Jun Jo
Model-Free Counterfactual Subset Selection at Scale
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Ensuring transparency in AI decision-making requires interpretable explanations, particularly at the instance level. Counterfactual explanations are a powerful tool for this purpose, but existing techniques frequently depend on synthetic examples, introducing biases from unrealistic assumptions, flawed models, or skewed data. Many methods also assume full dataset availability, an impractical constraint in real-time environments where data flows continuously. In contrast, streaming explanations offer adaptive, real-time insights without requiring persistent storage of the entire dataset. This work introduces a scalable, model-free approach to selecting diverse and relevant counterfactual examples directly from observed data. Our algorithm operates efficiently in streaming settings, maintaining $O(\log k)$ update complexity per item while ensuring high-quality counterfactual selection. Empirical evaluations on both real-world and synthetic datasets demonstrate superior performance over baseline methods, with robust behavior even under adversarial conditions.
Hypergraph Diffusion for High-Order Recommender Systems
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:Recommender systems rely on Collaborative Filtering (CF) to predict user preferences by leveraging patterns in historical user-item interactions. While traditional CF methods primarily focus on learning compact vector embeddings for users and items, graph neural network (GNN)-based approaches have emerged as a powerful alternative, utilizing the structure of user-item interaction graphs to enhance recommendation accuracy. However, existing GNN-based models, such as LightGCN and UltraGCN, often struggle with two major limitations: an inability to fully account for heterophilic interactions, where users engage with diverse item categories, and the over-smoothing problem in multi-layer GNNs, which hinders their ability to model complex, high-order relationships. To address these gaps, we introduce WaveHDNN, an innovative wavelet-enhanced hypergraph diffusion framework. WaveHDNN integrates a Heterophily-aware Collaborative Encoder, designed to capture user-item interactions across diverse categories, with a Multi-scale Group-wise Structure Encoder, which leverages wavelet transforms to effectively model localized graph structures. Additionally, cross-view contrastive learning is employed to maintain robust and consistent representations. Experiments on benchmark datasets validate the efficacy of WaveHDNN, demonstrating its superior ability to capture both heterophilic and localized structural information, leading to improved recommendation performance.
Technology Mapping with Large Language Models
Jan 25, 2025


Abstract:In today's fast-evolving business landscape, having insight into the technology stacks that organizations use is crucial for forging partnerships, uncovering market openings, and informing strategic choices. However, conventional technology mapping, which typically hinges on keyword searches, struggles with the sheer scale and variety of data available, often failing to capture nascent technologies. To overcome these hurdles, we present STARS (Semantic Technology and Retrieval System), a novel framework that harnesses Large Language Models (LLMs) and Sentence-BERT to pinpoint relevant technologies within unstructured content, build comprehensive company profiles, and rank each firm's technologies according to their operational importance. By integrating entity extraction with Chain-of-Thought prompting and employing semantic ranking, STARS provides a precise method for mapping corporate technology portfolios. Experimental results show that STARS markedly boosts retrieval accuracy, offering a versatile and high-performance solution for cross-industry technology mapping.
The use of a humanoid robot for older people with dementia in aged care facilities
May 30, 2024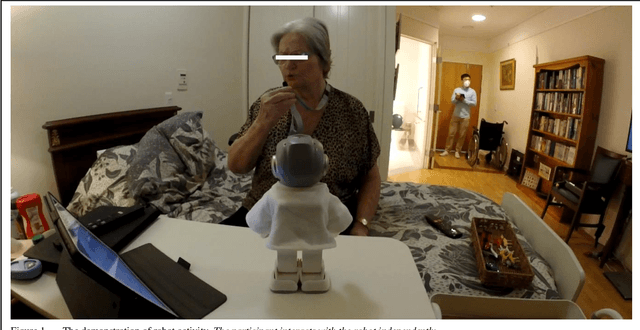
Abstract:This paper presents an interdisciplinary PhD project using a humanoid robot to encourage interactive activities for people with dementia living in two aged care facilities. The aim of the project was to develop software and use technologies to achieve successful robot-led engagement with older people with dementia. This paper outlines the qualitative findings from the project's feasibility stage. The researcher's observations, the participants' attitudes and the feedback from carers are presented and discussed.
A Comparative Study of Question Answering over Knowledge Bases
Nov 15, 2022



Abstract:Question answering over knowledge bases (KBQA) has become a popular approach to help users extract information from knowledge bases. Although several systems exist, choosing one suitable for a particular application scenario is difficult. In this article, we provide a comparative study of six representative KBQA systems on eight benchmark datasets. In that, we study various question types, properties, languages, and domains to provide insights on where existing systems struggle. On top of that, we propose an advanced mapping algorithm to aid existing models in achieving superior results. Moreover, we also develop a multilingual corpus COVID-KGQA, which encourages COVID-19 research and multilingualism for the diversity of future AI. Finally, we discuss the key findings and their implications as well as performance guidelines and some future improvements. Our source code is available at \url{https://github.com/tamlhp/kbqa}.
Model-Agnostic and Diverse Explanations for Streaming Rumour Graphs
Jul 17, 2022
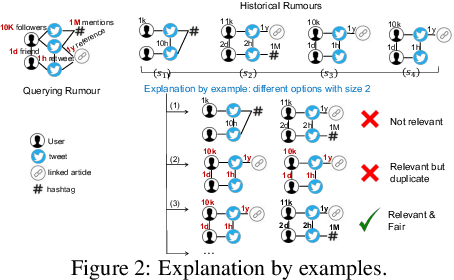
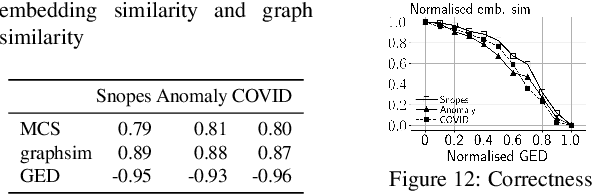
Abstract:The propagation of rumours on social media poses an important threat to societies, so that various techniques for rumour detection have been proposed recently. Yet, existing work focuses on \emph{what} entities constitute a rumour, but provides little support to understand \emph{why} the entities have been classified as such. This prevents an effective evaluation of the detected rumours as well as the design of countermeasures. In this work, we argue that explanations for detected rumours may be given in terms of examples of related rumours detected in the past. A diverse set of similar rumours helps users to generalize, i.e., to understand the properties that govern the detection of rumours. Since the spread of rumours in social media is commonly modelled using feature-annotated graphs, we propose a query-by-example approach that, given a rumour graph, extracts the $k$ most similar and diverse subgraphs from past rumours. The challenge is that all of the computations require fast assessment of similarities between graphs. To achieve an efficient and adaptive realization of the approach in a streaming setting, we present a novel graph representation learning technique and report on implementation considerations. Our evaluation experiments show that our approach outperforms baseline techniques in delivering meaningful explanations for various rumour propagation behaviours.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge