Mingyu You
HybridBooth: Hybrid Prompt Inversion for Efficient Subject-Driven Generation
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in text-to-image diffusion models have shown remarkable creative capabilities with textual prompts, but generating personalized instances based on specific subjects, known as subject-driven generation, remains challenging. To tackle this issue, we present a new hybrid framework called HybridBooth, which merges the benefits of optimization-based and direct-regression methods. HybridBooth operates in two stages: the Word Embedding Probe, which generates a robust initial word embedding using a fine-tuned encoder, and the Word Embedding Refinement, which further adapts the encoder to specific subject images by optimizing key parameters. This approach allows for effective and fast inversion of visual concepts into textual embedding, even from a single image, while maintaining the model's generalization capabilities.
Contrast, Imitate, Adapt: Learning Robotic Skills From Raw Human Videos
Aug 10, 2024Abstract:Learning robotic skills from raw human videos remains a non-trivial challenge. Previous works tackled this problem by leveraging behavior cloning or learning reward functions from videos. Despite their remarkable performances, they may introduce several issues, such as the necessity for robot actions, requirements for consistent viewpoints and similar layouts between human and robot videos, as well as low sample efficiency. To this end, our key insight is to learn task priors by contrasting videos and to learn action priors through imitating trajectories from videos, and to utilize the task priors to guide trajectories to adapt to novel scenarios. We propose a three-stage skill learning framework denoted as Contrast-Imitate-Adapt (CIA). An interaction-aware alignment transformer is proposed to learn task priors by temporally aligning video pairs. Then a trajectory generation model is used to learn action priors. To adapt to novel scenarios different from human videos, the Inversion-Interaction method is designed to initialize coarse trajectories and refine them by limited interaction. In addition, CIA introduces an optimization method based on semantic directions of trajectories for interaction security and sample efficiency. The alignment distances computed by IAAformer are used as the rewards. We evaluate CIA in six real-world everyday tasks, and empirically demonstrate that CIA significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art works in terms of task success rate and generalization to diverse novel scenarios layouts and object instances.
Goal-Conditioned Reinforcement Learning with Disentanglement-based Reachability Planning
Jul 20, 2023Abstract:Goal-Conditioned Reinforcement Learning (GCRL) can enable agents to spontaneously set diverse goals to learn a set of skills. Despite the excellent works proposed in various fields, reaching distant goals in temporally extended tasks remains a challenge for GCRL. Current works tackled this problem by leveraging planning algorithms to plan intermediate subgoals to augment GCRL. Their methods need two crucial requirements: (i) a state representation space to search valid subgoals, and (ii) a distance function to measure the reachability of subgoals. However, they struggle to scale to high-dimensional state space due to their non-compact representations. Moreover, they cannot collect high-quality training data through standard GC policies, which results in an inaccurate distance function. Both affect the efficiency and performance of planning and policy learning. In the paper, we propose a goal-conditioned RL algorithm combined with Disentanglement-based Reachability Planning (REPlan) to solve temporally extended tasks. In REPlan, a Disentangled Representation Module (DRM) is proposed to learn compact representations which disentangle robot poses and object positions from high-dimensional observations in a self-supervised manner. A simple REachability discrimination Module (REM) is also designed to determine the temporal distance of subgoals. Moreover, REM computes intrinsic bonuses to encourage the collection of novel states for training. We evaluate our REPlan in three vision-based simulation tasks and one real-world task. The experiments demonstrate that our REPlan significantly outperforms the prior state-of-the-art methods in solving temporally extended tasks.
3D Part Assembly Generation with Instance Encoded Transformer
Jul 05, 2022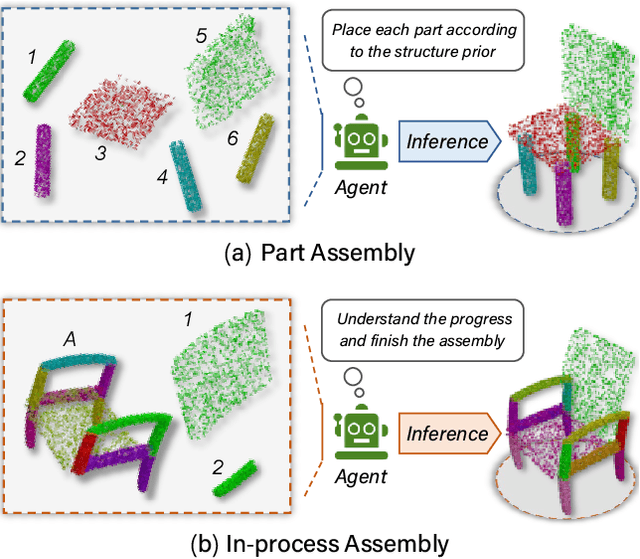
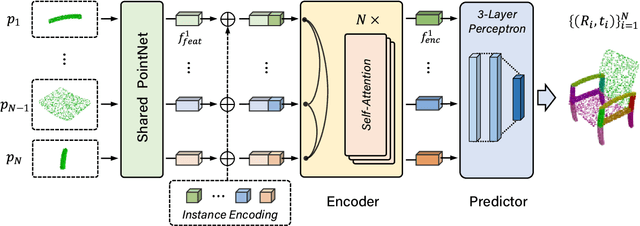
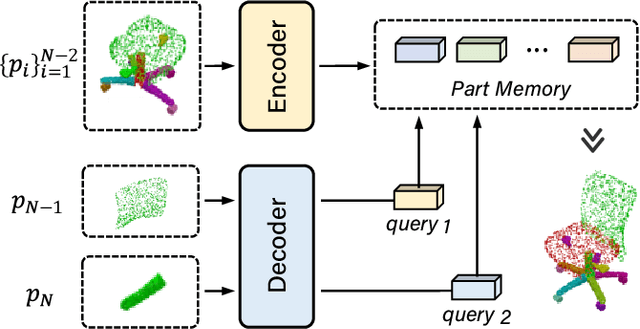
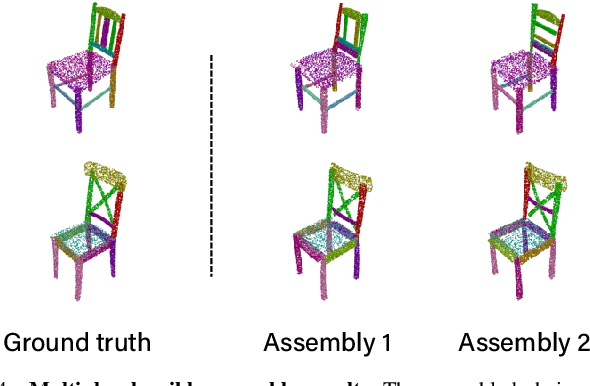
Abstract:It is desirable to enable robots capable of automatic assembly. Structural understanding of object parts plays a crucial role in this task yet remains relatively unexplored. In this paper, we focus on the setting of furniture assembly from a complete set of part geometries, which is essentially a 6-DoF part pose estimation problem. We propose a multi-layer transformer-based framework that involves geometric and relational reasoning between parts to update the part poses iteratively. We carefully design a unique instance encoding to solve the ambiguity between geometrically-similar parts so that all parts can be distinguished. In addition to assembling from scratch, we extend our framework to a new task called in-process part assembly. Analogous to furniture maintenance, it requires robots to continue with unfinished products and assemble the remaining parts into appropriate positions. Our method achieves far more than 10% improvements over the current state-of-the-art in multiple metrics on the public PartNet dataset. Extensive experiments and quantitative comparisons demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
* 8 pages, 7 figures
Weakly Supervised Disentangled Representation for Goal-conditioned Reinforcement Learning
Feb 28, 2022



Abstract:Goal-conditioned reinforcement learning is a crucial yet challenging algorithm which enables agents to achieve multiple user-specified goals when learning a set of skills in a dynamic environment. However, it typically requires millions of the environmental interactions explored by agents, which is sample-inefficient. In the paper, we propose a skill learning framework DR-GRL that aims to improve the sample efficiency and policy generalization by combining the Disentangled Representation learning and Goal-conditioned visual Reinforcement Learning. In a weakly supervised manner, we propose a Spatial Transform AutoEncoder (STAE) to learn an interpretable and controllable representation in which different parts correspond to different object attributes (shape, color, position). Due to the high controllability of the representations, STAE can simply recombine and recode the representations to generate unseen goals for agents to practice themselves. The manifold structure of the learned representation maintains consistency with the physical position, which is beneficial for reward calculation. We empirically demonstrate that DR-GRL significantly outperforms the previous methods in sample efficiency and policy generalization. In addition, DR-GRL is also easy to expand to the real robot.
* 8 pages; Accepted by RAL with ICRA 2022
Diverse Knowledge Distillation for End-to-End Person Search
Dec 21, 2020



Abstract:Person search aims to localize and identify a specific person from a gallery of images. Recent methods can be categorized into two groups, i.e., two-step and end-to-end approaches. The former views person search as two independent tasks and achieves dominant results using separately trained person detection and re-identification (Re-ID) models. The latter performs person search in an end-to-end fashion. Although the end-to-end approaches yield higher inference efficiency, they largely lag behind those two-step counterparts in terms of accuracy. In this paper, we argue that the gap between the two kinds of methods is mainly caused by the Re-ID sub-networks of end-to-end methods. To this end, we propose a simple yet strong end-to-end network with diverse knowledge distillation to break the bottleneck. We also design a spatial-invariant augmentation to assist model to be invariant to inaccurate detection results. Experimental results on the CUHK-SYSU and PRW datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method against existing approaches -- it achieves on par accuracy with state-of-the-art two-step methods while maintaining high efficiency due to the single joint model. Code is available at: https://git.io/DKD-PersonSearch.
Mask Encoding for Single Shot Instance Segmentation
Mar 26, 2020



Abstract:To date, instance segmentation is dominated by twostage methods, as pioneered by Mask R-CNN. In contrast, one-stage alternatives cannot compete with Mask R-CNN in mask AP, mainly due to the difficulty of compactly representing masks, making the design of one-stage methods very challenging. In this work, we propose a simple singleshot instance segmentation framework, termed mask encoding based instance segmentation (MEInst). Instead of predicting the two-dimensional mask directly, MEInst distills it into a compact and fixed-dimensional representation vector, which allows the instance segmentation task to be incorporated into one-stage bounding-box detectors and results in a simple yet efficient instance segmentation framework. The proposed one-stage MEInst achieves 36.4% in mask AP with single-model (ResNeXt-101-FPN backbone) and single-scale testing on the MS-COCO benchmark. We show that the much simpler and flexible one-stage instance segmentation method, can also achieve competitive performance. This framework can be easily adapted for other instance-level recognition tasks. Code is available at: https://git.io/AdelaiDet
Part-Guided Attention Learning for Vehicle Re-Identification
Sep 19, 2019



Abstract:Vehicle re-identification (Re-ID) often requires one to recognize the fine-grained visual differences between vehicles. Besides the holistic appearance of vehicles which is easily affected by the viewpoint variation and distortion, vehicle parts also provide crucial cues to differentiate near-identical vehicles. Motivated by these observations, we introduce a Part-Guided Attention Network (PGAN) to pinpoint the prominent part regions and effectively combine the global and part information for discriminative feature learning. PGAN first detects the locations of different part components and salient regions regardless of the vehicle identity, which serve as the bottom-up attention to narrow down the possible searching regions. To estimate the importance of detected parts, we propose a Part Attention Module (PAM) to adaptively locate the most discriminative regions with high-attention weights and suppress the distraction of irrelevant parts with relatively low weights. The PAM is guided by the Re-ID loss and therefore provides top-down attention that enables attention to be calculated at the level of car parts and other salient regions. Finally, we aggregate the global appearance and part features to improve the feature performance further. The PGAN combines part-guided bottom-up and top-down attention, global and part visual features in an end-to-end framework. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves new state-of-the-art vehicle Re-ID performance on four large-scale benchmark datasets.
Self-training with progressive augmentation for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification
Jul 31, 2019



Abstract:Person re-identification (Re-ID) has achieved great improvement with deep learning and a large amount of labelled training data. However, it remains a challenging task for adapting a model trained in a source domain of labelled data to a target domain of only unlabelled data available. In this work, we develop a self-training method with progressive augmentation framework (PAST) to promote the model performance progressively on the target dataset. Specially, our PAST framework consists of two stages, namely, conservative stage and promoting stage. The conservative stage captures the local structure of target-domain data points with triplet-based loss functions, leading to improved feature representations. The promoting stage continuously optimizes the network by appending a changeable classification layer to the last layer of the model, enabling the use of global information about the data distribution. Importantly, we propose a new self-training strategy that progressively augments the model capability by adopting conservative and promoting stages alternately. Furthermore, to improve the reliability of selected triplet samples, we introduce a ranking-based triplet loss in the conservative stage, which is a label-free objective function basing on the similarities between data pairs. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art person Re-ID performance under the unsupervised cross-domain setting. Code is available at: https://tinyurl.com/PASTReID
Adversarial Generation of Training Examples: Applications to Moving Vehicle License Plate Recognition
Nov 10, 2017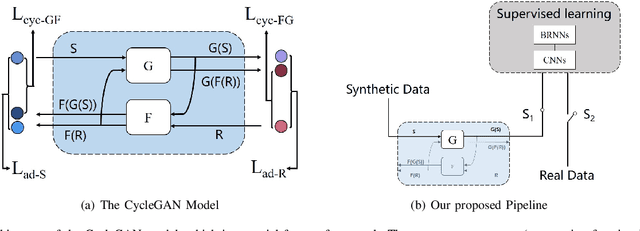

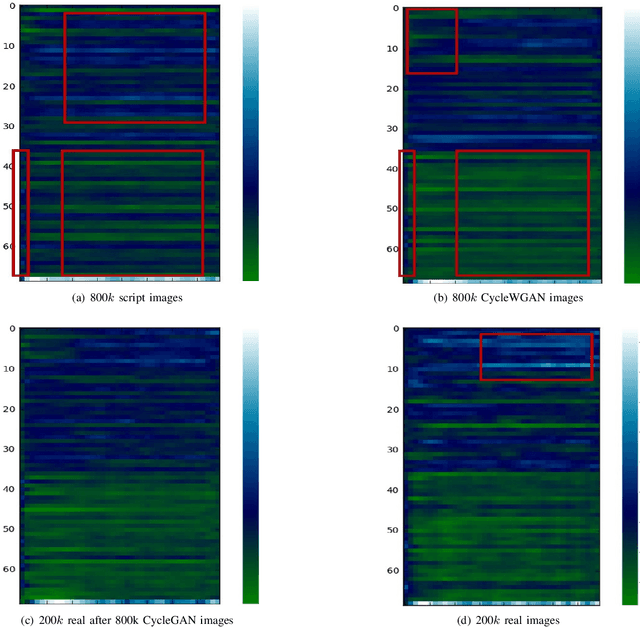

Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) have attracted much research attention recently, leading to impressive results for natural image generation. However, to date little success was observed in using GAN generated images for improving classification tasks. Here we attempt to explore, in the context of car license plate recognition, whether it is possible to generate synthetic training data using GAN to improve recognition accuracy. With a carefully-designed pipeline, we show that the answer is affirmative. First, a large-scale image set is generated using the generator of GAN, without manual annotation. Then, these images are fed to a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) followed by a bidirectional recurrent neural network (BRNN) with long short-term memory (LSTM), which performs the feature learning and sequence labelling. Finally, the pre-trained model is fine-tuned on real images. Our experimental results on a few data sets demonstrate the effectiveness of using GAN images: an improvement of 7.5% over a strong baseline with moderate-sized real data being available. We show that the proposed framework achieves competitive recognition accuracy on challenging test datasets. We also leverage the depthwise separate convolution to construct a lightweight convolutional RNN, which is about half size and 2x faster on CPU. Combining this framework and the proposed pipeline, we make progress in performing accurate recognition on mobile and embedded devices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge