Antonio Parziale
Writing Order Recovery in Complex and Long Static Handwriting
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:The order in which the trajectory is executed is a powerful source of information for recognizers. However, there is still no general approach for recovering the trajectory of complex and long handwriting from static images. Complex specimens can result in multiple pen-downs and in a high number of trajectory crossings yielding agglomerations of pixels (also known as clusters). While the scientific literature describes a wide range of approaches for recovering the writing order in handwriting, these approaches nevertheless lack a common evaluation metric. In this paper, we introduce a new system to estimate the order recovery of thinned static trajectories, which allows to effectively resolve the clusters and select the order of the executed pen-downs. We evaluate how knowing the starting points of the pen-downs affects the quality of the recovered writing. Once the stability and sensitivity of the system is analyzed, we describe a series of experiments with three publicly available databases, showing competitive results in all cases. We expect the proposed system, whose code is made publicly available to the research community, to reduce potential confusion when the order of complex trajectories are recovered, and this will in turn make the trajectories recovered to be viable for further applications, such as velocity estimation.
SM-DTW: Stability Modulated Dynamic Time Warping for signature verification
May 20, 2024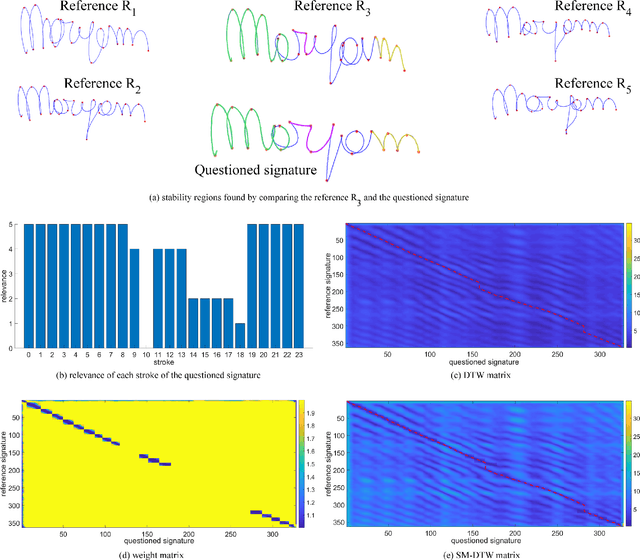
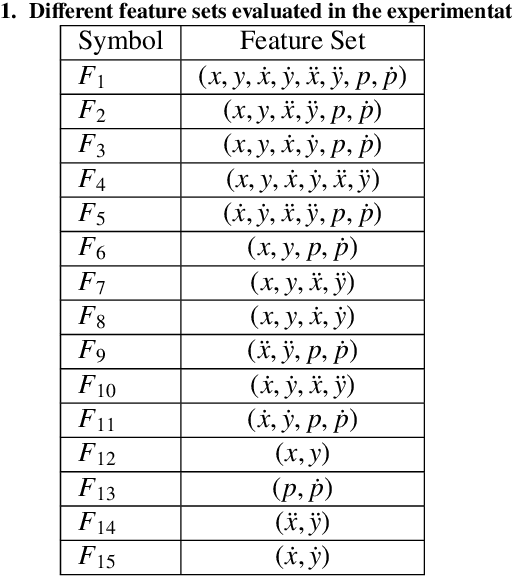
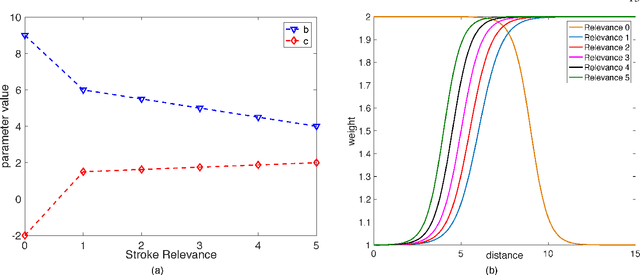
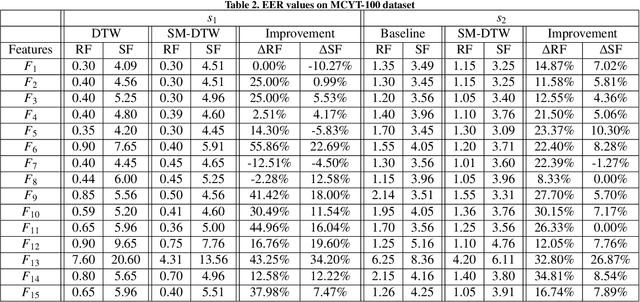
Abstract:Building upon findings in computational model of handwriting learning and execution, we introduce the concept of stability to explain the difference between the actual movements performed during multiple execution of the subject's signature, and conjecture that the most stable parts of the signature should play a paramount role in evaluating the similarity between a questioned signature and the reference ones during signature verification. We then introduce the Stability Modulated Dynamic Time Warping algorithm for incorporating the stability regions, i.e. the most similar parts between two signatures, into the distance measure between a pair of signatures computed by the Dynamic Time Warping for signature verification. Experiments were conducted on two datasets largely adopted for performance evaluation. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm improves the performance of the baseline system and compares favourably with other top performing signature verification systems.
Temporal evolution in synthetic handwriting
Jan 27, 2024Abstract:New methods for generating synthetic handwriting images for biometric applications have recently been developed. The temporal evolution of handwriting from childhood to adulthood is usually left unexplored in these works. This paper proposes a novel methodology for including temporal evolution in a handwriting synthesizer by means of simplifying the text trajectory plan and handwriting dynamics. This is achieved through a tailored version of the kinematic theory of rapid human movements and the neuromotor inspired handwriting synthesizer. The realism of the proposed method has been evaluated by comparing the temporal evolution of real and synthetic samples both quantitatively and subjectively. The quantitative test is based on a visual perception algorithm that compares the letter variability and the number of strokes in the real and synthetic handwriting produced at different ages. In the subjective test, 30 people are asked to evaluate the perceived realism of the evolution of the synthetic handwriting.
* Published in Pattern Recognition
I Can't Believe It's Not Better: In-air Movement For Alzheimer Handwriting Synthetic Generation
Dec 08, 2023Abstract:During recent years, there here has been a boom in terms of deep learning use for handwriting analysis and recognition. One main application for handwriting analysis is early detection and diagnosis in the health field. Unfortunately, most real case problems still suffer a scarcity of data, which makes difficult the use of deep learning-based models. To alleviate this problem, some works resort to synthetic data generation. Lately, more works are directed towards guided data synthetic generation, a generation that uses the domain and data knowledge to generate realistic data that can be useful to train deep learning models. In this work, we combine the domain knowledge about the Alzheimer's disease for handwriting and use it for a more guided data generation. Concretely, we have explored the use of in-air movements for synthetic data generation.
Machine Learning for Health symposium 2023 -- Findings track
Dec 01, 2023Abstract:A collection of the accepted Findings papers that were presented at the 3rd Machine Learning for Health symposium (ML4H 2023), which was held on December 10, 2023, in New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. ML4H 2023 invited high-quality submissions on relevant problems in a variety of health-related disciplines including healthcare, biomedicine, and public health. Two submission tracks were offered: the archival Proceedings track, and the non-archival Findings track. Proceedings were targeted at mature work with strong technical sophistication and a high impact to health. The Findings track looked for new ideas that could spark insightful discussion, serve as valuable resources for the community, or could enable new collaborations. Submissions to the Proceedings track, if not accepted, were automatically considered for the Findings track. All the manuscripts submitted to ML4H Symposium underwent a double-blind peer-review process.
Machine Learning for Health symposium 2022 -- Extended Abstract track
Nov 28, 2022Abstract:A collection of the extended abstracts that were presented at the 2nd Machine Learning for Health symposium (ML4H 2022), which was held both virtually and in person on November 28, 2022, in New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. Machine Learning for Health (ML4H) is a longstanding venue for research into machine learning for health, including both theoretical works and applied works. ML4H 2022 featured two submission tracks: a proceedings track, which encompassed full-length submissions of technically mature and rigorous work, and an extended abstract track, which would accept less mature, but innovative research for discussion. All the manuscripts submitted to ML4H Symposium underwent a double-blind peer-review process. Extended abstracts included in this collection describe innovative machine learning research focused on relevant problems in health and biomedicine.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge