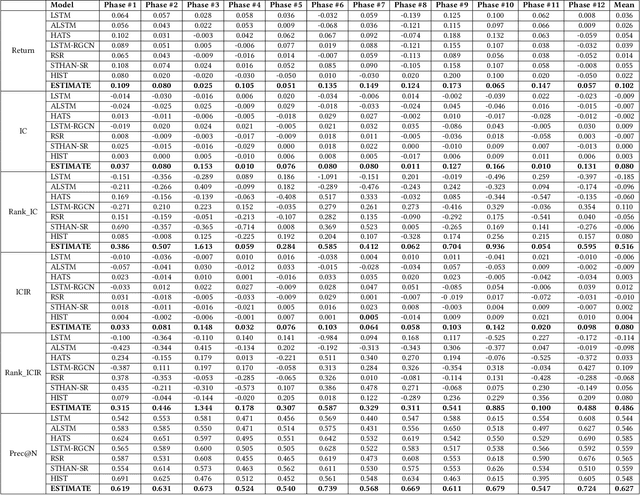
Abstract:Advances in deep neural network (DNN) architectures have enabled new prediction techniques for stock market data. Unlike other multivariate time-series data, stock markets show two unique characteristics: (i) \emph{multi-order dynamics}, as stock prices are affected by strong non-pairwise correlations (e.g., within the same industry); and (ii) \emph{internal dynamics}, as each individual stock shows some particular behaviour. Recent DNN-based methods capture multi-order dynamics using hypergraphs, but rely on the Fourier basis in the convolution, which is both inefficient and ineffective. In addition, they largely ignore internal dynamics by adopting the same model for each stock, which implies a severe information loss. In this paper, we propose a framework for stock movement prediction to overcome the above issues. Specifically, the framework includes temporal generative filters that implement a memory-based mechanism onto an LSTM network in an attempt to learn individual patterns per stock. Moreover, we employ hypergraph attentions to capture the non-pairwise correlations. Here, using the wavelet basis instead of the Fourier basis, enables us to simplify the message passing and focus on the localized convolution. Experiments with US market data over six years show that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of profit and stability. Our source code and data are available at \url{https://github.com/thanhtrunghuynh93/estimate}.
Model-Agnostic and Diverse Explanations for Streaming Rumour Graphs
Jul 17, 2022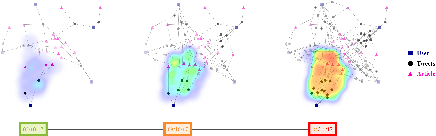
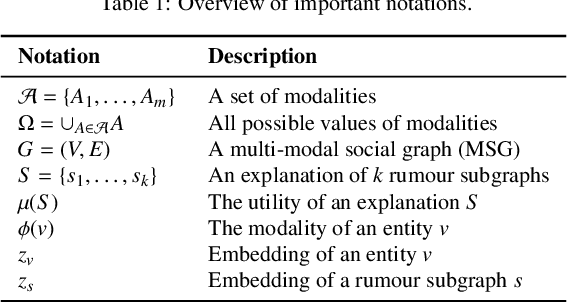
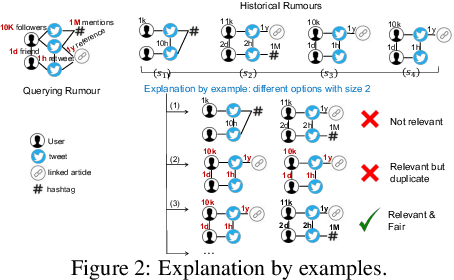
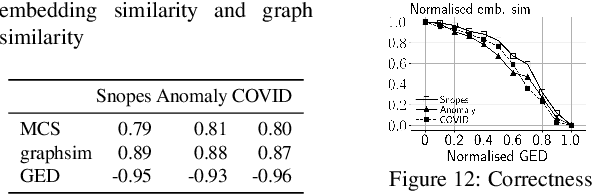
Abstract:The propagation of rumours on social media poses an important threat to societies, so that various techniques for rumour detection have been proposed recently. Yet, existing work focuses on \emph{what} entities constitute a rumour, but provides little support to understand \emph{why} the entities have been classified as such. This prevents an effective evaluation of the detected rumours as well as the design of countermeasures. In this work, we argue that explanations for detected rumours may be given in terms of examples of related rumours detected in the past. A diverse set of similar rumours helps users to generalize, i.e., to understand the properties that govern the detection of rumours. Since the spread of rumours in social media is commonly modelled using feature-annotated graphs, we propose a query-by-example approach that, given a rumour graph, extracts the $k$ most similar and diverse subgraphs from past rumours. The challenge is that all of the computations require fast assessment of similarities between graphs. To achieve an efficient and adaptive realization of the approach in a streaming setting, we present a novel graph representation learning technique and report on implementation considerations. Our evaluation experiments show that our approach outperforms baseline techniques in delivering meaningful explanations for various rumour propagation behaviours.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge