Miguel A. Ferrer
Telling Human and Machine Handwriting Apart
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Handwriting movements can be leveraged as a unique form of behavioral biometrics, to verify whether a real user is operating a device or application. This task can be framed as a reverse Turing test in which a computer has to detect if an input instance has been generated by a human or artificially. To tackle this task, we study ten public datasets of handwritten symbols (isolated characters, digits, gestures, pointing traces, and signatures) that are artificially reproduced using seven different synthesizers, including, among others, the Kinematic Theory (Sigma h model), generative adversarial networks, Transformers, and Diffusion models. We train a shallow recurrent neural network that achieves excellent performance (98.3 percent Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC) score and 1.4 percent equal error rate on average across all synthesizers and datasets) using nonfeaturized trajectory data as input. In few-shot settings, we show that our classifier achieves such an excellent performance when trained on just 10 percent of the data, as evaluated on the remaining 90% of the data as a test set. We further challenge our classifier in out-of-domain settings, and observe very competitive results as well. Our work has implications for computerized systems that need to verify human presence, and adds an additional layer of security to keep attackers at bay.
Online Signature Verification based on the Lagrange formulation with 2D and 3D robotic models
Mar 17, 2025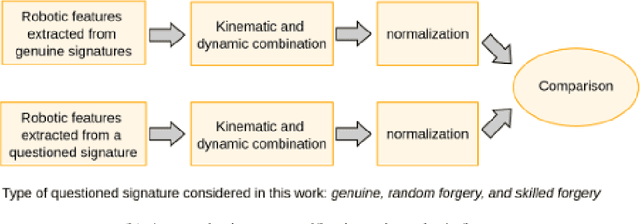
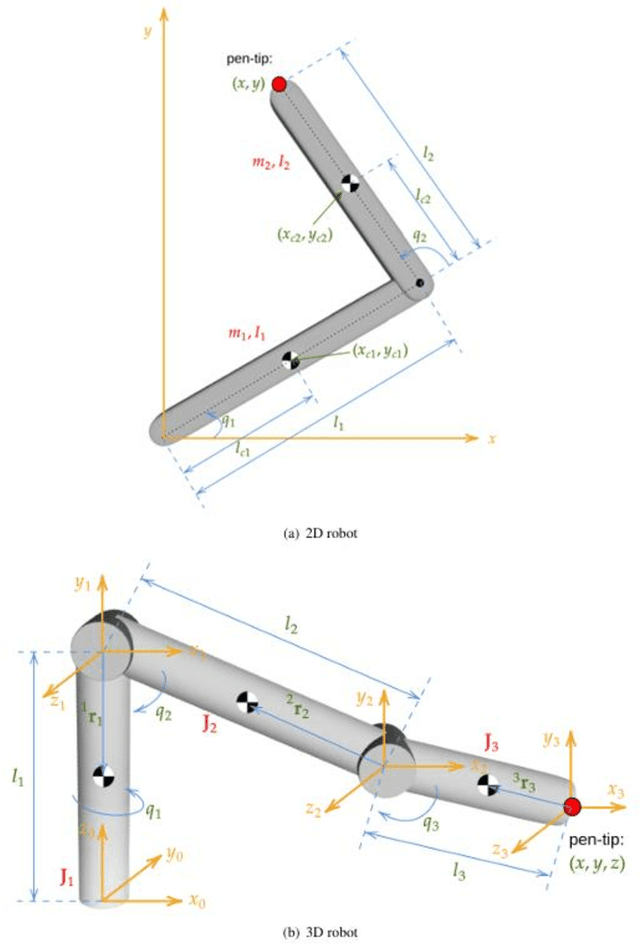
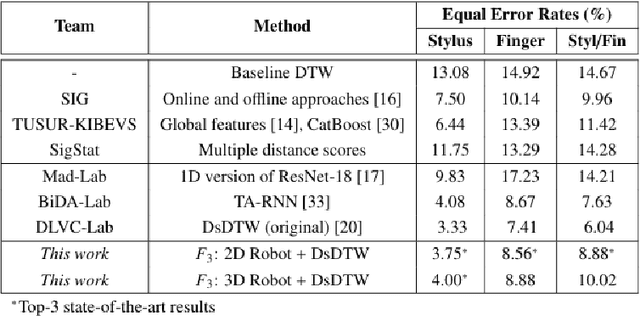
Abstract:Online Signature Verification commonly relies on function-based features, such as time-sampled horizontal and vertical coordinates, as well as the pressure exerted by the writer, obtained through a digitizer. Although inferring additional information about the writers arm pose, kinematics, and dynamics based on digitizer data can be useful, it constitutes a challenge. In this paper, we tackle this challenge by proposing a new set of features based on the dynamics of online signatures. These new features are inferred through a Lagrangian formulation, obtaining the sequences of generalized coordinates and torques for 2D and 3D robotic arm models. By combining kinematic and dynamic robotic features, our results demonstrate their significant effectiveness for online automatic signature verification and achieving state-of-the-art results when integrated into deep learning models.
Anthropomorphic Features for On-Line Signatures
Jan 15, 2025



Abstract:Many features have been proposed in on-line signature verification. Generally, these features rely on the position of the on-line signature samples and their dynamic properties, as recorded by a tablet. This paper proposes a novel feature space to describe efficiently on-line signatures. Since producing a signature requires a skeletal arm system and its associated muscles, the new feature space is based on characterizing the movement of the shoulder, the elbow and the wrist joints when signing. As this motion is not directly obtained from a digital tablet, the new features are calculated by means of a virtual skeletal arm (VSA) model, which simulates the architecture of a real arm and forearm. Specifically, the VSA motion is described by its 3D joint position and its joint angles. These anthropomorphic features are worked out from both pen position and orientation through the VSA forward and direct kinematic model. The anthropomorphic features' robustness is proved by achieving state-of-the-art performance with several verifiers and multiple benchmarks on third party signature databases, which were collected with different devices and in different languages and scripts.
Neural network modelling of kinematic and dynamic features for signature verification
Nov 26, 2024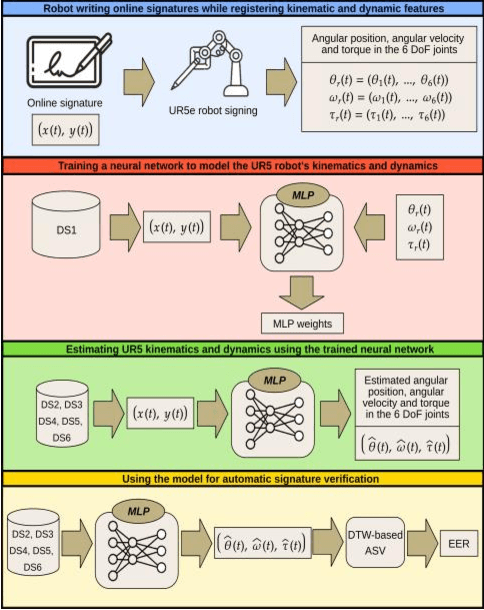
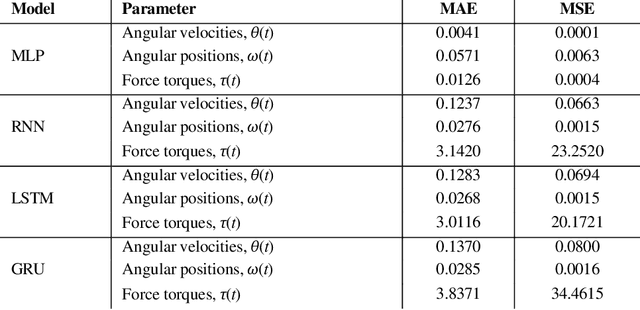
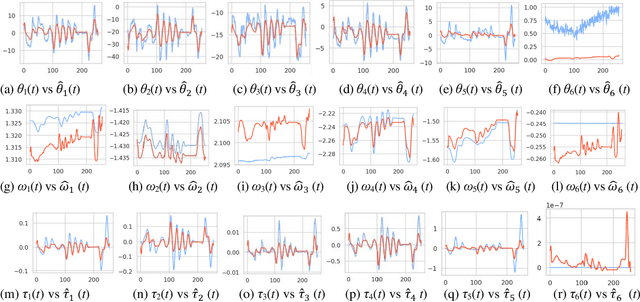
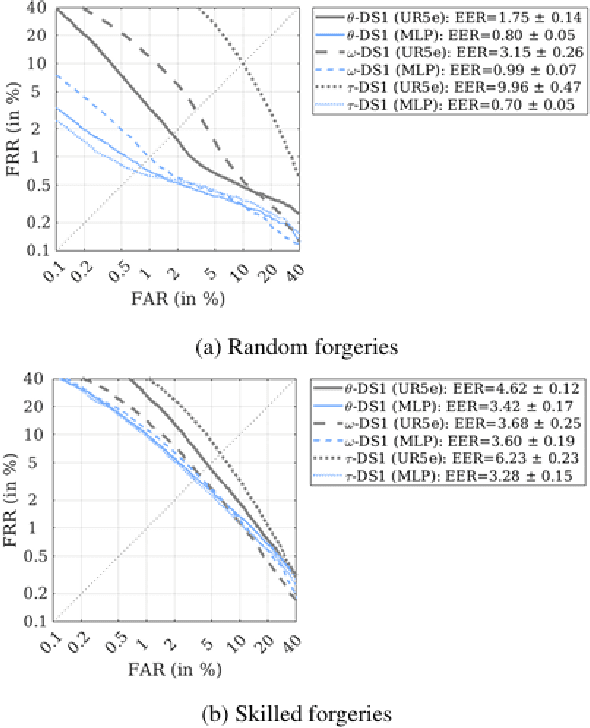
Abstract:Online signature parameters, which are based on human characteristics, broaden the applicability of an automatic signature verifier. Although kinematic and dynamic features have previously been suggested, accurately measuring features such as arm and forearm torques remains challenging. We present two approaches for estimating angular velocities, angular positions, and force torques. The first approach involves using a physical UR5e robotic arm to reproduce a signature while capturing those parameters over time. The second method, a cost effective approach, uses a neural network to estimate the same parameters. Our findings demonstrate that a simple neural network model can extract effective parameters for signature verification. Training the neural network with the MCYT300 dataset and cross validating with other databases, namely, BiosecurID, Visual, Blind, OnOffSigDevanagari 75 and OnOffSigBengali 75 confirm the models generalization capability.
Towards human-like kinematics in industrial robotic arms: a case study on a UR3 robot
Sep 25, 2024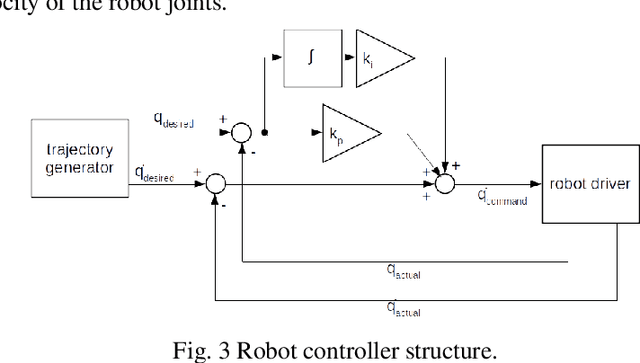
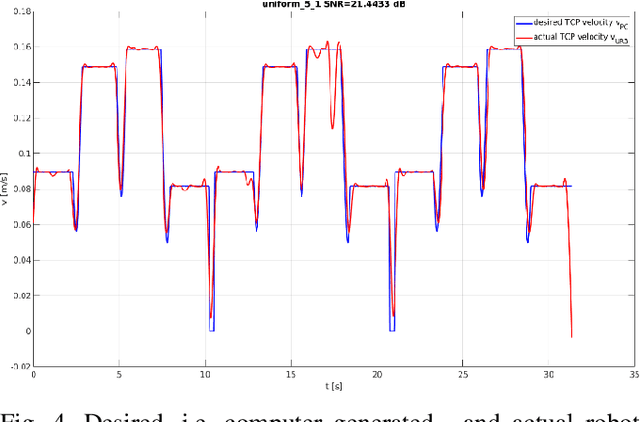
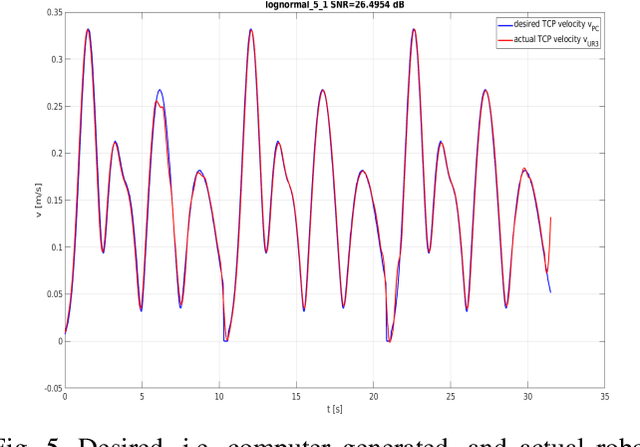
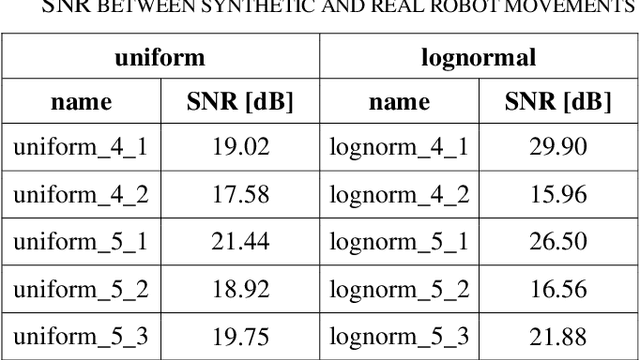
Abstract:Safety in industrial robotic environments is a hot research topic in the area of human-robot interaction (HRI). Up to now, a robotic arm on an assembly line interacts with other machines away from human workers. Nowadays, robotic arm manufactures are aimed to their robots could increasingly perform tasks collaborating with humans. One of the ways to improve this collaboration is by making the movement of robots more humanlike. This way, it would be easier for a human to foresee the movement of the robot and approach it without fear of contact. The main difference between the movement of a human and of a robotic arm is that the former has a bell-shaped speed profile while the latter has a uniform speed one. To generate this speed profile, the kinematic theory of rapid human movements and its Sigma-Lognormal model has been used. This model is widely used to explain most of the basic phenomena related to the control of human movements. Both human-like and robotic-like movements are transferred to the UR3 robot. In this paper we detail the how the UR3 robot was programmed to produce both kinds of movement. The dissimilarities result between the input motion and output motion to the robot confirm the possibility to develop human-like velocities in the UR3 robot.
* 6 pages, 5 figures
From operculum and body tail movements to different coupling of physical activity and respiratory frequency in farmed gilthead sea bream and European sea bass. Insights on aquaculture biosensing
Jun 06, 2024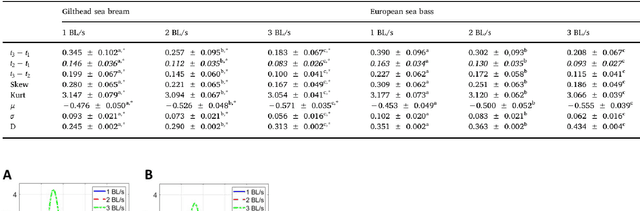
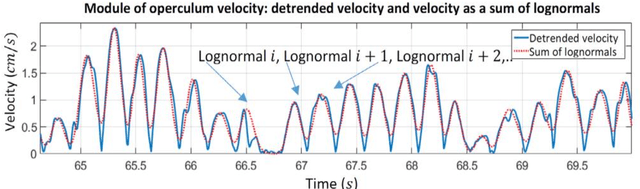
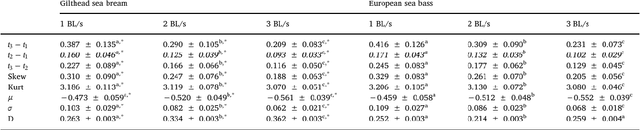
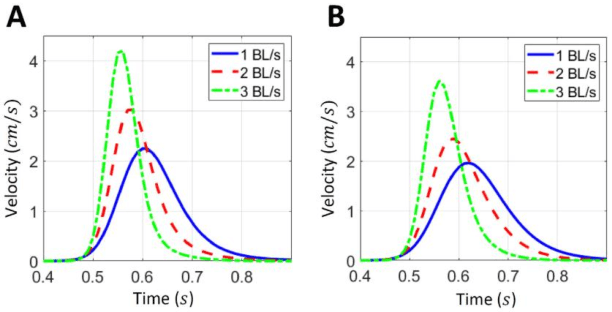
Abstract:The AEFishBIT tri-axial accelerometer was externally attached to the operculum to assess the divergent activity and respiratory patterns of two marine farmed fish, the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) and European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Analysis of raw data from exercised fish highlighted the large amplitude of operculum aperture and body tail movements in European sea bass, which were overall more stable at low-medium exercise intensity levels. Cosinor analysis in free-swimming fish (on-board data processing) highlighted a pronounced daily rhythmicity of locomotor activity and respiratory frequency in both gilthead sea bream and European sea bass. Acrophases of activity and respiration were coupled in gilthead sea bream, acting feeding time (once daily at 11:00 h) as a main synchronizing factor. By contrast, locomotor activity and respiratory frequency were out of phase in European sea bass with activity acrophase on early morning and respiration acrophase on the afternoon. The daily range of activity and respiration variation was also higher in European sea bass, probably as part of the adaptation of this fish species to act as a fast swimming predator. In any case, lower locomotor activity and enhanced respiration were associated with larger body weight in both fish species. This agrees with the notion that selection for fast growth in farming conditions is accompanied by a lower activity profile, which may favor an efficient feed conversion for growth purposes. Therefore, the use of behavioral monitoring is becoming a reliable and large-scale promising tool for selecting more efficient farmed fish, allowing researchers and farmers to establish stricter criteria of welfare for more sustainable and ethical fish production.
Writing Order Recovery in Complex and Long Static Handwriting
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:The order in which the trajectory is executed is a powerful source of information for recognizers. However, there is still no general approach for recovering the trajectory of complex and long handwriting from static images. Complex specimens can result in multiple pen-downs and in a high number of trajectory crossings yielding agglomerations of pixels (also known as clusters). While the scientific literature describes a wide range of approaches for recovering the writing order in handwriting, these approaches nevertheless lack a common evaluation metric. In this paper, we introduce a new system to estimate the order recovery of thinned static trajectories, which allows to effectively resolve the clusters and select the order of the executed pen-downs. We evaluate how knowing the starting points of the pen-downs affects the quality of the recovered writing. Once the stability and sensitivity of the system is analyzed, we describe a series of experiments with three publicly available databases, showing competitive results in all cases. We expect the proposed system, whose code is made publicly available to the research community, to reduce potential confusion when the order of complex trajectories are recovered, and this will in turn make the trajectories recovered to be viable for further applications, such as velocity estimation.
Uniform vs. Lognormal Kinematics in Robots: Perceptual Preferences for Robotic Movements
May 29, 2024



Abstract:Collaborative robots or cobots interact with humans in a common work environment. In cobots, one under investigated but important issue is related to their movement and how it is perceived by humans. This paper tries to analyze whether humans prefer a robot moving in a human or in a robotic fashion. To this end, the present work lays out what differentiates the movement performed by an industrial robotic arm from that performed by a human one. The main difference lies in the fact that the robotic movement has a trapezoidal speed profile, while for the human arm, the speed profile is bell-shaped and during complex movements, it can be considered as a sum of superimposed bell-shaped movements. Based on the lognormality principle, a procedure was developed for a robotic arm to perform human-like movements. Both speed profiles were implemented in two industrial robots, namely, an ABB IRB 120 and a Universal Robot UR3. Three tests were used to study the subjects' preference when seeing both movements and another analyzed the same when interacting with the robot by touching its ends with their fingers.
MDIW-13: a New Multi-Lingual and Multi-Script Database and Benchmark for Script Identification
May 29, 2024Abstract:Script identification plays a vital role in applications that involve handwriting and document analysis within a multi-script and multi-lingual environment. Moreover, it exhibits a profound connection with human cognition. This paper provides a new database for benchmarking script identification algorithms, which contains both printed and handwritten documents collected from a wide variety of scripts, such as Arabic, Bengali (Bangla), Gujarati, Gurmukhi, Devanagari, Japanese, Kannada, Malayalam, Oriya, Roman, Tamil, Telugu, and Thai. The dataset consists of 1,135 documents scanned from local newspaper and handwritten letters as well as notes from different native writers. Further, these documents are segmented into lines and words, comprising a total of 13,979 and 86,655 lines and words, respectively, in the dataset. Easy-to-go benchmarks are proposed with handcrafted and deep learning methods. The benchmark includes results at the document, line, and word levels with printed and handwritten documents. Results of script identification independent of the document/line/word level and independent of the printed/handwritten letters are also given. The new multi-lingual database is expected to create new script identifiers, present various challenges, including identifying handwritten and printed samples and serve as a foundation for future research in script identification based on the reported results of the three benchmarks.
Graphomotor and Handwriting Disabilities Rating Scale (GHDRS):towards complex and objective assessment
May 28, 2024Abstract:Graphomotor and handwriting disabilities (GD and HD, respectively) could significantly reduce children's quality of life. Effective remediation depends on proper diagnosis; however, current approaches to diagnosis and assessment of GD and HD have several limitations and knowledge gaps, e.g. they are subjective, they do not facilitate identification of specific manifestations, etc. The aim of this work is to introduce a new scale (GHDRS Graphomotor and Handwriting Disabilities Rating Scale) that will enable experts to perform objective and complex computeraided diagnosis and assessment of GD and HD. The scale supports quantification of 17 manifestations associated with the process/product of drawing/ handwriting. The whole methodology of GHDRS design is made maximally transparent so that it could be adapted for other languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge