Mike D'Arcy
AstaBench: Rigorous Benchmarking of AI Agents with a Scientific Research Suite
Oct 24, 2025Abstract:AI agents hold the potential to revolutionize scientific productivity by automating literature reviews, replicating experiments, analyzing data, and even proposing new directions of inquiry; indeed, there are now many such agents, ranging from general-purpose "deep research" systems to specialized science-specific agents, such as AI Scientist and AIGS. Rigorous evaluation of these agents is critical for progress. Yet existing benchmarks fall short on several fronts: they (1) fail to provide holistic, product-informed measures of real-world use cases such as science research; (2) lack reproducible agent tools necessary for a controlled comparison of core agentic capabilities; (3) do not account for confounding variables such as model cost and tool access; (4) do not provide standardized interfaces for quick agent prototyping and evaluation; and (5) lack comprehensive baseline agents necessary to identify true advances. In response, we define principles and tooling for more rigorously benchmarking agents. Using these, we present AstaBench, a suite that provides the first holistic measure of agentic ability to perform scientific research, comprising 2400+ problems spanning the entire scientific discovery process and multiple scientific domains, and including many problems inspired by actual user requests to deployed Asta agents. Our suite comes with the first scientific research environment with production-grade search tools that enable controlled, reproducible evaluation, better accounting for confounders. Alongside, we provide a comprehensive suite of nine science-optimized classes of Asta agents and numerous baselines. Our extensive evaluation of 57 agents across 22 agent classes reveals several interesting findings, most importantly that despite meaningful progress on certain individual aspects, AI remains far from solving the challenge of science research assistance.
MARG: Multi-Agent Review Generation for Scientific Papers
Jan 08, 2024Abstract:We study the ability of LLMs to generate feedback for scientific papers and develop MARG, a feedback generation approach using multiple LLM instances that engage in internal discussion. By distributing paper text across agents, MARG can consume the full text of papers beyond the input length limitations of the base LLM, and by specializing agents and incorporating sub-tasks tailored to different comment types (experiments, clarity, impact) it improves the helpfulness and specificity of feedback. In a user study, baseline methods using GPT-4 were rated as producing generic or very generic comments more than half the time, and only 1.7 comments per paper were rated as good overall in the best baseline. Our system substantially improves the ability of GPT-4 to generate specific and helpful feedback, reducing the rate of generic comments from 60% to 29% and generating 3.7 good comments per paper (a 2.2x improvement).
ARIES: A Corpus of Scientific Paper Edits Made in Response to Peer Reviews
Jun 21, 2023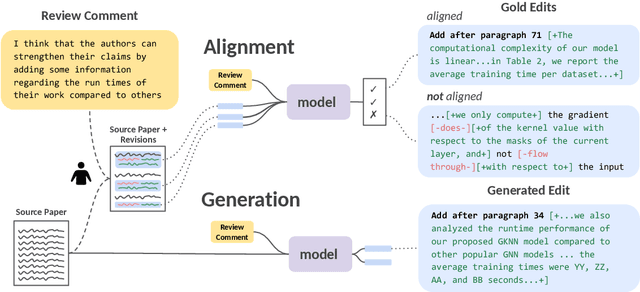

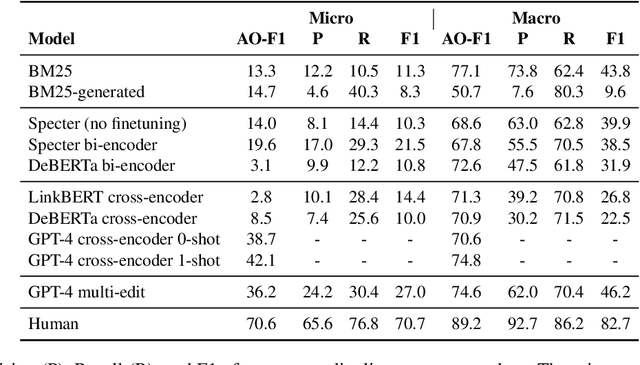
Abstract:Revising scientific papers based on peer feedback is a challenging task that requires not only deep scientific knowledge and reasoning, but also the ability to recognize the implicit requests in high-level feedback and to choose the best of many possible ways to update the manuscript in response. We introduce this task for large language models and release ARIES, a dataset of review comments and their corresponding paper edits, to enable training and evaluating models. We study two versions of the task: comment-edit alignment and edit generation, and evaluate several baselines, including GPT-4. We find that models struggle even to identify the edits that correspond to a comment, especially in cases where the comment is phrased in an indirect way or where the edit addresses the spirit of a comment but not the precise request. When tasked with generating edits, GPT-4 often succeeds in addressing comments on a surface level, but it rigidly follows the wording of the feedback rather than the underlying intent, and includes fewer technical details than human-written edits. We hope that our formalization, dataset, and analysis will form a foundation for future work in this area.
SciRepEval: A Multi-Format Benchmark for Scientific Document Representations
Nov 23, 2022



Abstract:Learned representations of scientific documents can serve as valuable input features for downstream tasks, without the need for further fine-tuning. However, existing benchmarks for evaluating these representations fail to capture the diversity of relevant tasks. In response, we introduce SciRepEval, the first comprehensive benchmark for training and evaluating scientific document representations. It includes 25 challenging and realistic tasks, 11 of which are new, across four formats: classification, regression, ranking and search. We then use the benchmark to study and improve the generalization ability of scientific document representation models. We show how state-of-the-art models struggle to generalize across task formats, and that simple multi-task training fails to improve them. However, a new approach that learns multiple embeddings per document, each tailored to a different format, can improve performance. We experiment with task-format-specific control codes and adapters in a multi-task setting and find that they outperform the existing single-embedding state-of-the-art by up to 1.5 points absolute.
Embedding Recycling for Language Models
Jul 11, 2022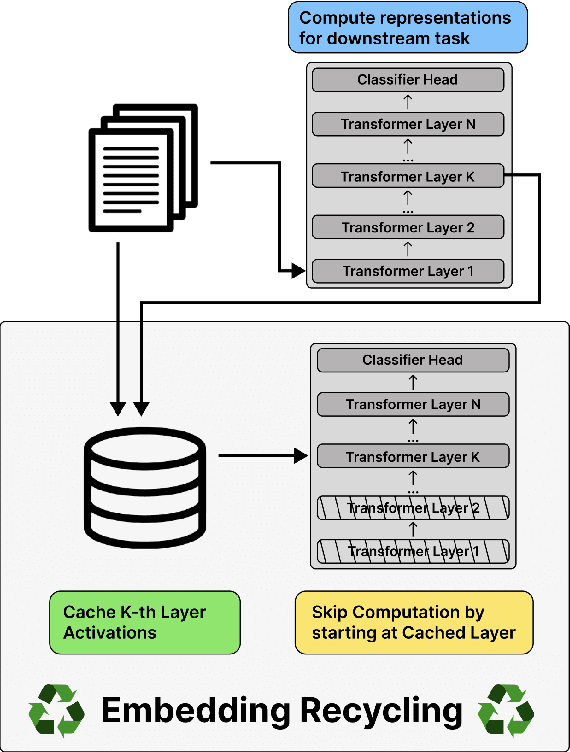
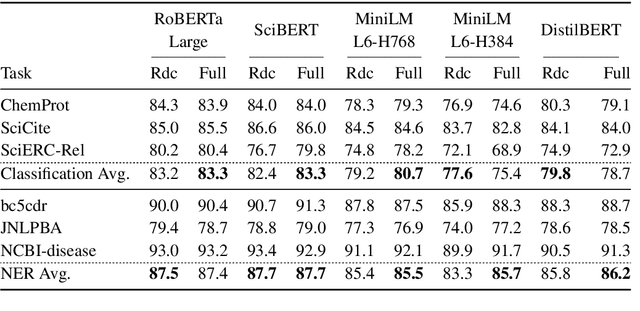
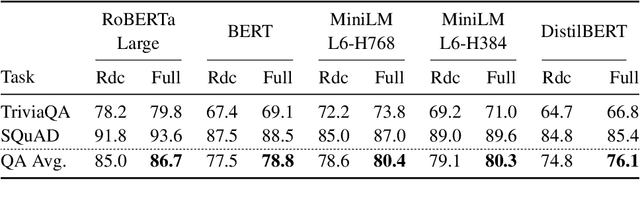
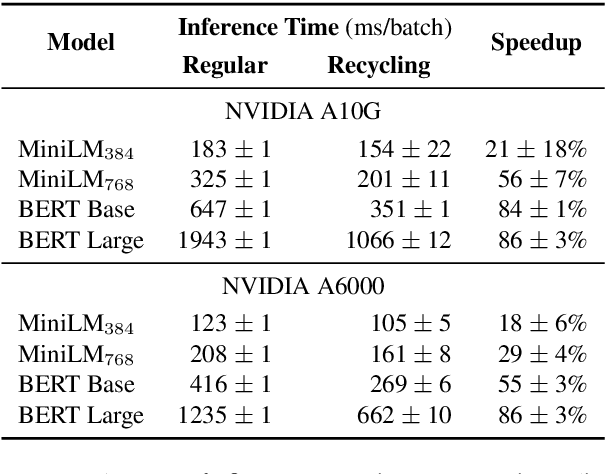
Abstract:Training and inference with large neural models is expensive. However, for many application domains, while new tasks and models arise frequently, the underlying documents being modeled remain mostly unchanged. We study how to decrease computational cost in such settings through embedding recycling (ER): re-using activations from previous model runs when performing training or inference. In contrast to prior work focusing on freezing small classification heads for finetuning which often leads to notable drops in performance, we propose caching an intermediate layer's output from a pretrained model and finetuning the remaining layers for new tasks. We show that our method provides a 100% speedup during training and a 55-86% speedup for inference, and has negligible impacts on accuracy for text classification and entity recognition tasks in the scientific domain. For general-domain question answering tasks, ER offers a similar speedup and lowers accuracy by a small amount. Finally, we identify several open challenges and future directions for ER.
CODAH: An Adversarially Authored Question-Answer Dataset for Common Sense
Apr 12, 2019
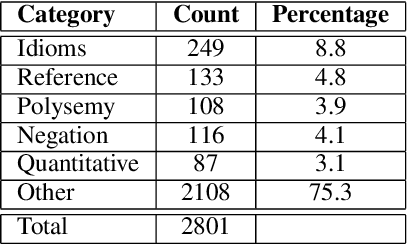
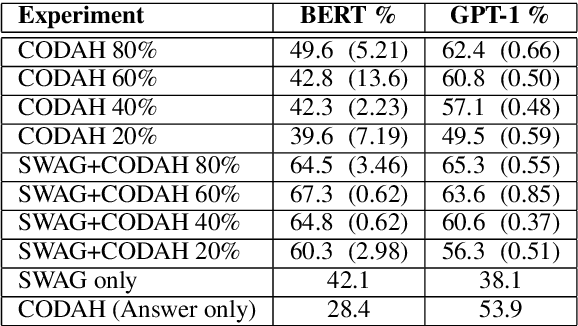
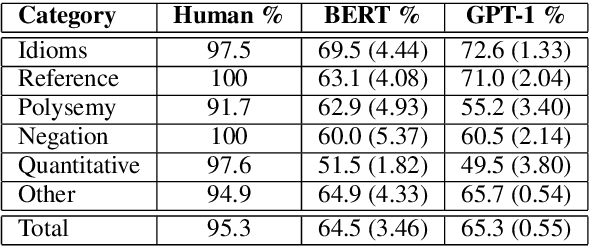
Abstract:Commonsense reasoning is a critical AI capability, but it is difficult to construct challenging datasets that test common sense. Recent neural question-answering systems, based on large pre-trained models of language, have already achieved near-human-level performance on commonsense knowledge benchmarks. These systems do not possess human-level common sense, but are able to exploit limitations of the datasets to achieve human-level scores. We introduce the CODAH dataset, an adversarially-constructed evaluation dataset for testing common sense. CODAH forms a challenging extension to the recently-proposed SWAG dataset, which tests commonsense knowledge using sentence-completion questions that describe situations observed in video. To produce a more difficult dataset, we introduce a novel procedure for question acquisition in which workers author questions designed to target weaknesses of state-of-the-art neural question answering systems. Workers are rewarded for submissions that models fail to answer correctly both before and after fine-tuning (in cross-validation). We create 2.8k questions via this procedure and evaluate the performance of multiple state-of-the-art question answering systems on our dataset. We observe a significant gap between human performance, which is 95.3%, and the performance of the best baseline accuracy of 65.3% by the OpenAI GPT model.
DeepMoTIon: Learning to Navigate Like Humans
Mar 02, 2019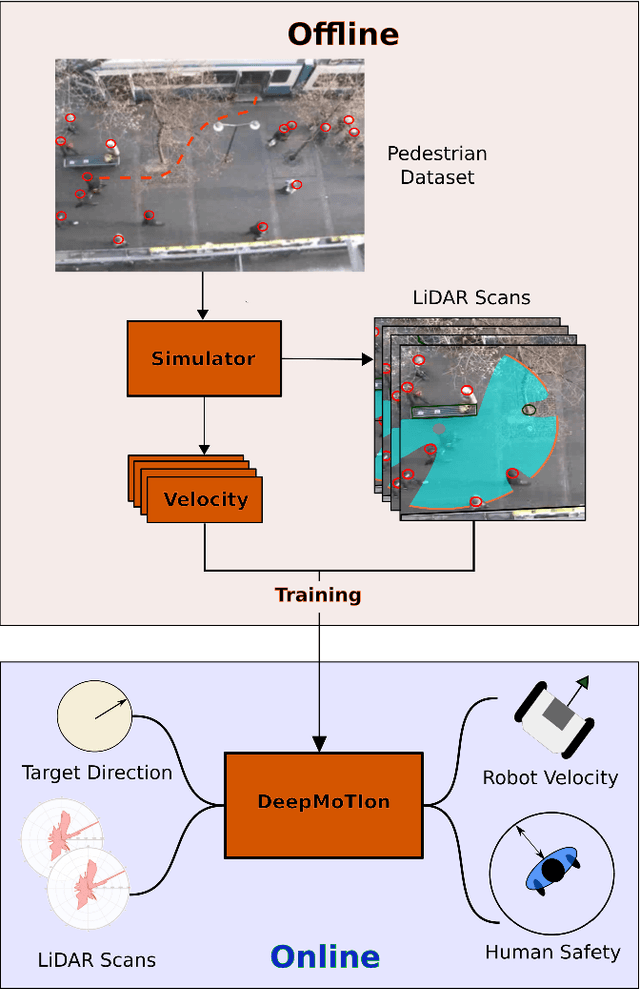
Abstract:We present a novel human-aware navigation approach, where the robot learns to mimic humans to navigate safely in crowds. The presented model referred to as DeepMoTIon, is trained with pedestrian surveillance data to predict human velocity. The robot processes LiDAR scans via the trained network to navigate to the target location. We conduct extensive experiments to assess the different components of our network and prove the necessity of each to imitate humans. Our experiments show that DeepMoTIon outperforms state-of-the-art in terms of human imitation and reaches the target on 100% of the test cases without breaching humans' safe distance.
Setting Up the Beam for Human-Centered Service Tasks
Oct 18, 2017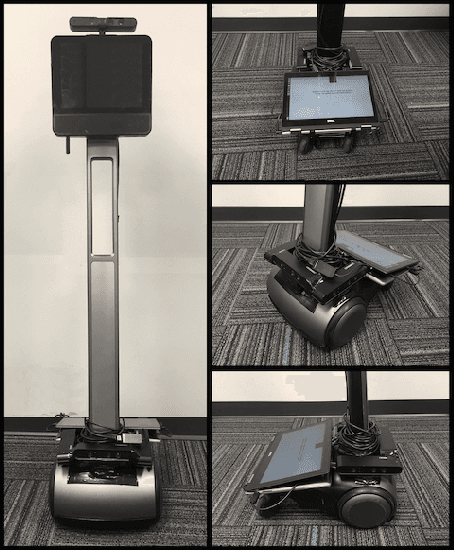
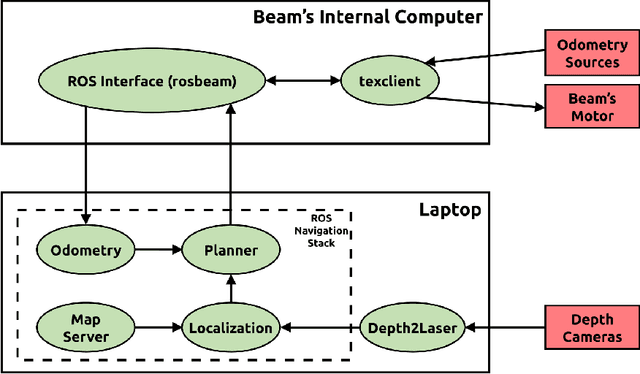
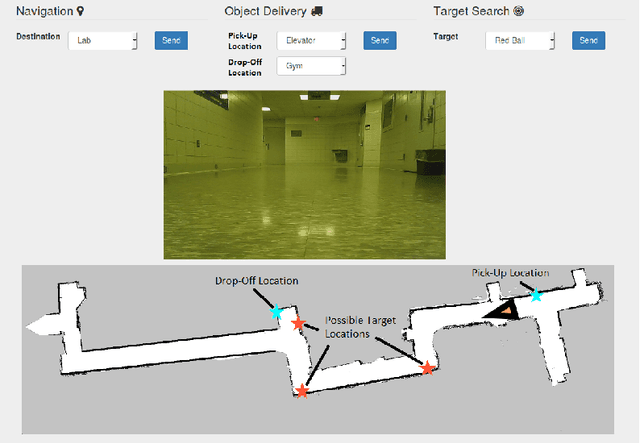
Abstract:We introduce the Beam, a collaborative autonomous mobile service robot, based on SuitableTech's Beam telepresence system. We present a set of enhancements to the telepresence system, including autonomy, human awareness, increased computation and sensing capabilities, and integration with the popular Robot Operating System (ROS) framework. Together, our improvements transform the Beam into a low-cost platform for research on service robots. We examine the Beam on target search and object delivery tasks and demonstrate that the robot achieves a 100% success rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge