Michael Glass
Rationalization Models for Text-to-SQL
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:We introduce a framework for generating Chain-of-Thought (CoT) rationales to enhance text-to-SQL model fine-tuning. These rationales consist of intermediate SQL statements and explanations, serving as incremental steps toward constructing the final SQL query. The process begins with manually annotating a small set of examples, which are then used to prompt a large language model in an iterative, dynamic few-shot knowledge distillation procedure from a teacher model. A rationalization model is subsequently trained on the validated decomposed queries, enabling extensive synthetic CoT annotations for text-to-SQL datasets. To evaluate the approach, we fine-tune small language models with and without these rationales on the BIRD dataset. Results indicate that step-by-step query generation improves execution accuracy, especially for moderately and highly complex queries, while also enhancing explainability.
Retrieval-Based Transformer for Table Augmentation
Jun 20, 2023Abstract:Data preparation, also called data wrangling, is considered one of the most expensive and time-consuming steps when performing analytics or building machine learning models. Preparing data typically involves collecting and merging data from complex heterogeneous, and often large-scale data sources, such as data lakes. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach toward automatic data wrangling in an attempt to alleviate the effort of end-users, e.g. data analysts, in structuring dynamic views from data lakes in the form of tabular data. We aim to address table augmentation tasks, including row/column population and data imputation. Given a corpus of tables, we propose a retrieval augmented self-trained transformer model. Our self-learning strategy consists in randomly ablating tables from the corpus and training the retrieval-based model to reconstruct the original values or headers given the partial tables as input. We adopt this strategy to first train the dense neural retrieval model encoding table-parts to vectors, and then the end-to-end model trained to perform table augmentation tasks. We test on EntiTables, the standard benchmark for table augmentation, as well as introduce a new benchmark to advance further research: WebTables. Our model consistently and substantially outperforms both supervised statistical methods and the current state-of-the-art transformer-based models.
Re2G: Retrieve, Rerank, Generate
Jul 13, 2022
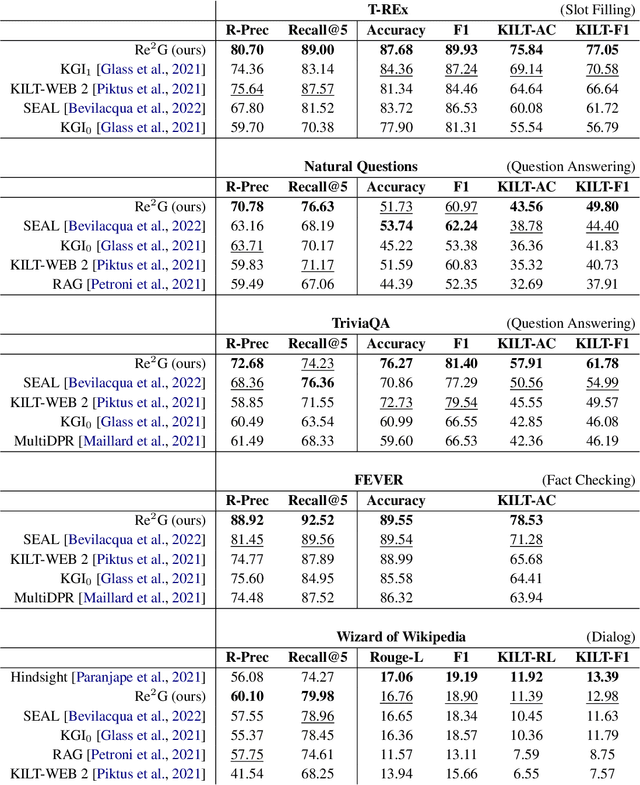
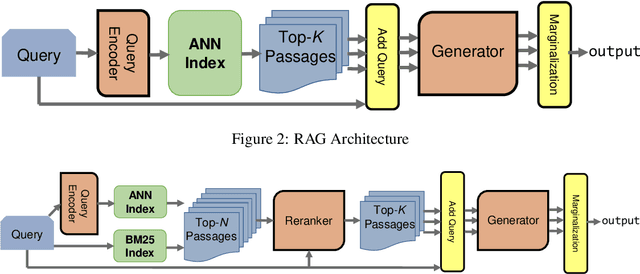
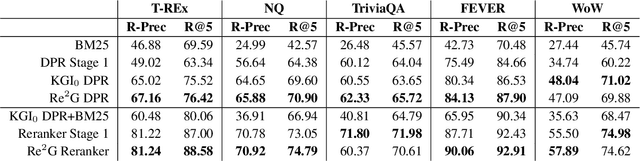
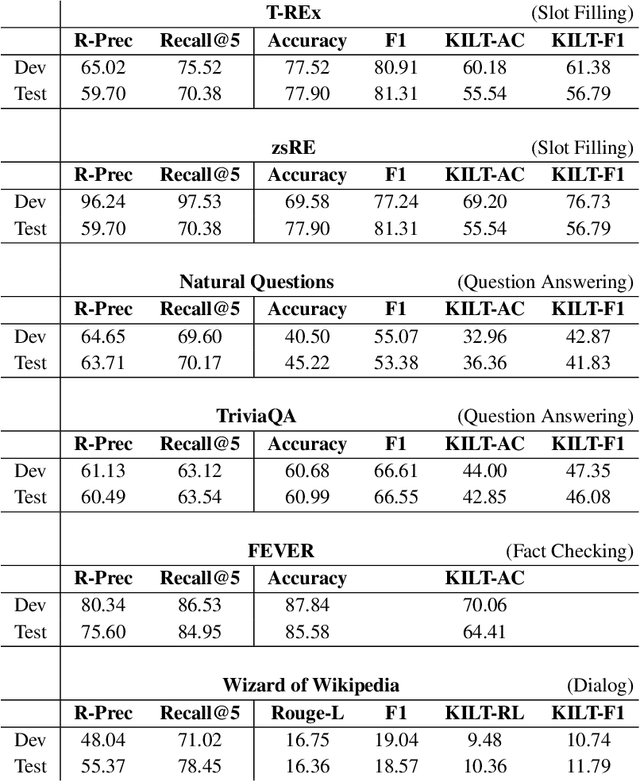
Abstract:As demonstrated by GPT-3 and T5, transformers grow in capability as parameter spaces become larger and larger. However, for tasks that require a large amount of knowledge, non-parametric memory allows models to grow dramatically with a sub-linear increase in computational cost and GPU memory requirements. Recent models such as RAG and REALM have introduced retrieval into conditional generation. These models incorporate neural initial retrieval from a corpus of passages. We build on this line of research, proposing Re2G, which combines both neural initial retrieval and reranking into a BART-based sequence-to-sequence generation. Our reranking approach also permits merging retrieval results from sources with incomparable scores, enabling an ensemble of BM25 and neural initial retrieval. To train our system end-to-end, we introduce a novel variation of knowledge distillation to train the initial retrieval, reranker, and generation using only ground truth on the target sequence output. We find large gains in four diverse tasks: zero-shot slot filling, question answering, fact-checking, and dialog, with relative gains of 9% to 34% over the previous state-of-the-art on the KILT leaderboard. We make our code available as open source at https://github.com/IBM/kgi-slot-filling/tree/re2g.
KGI: An Integrated Framework for Knowledge Intensive Language Tasks
Apr 08, 2022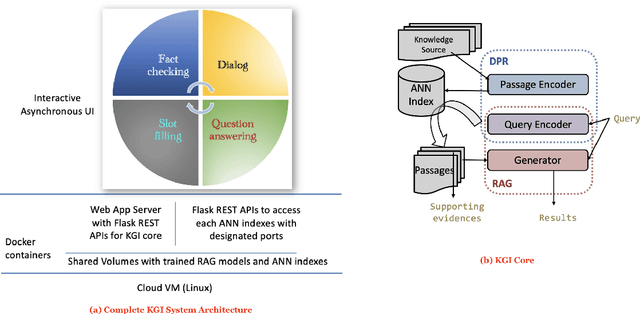
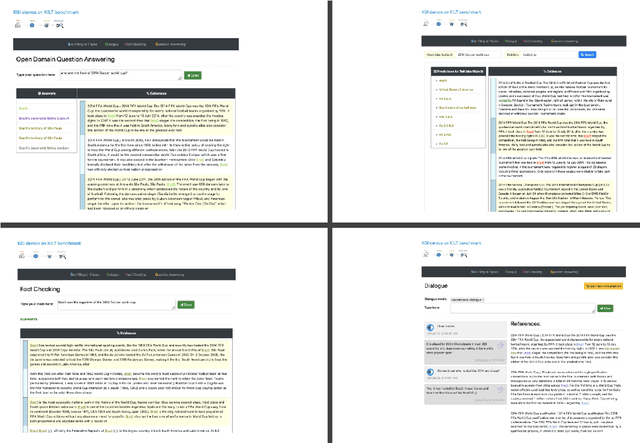
Abstract:In a recent work, we presented a novel state-of-the-art approach to zero-shot slot filling that extends dense passage retrieval with hard negatives and robust training procedures for retrieval augmented generation models. In this paper, we propose a system based on an enhanced version of this approach where we train task specific models for other knowledge intensive language tasks, such as open domain question answering (QA), dialogue and fact checking. Our system achieves results comparable to the best models in the KILT leaderboards. Moreover, given a user query, we show how the output from these different models can be combined to cross-examine each other. Particularly, we show how accuracy in dialogue can be improved using the QA model. A short video demonstrating the system is available here - \url{https://ibm.box.com/v/kgi-interactive-demo} .
End-to-End Table Question Answering via Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Mar 30, 2022
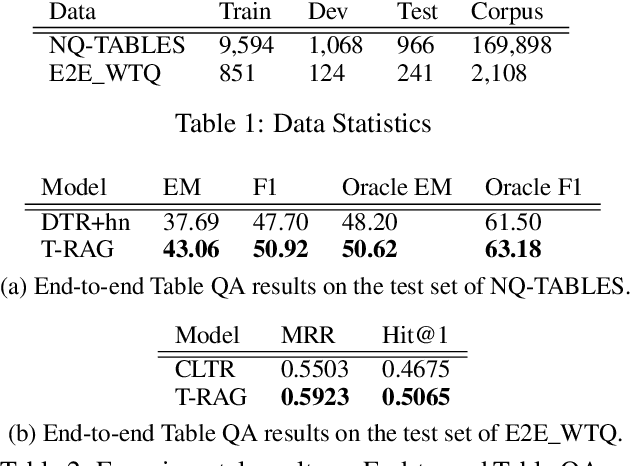
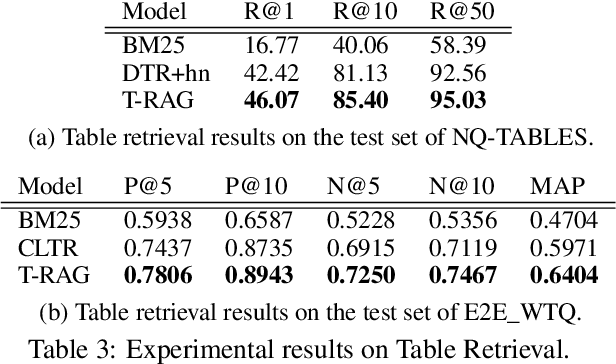
Abstract:Most existing end-to-end Table Question Answering (Table QA) models consist of a two-stage framework with a retriever to select relevant table candidates from a corpus and a reader to locate the correct answers from table candidates. Even though the accuracy of the reader models is significantly improved with the recent transformer-based approaches, the overall performance of such frameworks still suffers from the poor accuracy of using traditional information retrieval techniques as retrievers. To alleviate this problem, we introduce T-RAG, an end-to-end Table QA model, where a non-parametric dense vector index is fine-tuned jointly with BART, a parametric sequence-to-sequence model to generate answer tokens. Given any natural language question, T-RAG utilizes a unified pipeline to automatically search through a table corpus to directly locate the correct answer from the table cells. We apply T-RAG to recent open-domain Table QA benchmarks and demonstrate that the fine-tuned T-RAG model is able to achieve state-of-the-art performance in both the end-to-end Table QA and the table retrieval tasks.
Multi-Objective Design Space Exploration for the Optimization of the HEVC Mode Decision Process
Mar 03, 2022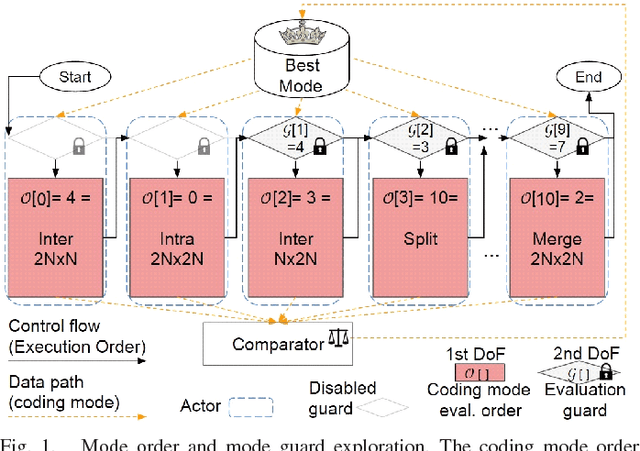


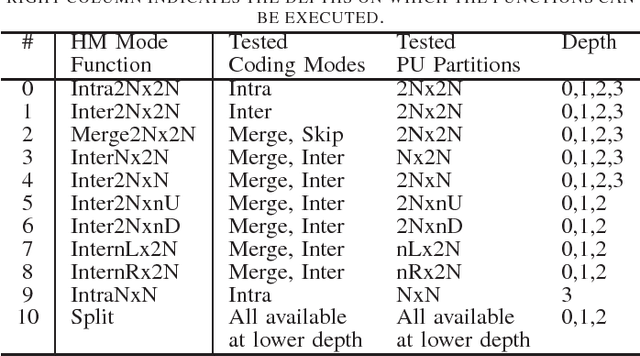
Abstract:Finding the best possible encoding decisions for compressing a video sequence is a highly complex problem. In this work, we propose a multi-objective Design Space Exploration (DSE) method to automatically find HEVC encoder implementations that are optimized for several different criteria. The DSE shall optimize the coding mode evaluation order of the mode decision process and jointly explore early skip conditions to minimize the four objectives a) bitrate, b) distortion, c) encoding time, and d) decoding energy. In this context, we use a SystemC-based actor model of the HM test model encoder for the evaluation of each explored solution. The evaluation that is based on real measurements shows that our framework can automatically generate encoder solutions that save more than 60% of encoding time or 3% of decoding energy when accepting bitrate increases of around 3%.
Applying a Generic Sequence-to-Sequence Model for Simple and Effective Keyphrase Generation
Jan 14, 2022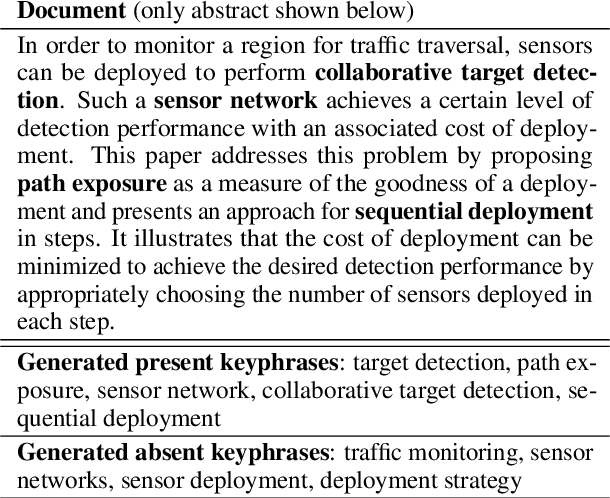
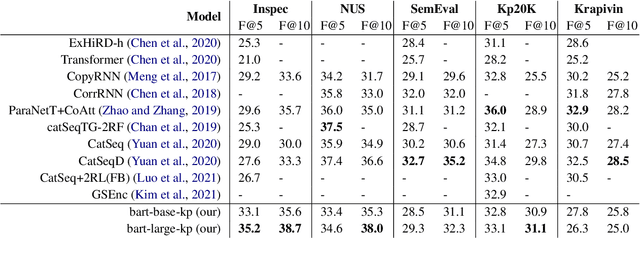
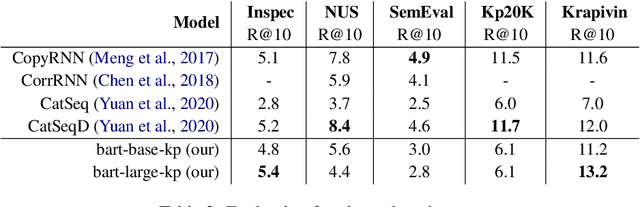
Abstract:In recent years, a number of keyphrase generation (KPG) approaches were proposed consisting of complex model architectures, dedicated training paradigms and decoding strategies. In this work, we opt for simplicity and show how a commonly used seq2seq language model, BART, can be easily adapted to generate keyphrases from the text in a single batch computation using a simple training procedure. Empirical results on five benchmarks show that our approach is as good as the existing state-of-the-art KPG systems, but using a much simpler and easy to deploy framework.
Robust Retrieval Augmented Generation for Zero-shot Slot Filling
Aug 31, 2021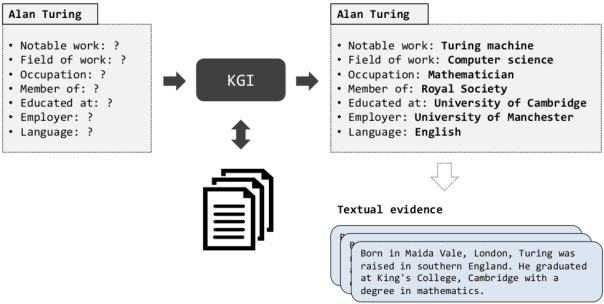
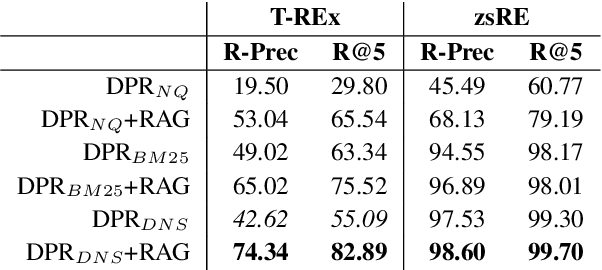
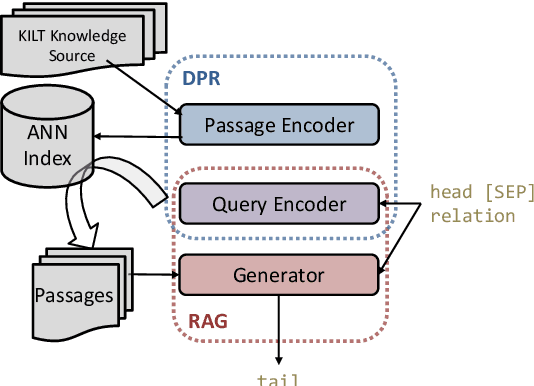
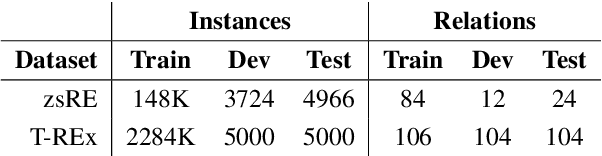
Abstract:Automatically inducing high quality knowledge graphs from a given collection of documents still remains a challenging problem in AI. One way to make headway for this problem is through advancements in a related task known as slot filling. In this task, given an entity query in form of [Entity, Slot, ?], a system is asked to fill the slot by generating or extracting the missing value exploiting evidence extracted from relevant passage(s) in the given document collection. The recent works in the field try to solve this task in an end-to-end fashion using retrieval-based language models. In this paper, we present a novel approach to zero-shot slot filling that extends dense passage retrieval with hard negatives and robust training procedures for retrieval augmented generation models. Our model reports large improvements on both T-REx and zsRE slot filling datasets, improving both passage retrieval and slot value generation, and ranking at the top-1 position in the KILT leaderboard. Moreover, we demonstrate the robustness of our system showing its domain adaptation capability on a new variant of the TACRED dataset for slot filling, through a combination of zero/few-shot learning. We release the source code and pre-trained models.
AIT-QA: Question Answering Dataset over Complex Tables in the Airline Industry
Jun 24, 2021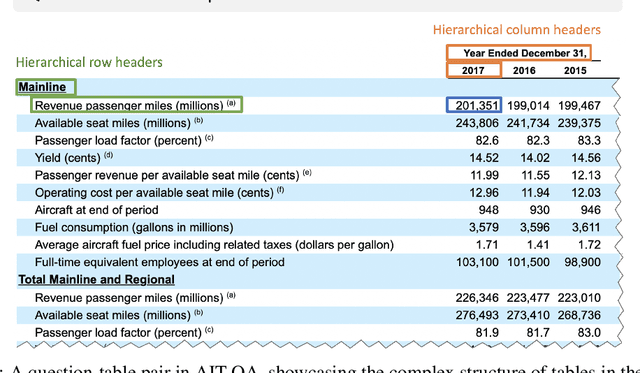

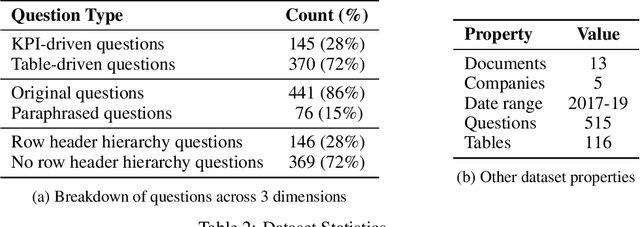

Abstract:Recent advances in transformers have enabled Table Question Answering (Table QA) systems to achieve high accuracy and SOTA results on open domain datasets like WikiTableQuestions and WikiSQL. Such transformers are frequently pre-trained on open-domain content such as Wikipedia, where they effectively encode questions and corresponding tables from Wikipedia as seen in Table QA dataset. However, web tables in Wikipedia are notably flat in their layout, with the first row as the sole column header. The layout lends to a relational view of tables where each row is a tuple. Whereas, tables in domain-specific business or scientific documents often have a much more complex layout, including hierarchical row and column headers, in addition to having specialized vocabulary terms from that domain. To address this problem, we introduce the domain-specific Table QA dataset AIT-QA (Airline Industry Table QA). The dataset consists of 515 questions authored by human annotators on 116 tables extracted from public U.S. SEC filings (publicly available at: https://www.sec.gov/edgar.shtml) of major airline companies for the fiscal years 2017-2019. We also provide annotations pertaining to the nature of questions, marking those that require hierarchical headers, domain-specific terminology, and paraphrased forms. Our zero-shot baseline evaluation of three transformer-based SOTA Table QA methods - TaPAS (end-to-end), TaBERT (semantic parsing-based), and RCI (row-column encoding-based) - clearly exposes the limitation of these methods in this practical setting, with the best accuracy at just 51.8\% (RCI). We also present pragmatic table preprocessing steps used to pivot and project these complex tables into a layout suitable for the SOTA Table QA models.
CLTR: An End-to-End, Transformer-Based System for Cell Level Table Retrieval and Table Question Answering
Jun 09, 2021



Abstract:We present the first end-to-end, transformer-based table question answering (QA) system that takes natural language questions and massive table corpus as inputs to retrieve the most relevant tables and locate the correct table cells to answer the question. Our system, CLTR, extends the current state-of-the-art QA over tables model to build an end-to-end table QA architecture. This system has successfully tackled many real-world table QA problems with a simple, unified pipeline. Our proposed system can also generate a heatmap of candidate columns and rows over complex tables and allow users to quickly identify the correct cells to answer questions. In addition, we introduce two new open-domain benchmarks, E2E_WTQ and E2E_GNQ, consisting of 2,005 natural language questions over 76,242 tables. The benchmarks are designed to validate CLTR as well as accommodate future table retrieval and end-to-end table QA research and experiments. Our experiments demonstrate that our system is the current state-of-the-art model on the table retrieval task and produces promising results for end-to-end table QA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge