Mei-Yuh Hwang
DISGO: Automatic End-to-End Evaluation for Scene Text OCR
Aug 25, 2023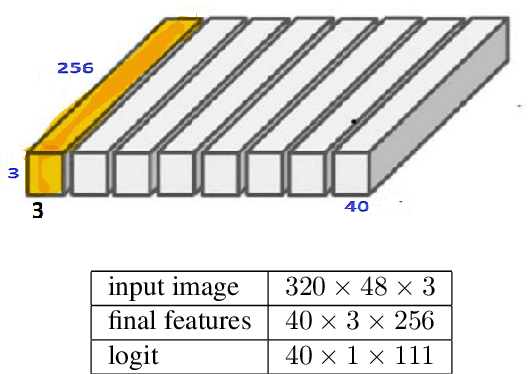
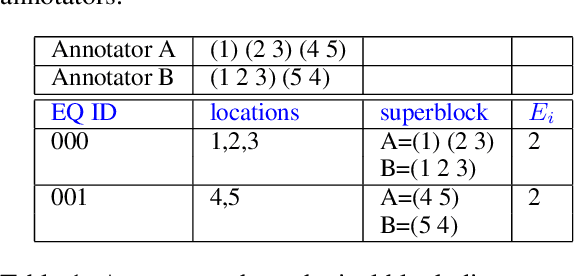
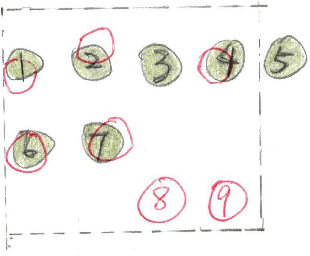

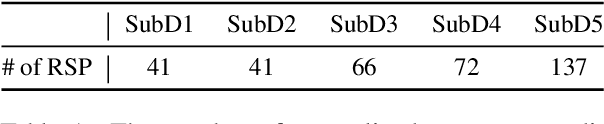
Abstract:This paper discusses the challenges of optical character recognition (OCR) on natural scenes, which is harder than OCR on documents due to the wild content and various image backgrounds. We propose to uniformly use word error rates (WER) as a new measurement for evaluating scene-text OCR, both end-to-end (e2e) performance and individual system component performances. Particularly for the e2e metric, we name it DISGO WER as it considers Deletion, Insertion, Substitution, and Grouping/Ordering errors. Finally we propose to utilize the concept of super blocks to automatically compute BLEU scores for e2e OCR machine translation. The small SCUT public test set is used to demonstrate WER performance by a modularized OCR system.
Incremental Learning from Scratch for Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems
Jun 12, 2019
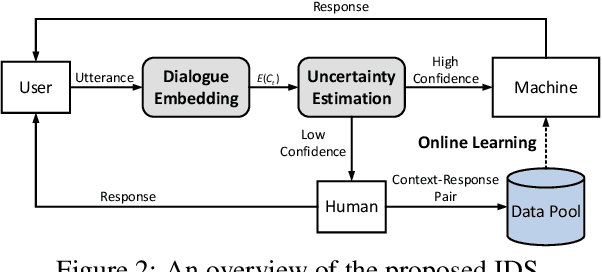
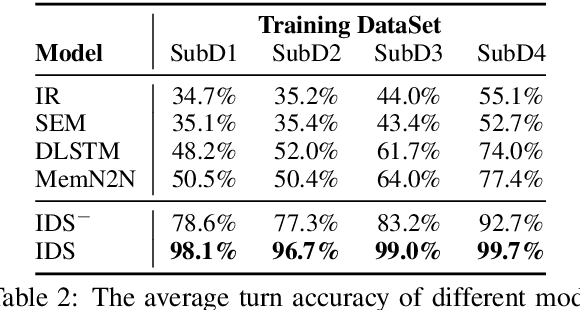
Abstract:Clarifying user needs is essential for existing task-oriented dialogue systems. However, in real-world applications, developers can never guarantee that all possible user demands are taken into account in the design phase. Consequently, existing systems will break down when encountering unconsidered user needs. To address this problem, we propose a novel incremental learning framework to design task-oriented dialogue systems, or for short Incremental Dialogue System (IDS), without pre-defining the exhaustive list of user needs. Specifically, we introduce an uncertainty estimation module to evaluate the confidence of giving correct responses. If there is high confidence, IDS will provide responses to users. Otherwise, humans will be involved in the dialogue process, and IDS can learn from human intervention through an online learning module. To evaluate our method, we propose a new dataset which simulates unanticipated user needs in the deployment stage. Experiments show that IDS is robust to unconsidered user actions, and can update itself online by smartly selecting only the most effective training data, and hence attains better performance with less annotation cost.
Knowledge Distillation For Recurrent Neural Network Language Modeling With Trust Regularization
Apr 08, 2019



Abstract:Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) have dominated language modeling because of their superior performance over traditional N-gram based models. In many applications, a large Recurrent Neural Network language model (RNNLM) or an ensemble of several RNNLMs is used. These models have large memory footprints and require heavy computation. In this paper, we examine the effect of applying knowledge distillation in reducing the model size for RNNLMs. In addition, we propose a trust regularization method to improve the knowledge distillation training for RNNLMs. Using knowledge distillation with trust regularization, we reduce the parameter size to a third of that of the previously published best model while maintaining the state-of-the-art perplexity result on Penn Treebank data. In a speech recognition N-bestrescoring task, we reduce the RNNLM model size to 18.5% of the baseline system, with no degradation in word error rate(WER) performance on Wall Street Journal data set.
End-To-End Speech Recognition Using A High Rank LSTM-CTC Based Model
Mar 12, 2019


Abstract:Long Short Term Memory Connectionist Temporal Classification (LSTM-CTC) based end-to-end models are widely used in speech recognition due to its simplicity in training and efficiency in decoding. In conventional LSTM-CTC based models, a bottleneck projection matrix maps the hidden feature vectors obtained from LSTM to softmax output layer. In this paper, we propose to use a high rank projection layer to replace the projection matrix. The output from the high rank projection layer is a weighted combination of vectors that are projected from the hidden feature vectors via different projection matrices and non-linear activation function. The high rank projection layer is able to improve the expressiveness of LSTM-CTC models. The experimental results show that on Wall Street Journal (WSJ) corpus and LibriSpeech data set, the proposed method achieves 4%-6% relative word error rate (WER) reduction over the baseline CTC system. They outperform other published CTC based end-to-end (E2E) models under the condition that no external data or data augmentation is applied. Code has been made available at https://github.com/mobvoi/lstm_ctc.
Source-Critical Reinforcement Learning for Transferring Spoken Language Understanding to a New Language
Aug 22, 2018



Abstract:To deploy a spoken language understanding (SLU) model to a new language, language transferring is desired to avoid the trouble of acquiring and labeling a new big SLU corpus. Translating the original SLU corpus into the target language is an attractive strategy. However, SLU corpora consist of plenty of semantic labels (slots), which general-purpose translators cannot handle well, not to mention additional culture differences. This paper focuses on the language transferring task given a tiny in-domain parallel SLU corpus. The in-domain parallel corpus can be used as the first adaptation on the general translator. But more importantly, we show how to use reinforcement learning (RL) to further finetune the adapted translator, where translated sentences with more proper slot tags receive higher rewards. We evaluate our approach on Chinese to English language transferring for SLU systems. The experimental results show that the generated English SLU corpus via adaptation and reinforcement learning gives us over 97% in the slot F1 score and over 84% accuracy in domain classification. It demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed language transferring method. Compared with naive translation, our proposed method improves domain classification accuracy by relatively 22%, and the slot filling F1 score by relatively more than 71%.
Training Augmentation with Adversarial Examples for Robust Speech Recognition
Jun 17, 2018



Abstract:This paper explores the use of adversarial examples in training speech recognition systems to increase robustness of deep neural network acoustic models. During training, the fast gradient sign method is used to generate adversarial examples augmenting the original training data. Different from conventional data augmentation based on data transformations, the examples are dynamically generated based on current acoustic model parameters. We assess the impact of adversarial data augmentation in experiments on the Aurora-4 and CHiME-4 single-channel tasks, showing improved robustness against noise and channel variation. Further improvement is obtained when combining adversarial examples with teacher/student training, leading to a 23% relative word error rate reduction on Aurora-4.
Domain Adversarial Training for Accented Speech Recognition
Jun 07, 2018


Abstract:In this paper, we propose a domain adversarial training (DAT) algorithm to alleviate the accented speech recognition problem. In order to reduce the mismatch between labeled source domain data ("standard" accent) and unlabeled target domain data (with heavy accents), we augment the learning objective for a Kaldi TDNN network with a domain adversarial training (DAT) objective to encourage the model to learn accent-invariant features. In experiments with three Mandarin accents, we show that DAT yields up to 7.45% relative character error rate reduction when we do not have transcriptions of the accented speech, compared with the baseline trained on standard accent data only. We also find a benefit from DAT when used in combination with training from automatic transcriptions on the accented data. Furthermore, we find that DAT is superior to multi-task learning for accented speech recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge