Mi Tian
Selective Mixup for Debiasing Question Selection in Computerized Adaptive Testing
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Computerized Adaptive Testing (CAT) is a widely used technology for evaluating learners' proficiency in online education platforms. By leveraging prior estimates of proficiency to select questions and updating the estimates iteratively based on responses, CAT enables personalized learner modeling and has attracted substantial attention. Despite this progress, most existing works focus primarily on improving diagnostic accuracy, while overlooking the selection bias inherent in the adaptive process. Selection Bias arises because the question selection is strongly influenced by the estimated proficiency, such as assigning easier questions to learners with lower proficiency and harder ones to learners with higher proficiency. Since the selection depends on prior estimation, this bias propagates into the diagnosis model, which is further amplified during iterative updates, leading to misalignment and biased predictions. Moreover, the imbalanced nature of learners' historical interactions often exacerbates the bias in diagnosis models. To address this issue, we propose a debiasing framework consisting of two key modules: Cross-Attribute Examinee Retrieval and Selective Mixup-based Regularization. First, we retrieve balanced examinees with relatively even distributions of correct and incorrect responses and use them as neutral references for biased examinees. Then, mixup is applied between each biased examinee and its matched balanced counterpart under label consistency. This augmentation enriches the diversity of bias-conflicting samples and smooths selection boundaries. Finally, extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets with multiple advanced diagnosis models demonstrate that our method substantially improves both the generalization ability and fairness of question selection in CAT.
P-MIA: A Profiled-Based Membership Inference Attack on Cognitive Diagnosis Models
Nov 06, 2025



Abstract:Cognitive diagnosis models (CDMs) are pivotal for creating fine-grained learner profiles in modern intelligent education platforms. However, these models are trained on sensitive student data, raising significant privacy concerns. While membership inference attacks (MIA) have been studied in various domains, their application to CDMs remains a critical research gap, leaving their privacy risks unquantified. This paper is the first to systematically investigate MIA against CDMs. We introduce a novel and realistic grey box threat model that exploits the explainability features of these platforms, where a model's internal knowledge state vectors are exposed to users through visualizations such as radar charts. We demonstrate that these vectors can be accurately reverse-engineered from such visualizations, creating a potent attack surface. Based on this threat model, we propose a profile-based MIA (P-MIA) framework that leverages both the model's final prediction probabilities and the exposed internal knowledge state vectors as features. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets against mainstream CDMs show that our grey-box attack significantly outperforms standard black-box baselines. Furthermore, we showcase the utility of P-MIA as an auditing tool by successfully evaluating the efficacy of machine unlearning techniques and revealing their limitations.
PrivacyCD: Hierarchical Unlearning for Protecting Student Privacy in Cognitive Diagnosis
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:The need to remove specific student data from cognitive diagnosis (CD) models has become a pressing requirement, driven by users' growing assertion of their "right to be forgotten". However, existing CD models are largely designed without privacy considerations and lack effective data unlearning mechanisms. Directly applying general purpose unlearning algorithms is suboptimal, as they struggle to balance unlearning completeness, model utility, and efficiency when confronted with the unique heterogeneous structure of CD models. To address this, our paper presents the first systematic study of the data unlearning problem for CD models, proposing a novel and efficient algorithm: hierarchical importanceguided forgetting (HIF). Our key insight is that parameter importance in CD models exhibits distinct layer wise characteristics. HIF leverages this via an innovative smoothing mechanism that combines individual and layer, level importance, enabling a more precise distinction of parameters associated with the data to be unlearned. Experiments on three real world datasets show that HIF significantly outperforms baselines on key metrics, offering the first effective solution for CD models to respond to user data removal requests and for deploying high-performance, privacy preserving AI systems
Mixture of Group Experts for Learning Invariant Representations
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:Sparsely activated Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models effectively increase the number of parameters while maintaining consistent computational costs per token. However, vanilla MoE models often suffer from limited diversity and specialization among experts, constraining their performance and scalability, especially as the number of experts increases. In this paper, we present a novel perspective on vanilla MoE with top-$k$ routing inspired by sparse representation. This allows us to bridge established theoretical insights from sparse representation into MoE models. Building on this foundation, we propose a group sparse regularization approach for the input of top-$k$ routing, termed Mixture of Group Experts (MoGE). MoGE indirectly regularizes experts by imposing structural constraints on the routing inputs, while preserving the original MoE architecture. Furthermore, we organize the routing input into a 2D topographic map, spatially grouping neighboring elements. This structure enables MoGE to capture representations invariant to minor transformations, thereby significantly enhancing expert diversity and specialization. Comprehensive evaluations across various Transformer models for image classification and language modeling tasks demonstrate that MoGE substantially outperforms its MoE counterpart, with minimal additional memory and computation overhead. Our approach provides a simple yet effective solution to scale the number of experts and reduce redundancy among them. The source code is included in the supplementary material and will be publicly released.
Pi-GPS: Enhancing Geometry Problem Solving by Unleashing the Power of Diagrammatic Information
Mar 07, 2025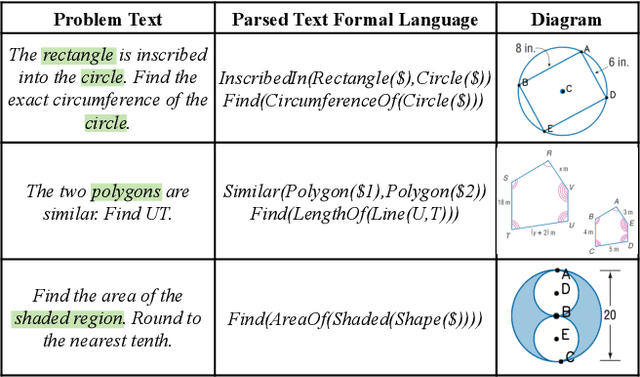



Abstract:Geometry problem solving has garnered increasing attention due to its potential applications in intelligent education field. Inspired by the observation that text often introduces ambiguities that diagrams can clarify, this paper presents Pi-GPS, a novel framework that unleashes the power of diagrammatic information to resolve textual ambiguities, an aspect largely overlooked in prior research. Specifically, we design a micro module comprising a rectifier and verifier: the rectifier employs MLLMs to disambiguate text based on the diagrammatic context, while the verifier ensures the rectified output adherence to geometric rules, mitigating model hallucinations. Additionally, we explore the impact of LLMs in theorem predictor based on the disambiguated formal language. Empirical results demonstrate that Pi-GPS surpasses state-of-the-art models, achieving a nearly 10\% improvement on Geometry3K over prior neural-symbolic approaches. We hope this work highlights the significance of resolving textual ambiguity in multimodal mathematical reasoning, a crucial factor limiting performance.
Advancing Math Reasoning in Language Models: The Impact of Problem-Solving Data, Data Synthesis Methods, and Training Stages
Jan 23, 2025Abstract:Advancements in LLMs have significantly expanded their capabilities across various domains. However, mathematical reasoning remains a challenging area, prompting the development of math-specific LLMs. These models typically follow a two-stage training paradigm: pre-training with math-related corpora and post-training with problem datasets for SFT. Despite these efforts, the improvements in mathematical reasoning achieved through continued pre-training (CPT) are often less significant compared to those obtained via SFT. This study addresses this discrepancy by exploring alternative strategies during the pre-training phase, focusing on the use of problem-solving data over general mathematical corpora. We investigate three primary research questions: (1) Can problem-solving data enhance the model's mathematical reasoning capabilities more effectively than general mathematical corpora during CPT? (2) Are synthetic data from the same source equally effective, and which synthesis methods are most efficient? (3) How do the capabilities developed from the same problem-solving data differ between the CPT and SFT stages, and what factors contribute to these differences? Our findings indicate that problem-solving data significantly enhances the model's mathematical capabilities compared to general mathematical corpora. We also identify effective data synthesis methods, demonstrating that the tutorship amplification synthesis method achieves the best performance. Furthermore, while SFT facilitates instruction-following abilities, it underperforms compared to CPT with the same data, which can be partially attributed to its poor learning capacity for hard multi-step problem-solving data. These insights provide valuable guidance for optimizing the mathematical reasoning capabilities of LLMs, culminating in our development of a powerful mathematical base model called JiuZhang-8B.
What Are Step-Level Reward Models Rewarding? Counterintuitive Findings from MCTS-Boosted Mathematical Reasoning
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:Step-level reward models (SRMs) can significantly enhance mathematical reasoning performance through process supervision or step-level preference alignment based on reinforcement learning. The performance of SRMs is pivotal, as they serve as critical guidelines, ensuring that each step in the reasoning process is aligned with desired outcomes. Recently, AlphaZero-like methods, where Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) is employed for automatic step-level preference annotation, have proven particularly effective. However, the precise mechanisms behind the success of SRMs remain largely unexplored. To address this gap, this study delves into the counterintuitive aspects of SRMs, particularly focusing on MCTS-based approaches. Our findings reveal that the removal of natural language descriptions of thought processes has minimal impact on the efficacy of SRMs. Furthermore, we demonstrate that SRMs are adept at assessing the complex logical coherence present in mathematical language while having difficulty in natural language. These insights provide a nuanced understanding of the core elements that drive effective step-level reward modeling in mathematical reasoning. By shedding light on these mechanisms, this study offers valuable guidance for developing more efficient and streamlined SRMs, which can be achieved by focusing on the crucial parts of mathematical reasoning.
Expediting and Elevating Large Language Model Reasoning via Hidden Chain-of-Thought Decoding
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in tasks requiring reasoning and multi-step problem-solving through the use of chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting. However, generating the full CoT process results in significantly longer output sequences, leading to increased computational costs and latency during inference. To address this challenge, we propose a novel approach to compress the CoT process through semantic alignment, enabling more efficient decoding while preserving the benefits of CoT reasoning. Our method introduces an auxiliary CoT model that learns to generate and compress the full thought process into a compact special token representation semantically aligned with the original CoT output. This compressed representation is then integrated into the input of the Hidden Chain-of-Thought (HCoT) model. The training process follows a two-stage procedure: First, the CoT model is optimized to generate the compressed token representations aligned with the ground-truth CoT outputs using a contrastive loss. Subsequently, with the CoT model parameters frozen, the HCoT model is fine-tuned to generate accurate subsequent predictions conditioned on the prefix instruction and the compressed CoT representations from the CoT model. Extensive experiments across three challenging domains - mathematical reasoning, agent invocation, and question answering - demonstrate that our semantic compression approach achieves competitive or improved performance compared to the full CoT baseline, while providing significant speedups of at least 1.5x in decoding time. Moreover, incorporating contrastive learning objectives further enhances the quality of the compressed representations, leading to better CoT prompting and improved task accuracy. Our work paves the way for more efficient exploitation of multi-step reasoning capabilities in LLMs across a wide range of applications.
Path-Specific Causal Reasoning for Fairness-aware Cognitive Diagnosis
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:Cognitive Diagnosis~(CD), which leverages students and exercise data to predict students' proficiency levels on different knowledge concepts, is one of fundamental components in Intelligent Education. Due to the scarcity of student-exercise interaction data, most existing methods focus on making the best use of available data, such as exercise content and student information~(e.g., educational context). Despite the great progress, the abuse of student sensitive information has not been paid enough attention. Due to the important position of CD in Intelligent Education, employing sensitive information when making diagnosis predictions will cause serious social issues. Moreover, data-driven neural networks are easily misled by the shortcut between input data and output prediction, exacerbating this problem. Therefore, it is crucial to eliminate the negative impact of sensitive information in CD models. In response, we argue that sensitive attributes of students can also provide useful information, and only the shortcuts directly related to the sensitive information should be eliminated from the diagnosis process. Thus, we employ causal reasoning and design a novel Path-Specific Causal Reasoning Framework (PSCRF) to achieve this goal. Specifically, we first leverage an encoder to extract features and generate embeddings for general information and sensitive information of students. Then, we design a novel attribute-oriented predictor to decouple the sensitive attributes, in which fairness-related sensitive features will be eliminated and other useful information will be retained. Finally, we designed a multi-factor constraint to ensure the performance of fairness and diagnosis performance simultaneously. Extensive experiments over real-world datasets (e.g., PISA dataset) demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed PSCRF.
Deep auxiliary learning for visual localization using colorization task
Jul 01, 2021



Abstract:Visual localization is one of the most important components for robotics and autonomous driving. Recently, inspiring results have been shown with CNN-based methods which provide a direct formulation to end-to-end regress 6-DoF absolute pose. Additional information like geometric or semantic constraints is generally introduced to improve performance. Especially, the latter can aggregate high-level semantic information into localization task, but it usually requires enormous manual annotations. To this end, we propose a novel auxiliary learning strategy for camera localization by introducing scene-specific high-level semantics from self-supervised representation learning task. Viewed as a powerful proxy task, image colorization task is chosen as complementary task that outputs pixel-wise color version of grayscale photograph without extra annotations. In our work, feature representations from colorization network are embedded into localization network by design to produce discriminative features for pose regression. Meanwhile an attention mechanism is introduced for the benefit of localization performance. Extensive experiments show that our model significantly improve localization accuracy over state-of-the-arts on both indoor and outdoor datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge