Min Yan
MAN TruckScenes: A multimodal dataset for autonomous trucking in diverse conditions
Jul 10, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous trucking is a promising technology that can greatly impact modern logistics and the environment. Ensuring its safety on public roads is one of the main duties that requires an accurate perception of the environment. To achieve this, machine learning methods rely on large datasets, but to this day, no such datasets are available for autonomous trucks. In this work, we present MAN TruckScenes, the first multimodal dataset for autonomous trucking. MAN TruckScenes allows the research community to come into contact with truck-specific challenges, such as trailer occlusions, novel sensor perspectives, and terminal environments for the first time. It comprises more than 740 scenes of 20 s each within a multitude of different environmental conditions. The sensor set includes 4 cameras, 6 lidar, 6 radar sensors, 2 IMUs, and a high-precision GNSS. The dataset's 3D bounding boxes were manually annotated and carefully reviewed to achieve a high quality standard. Bounding boxes are available for 27 object classes, 15 attributes, and a range of more than 230 m. The scenes are tagged according to 34 distinct scene tags, and all objects are tracked throughout the scene to promote a wide range of applications. Additionally, MAN TruckScenes is the first dataset to provide 4D radar data with 360{\deg} coverage and is thereby the largest radar dataset with annotated 3D bounding boxes. Finally, we provide extensive dataset analysis and baseline results. The dataset, development kit and more are available online.
Real-Time 4K Super-Resolution of Compressed AVIF Images. AIS 2024 Challenge Survey
Apr 25, 2024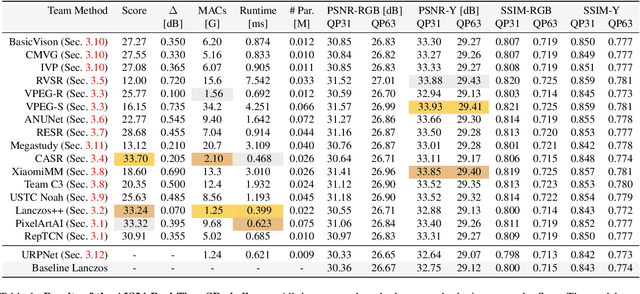
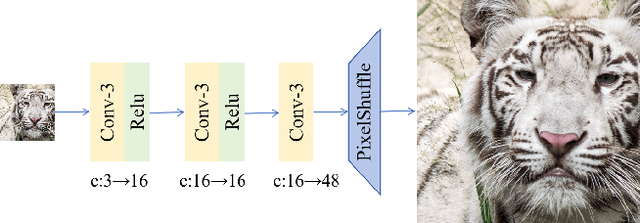
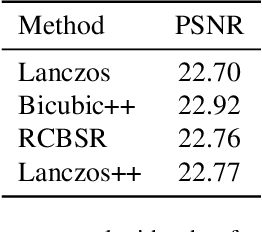
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel benchmark as part of the AIS 2024 Real-Time Image Super-Resolution (RTSR) Challenge, which aims to upscale compressed images from 540p to 4K resolution (4x factor) in real-time on commercial GPUs. For this, we use a diverse test set containing a variety of 4K images ranging from digital art to gaming and photography. The images are compressed using the modern AVIF codec, instead of JPEG. All the proposed methods improve PSNR fidelity over Lanczos interpolation, and process images under 10ms. Out of the 160 participants, 25 teams submitted their code and models. The solutions present novel designs tailored for memory-efficiency and runtime on edge devices. This survey describes the best solutions for real-time SR of compressed high-resolution images.
The Ninth NTIRE 2024 Efficient Super-Resolution Challenge Report
Apr 16, 2024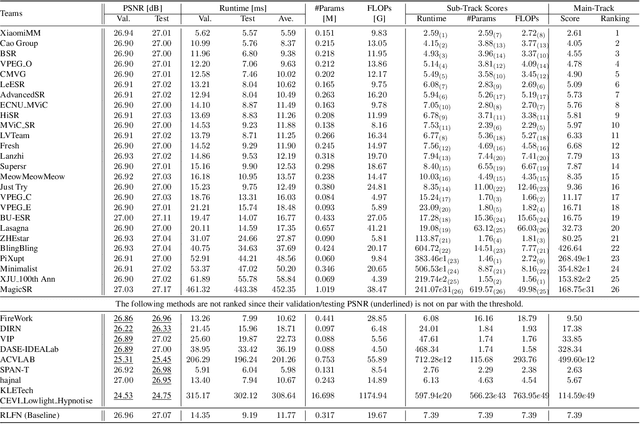
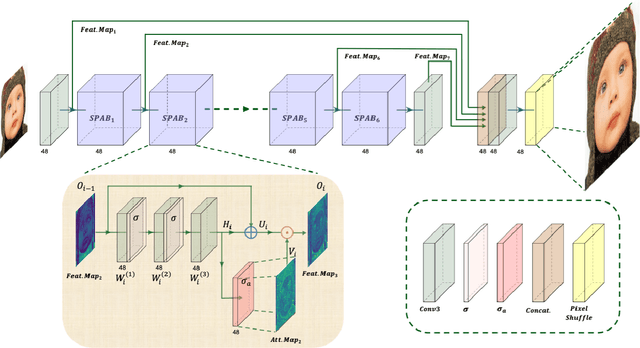
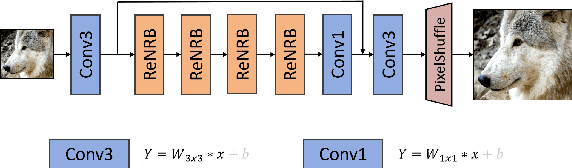
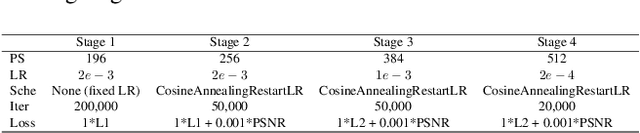
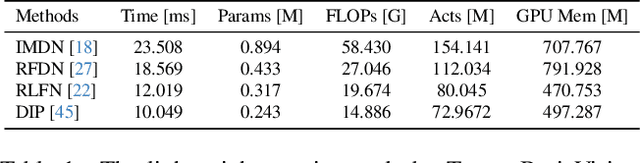
Abstract:This paper provides a comprehensive review of the NTIRE 2024 challenge, focusing on efficient single-image super-resolution (ESR) solutions and their outcomes. The task of this challenge is to super-resolve an input image with a magnification factor of x4 based on pairs of low and corresponding high-resolution images. The primary objective is to develop networks that optimize various aspects such as runtime, parameters, and FLOPs, while still maintaining a peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) of approximately 26.90 dB on the DIV2K_LSDIR_valid dataset and 26.99 dB on the DIV2K_LSDIR_test dataset. In addition, this challenge has 4 tracks including the main track (overall performance), sub-track 1 (runtime), sub-track 2 (FLOPs), and sub-track 3 (parameters). In the main track, all three metrics (ie runtime, FLOPs, and parameter count) were considered. The ranking of the main track is calculated based on a weighted sum-up of the scores of all other sub-tracks. In sub-track 1, the practical runtime performance of the submissions was evaluated, and the corresponding score was used to determine the ranking. In sub-track 2, the number of FLOPs was considered. The score calculated based on the corresponding FLOPs was used to determine the ranking. In sub-track 3, the number of parameters was considered. The score calculated based on the corresponding parameters was used to determine the ranking. RLFN is set as the baseline for efficiency measurement. The challenge had 262 registered participants, and 34 teams made valid submissions. They gauge the state-of-the-art in efficient single-image super-resolution. To facilitate the reproducibility of the challenge and enable other researchers to build upon these findings, the code and the pre-trained model of validated solutions are made publicly available at https://github.com/Amazingren/NTIRE2024_ESR/.
Semantic Segmentation on VSPW Dataset through Contrastive Loss and Multi-dataset Training Approach
Jun 06, 2023Abstract:Video scene parsing incorporates temporal information, which can enhance the consistency and accuracy of predictions compared to image scene parsing. The added temporal dimension enables a more comprehensive understanding of the scene, leading to more reliable results. This paper presents the winning solution of the CVPR2023 workshop for video semantic segmentation, focusing on enhancing Spatial-Temporal correlations with contrastive loss. We also explore the influence of multi-dataset training by utilizing a label-mapping technique. And the final result is aggregating the output of the above two models. Our approach achieves 65.95% mIoU performance on the VSPW dataset, ranked 1st place on the VSPW challenge at CVPR 2023.
Nondiscriminatory Treatment: a straightforward framework for multi-human parsing
Jan 26, 2021
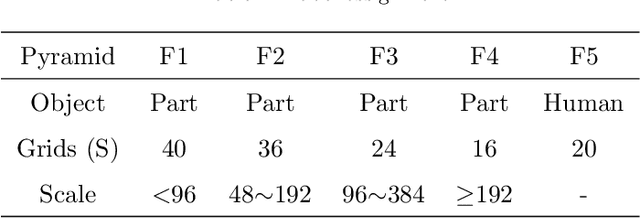
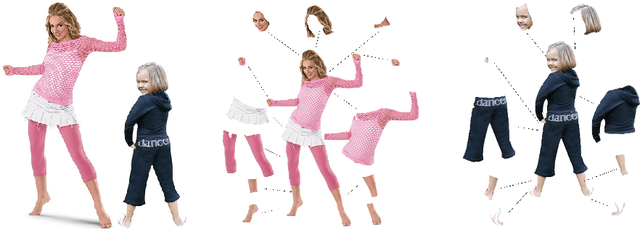
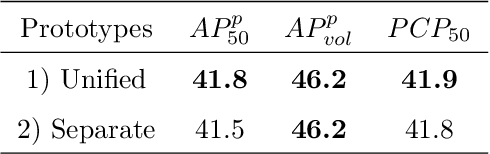
Abstract:Multi-human parsing aims to segment every body part of every human instance. Nearly all state-of-the-art methods follow the "detection first" or "segmentation first" pipelines. Different from them, we present an end-to-end and box-free pipeline from a new and more human-intuitive perspective. In training time, we directly do instance segmentation on humans and parts. More specifically, we introduce a notion of "indiscriminate objects with categorie" which treats humans and parts without distinction and regards them both as instances with categories. In the mask prediction, each binary mask is obtained by a combination of prototypes shared among all human and part categories. In inference time, we design a brand-new grouping post-processing method that relates each part instance with one single human instance and groups them together to obtain the final human-level parsing result. We name our method as Nondiscriminatory Treatment between Humans and Parts for Human Parsing (NTHP). Experiments show that our network performs superiorly against state-of-the-art methods by a large margin on the MHP v2.0 and PASCAL-Person-Part datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge