Mehrdad Mahdavi
Michigan State University
Merge before Forget: A Single LoRA Continual Learning via Continual Merging
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Parameter-efficient continual learning has emerged as a promising approach for large language models (LLMs) to mitigate catastrophic forgetting while enabling adaptation to new tasks. Current Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) continual learning techniques often retain and freeze previously learned LoRAs or generate data representations to overcome forgetting, typically utilizing these to support new LoRAs learn new tasks. However, these methods not only ignore growing computational memory with tasks and limited storage space but also suffer from potential task interference due to the lack of effective LoRA merging mechanisms. In this paper, we propose a novel continual learning method that orthogonally initializes and sequentially merges LoRAs updates into a single unified LoRA. Our method leverages orthogonal basis extraction from previously learned LoRA to initialize the learning of new tasks, further exploits the intrinsic asymmetry property of LoRA components by using a time-aware scaling mechanism to balance new and old knowledge during continual merging. Our approach maintains constant memory complexity with respect to the number of tasks, minimizes interference between past and new tasks via orthogonal basis initialization, and improves performance over asymmetric LoRA merging via adaptive scaling. We provide theoretical analysis to justify our design and conduct extensive experiments across diverse continual learning benchmarks using various Llama models, demonstrating the effectiveness and efficiency of our method.
Model Merging via Multi-Teacher Knowledge Distillation
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Model merging has emerged as a lightweight alternative to joint multi-task learning (MTL), yet the generalization properties of merged models remain largely unexplored. Establishing such theoretical guarantees is non-trivial, as the merging process typically forbids access to the original training data and involves combining fine-tuned models trained on fundamentally heterogeneous data distributions. Without a principled understanding of these dynamics, current methods often rely on heuristics to approximate the optimal combination of parameters. This dependence is most critical in coefficient scaling, the weighting factors that modulate the magnitude of each fine-tuned model's contribution to the shared parameter. However, without a principled objective to guide their selection, these methods lead to brittle performance and are highly sensitive to scaling initialization. We address this gap by (i) establishing a novel flatness-aware PAC-Bayes generalization bound specifically for the model merging setting. This analysis introduces a "cross-task heterogeneity" term that formally captures the mismatch between diverse fine-tuned model priors and the target multi-task distributions. Guided by this theoretical insight, (ii) we frame model merging as multi-teacher knowledge distillation on scarce, unlabeled data. We formally demonstrate that minimizing the student-teacher Kullback-Leibler divergence directly tightens the upper bound on the merged model's excess risk. Guided by the flatness-aware bound derived, (iii) we operationalize this objective via SAMerging, a method that employs Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) to find flat minima. Empirically, SAMerging establishes a new state of the art across vision and NLP benchmarks, achieving remarkable performance. The code is available at https://github.com/arshandalili/SAMerging.
On the Convergence and Stability of Distributed Sub-model Training
Nov 08, 2025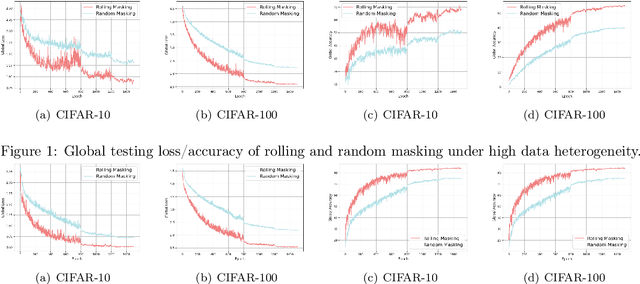
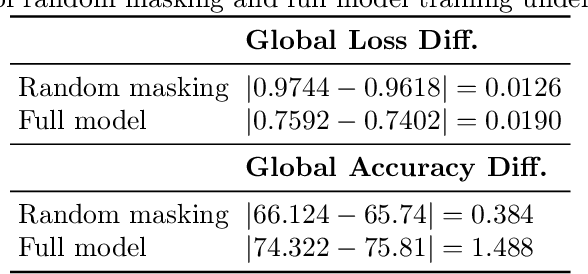
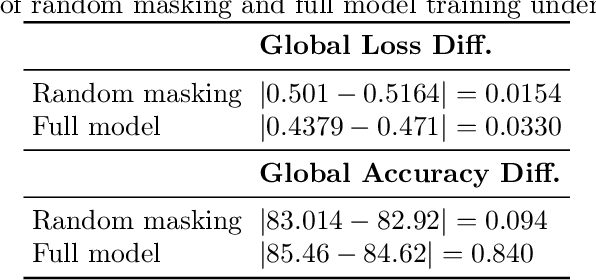
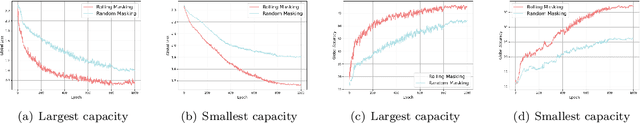
Abstract:As learning models continue to grow in size, enabling on-device local training of these models has emerged as a critical challenge in federated learning. A popular solution is sub-model training, where the server only distributes randomly sampled sub-models to the edge clients, and clients only update these small models. However, those random sampling of sub-models may not give satisfying convergence performance. In this paper, observing the success of SGD with shuffling, we propose a distributed shuffled sub-model training, where the full model is partitioned into several sub-models in advance, and the server shuffles those sub-models, sends each of them to clients at each round, and by the end of local updating period, clients send back the updated sub-models, and server averages them. We establish the convergence rate of this algorithm. We also study the generalization of distributed sub-model training via stability analysis, and find that the sub-model training can improve the generalization via amplifying the stability of training process. The extensive experiments also validate our theoretical findings.
Quantum Speedups for Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods with Application to Optimization
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:We propose quantum algorithms that provide provable speedups for Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods commonly used for sampling from probability distributions of the form $\pi \propto e^{-f}$, where $f$ is a potential function. Our first approach considers Gibbs sampling for finite-sum potentials in the stochastic setting, employing an oracle that provides gradients of individual functions. In the second setting, we consider access only to a stochastic evaluation oracle, allowing simultaneous queries at two points of the potential function under the same stochastic parameter. By introducing novel techniques for stochastic gradient estimation, our algorithms improve the gradient and evaluation complexities of classical samplers, such as Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (HMC) and Langevin Monte Carlo (LMC) in terms of dimension, precision, and other problem-dependent parameters. Furthermore, we achieve quantum speedups in optimization, particularly for minimizing non-smooth and approximately convex functions that commonly appear in empirical risk minimization problems.
Stochastic Compositional Minimax Optimization with Provable Convergence Guarantees
Aug 22, 2024Abstract:Stochastic compositional minimax problems are prevalent in machine learning, yet there are only limited established on the convergence of this class of problems. In this paper, we propose a formal definition of the stochastic compositional minimax problem, which involves optimizing a minimax loss with a compositional structure either in primal , dual, or both primal and dual variables. We introduce a simple yet effective algorithm, stochastically Corrected stOchastic gradient Descent Ascent (CODA), which is a descent ascent type algorithm with compositional correction steps, and establish its convergence rate in aforementioned three settings. In the presence of the compositional structure in primal, the objective function typically becomes nonconvex in primal due to function composition. Thus, we consider the nonconvex-strongly-concave and nonconvex-concave settings and show that CODA can efficiently converge to a stationary point. In the case of composition on the dual, the objective function becomes nonconcave in the dual variable, and we demonstrate convergence in the strongly-convex-nonconcave and convex-nonconcave setting. In the case of composition on both variables, the primal and dual variables may lose convexity and concavity, respectively. Therefore, we anaylze the convergence in weakly-convex-weakly-concave setting. We also give a variance reduction version algorithm, CODA+, which achieves the best known rate on nonconvex-strongly-concave and nonconvex-concave compositional minimax problem. This work initiates the theoretical study of the stochastic compositional minimax problem on various settings and may inform modern machine learning scenarios such as domain adaptation or robust model-agnostic meta-learning.
On the Generalization Ability of Unsupervised Pretraining
Mar 11, 2024


Abstract:Recent advances in unsupervised learning have shown that unsupervised pre-training, followed by fine-tuning, can improve model generalization. However, a rigorous understanding of how the representation function learned on an unlabeled dataset affects the generalization of the fine-tuned model is lacking. Existing theoretical research does not adequately account for the heterogeneity of the distribution and tasks in pre-training and fine-tuning stage. To bridge this gap, this paper introduces a novel theoretical framework that illuminates the critical factor influencing the transferability of knowledge acquired during unsupervised pre-training to the subsequent fine-tuning phase, ultimately affecting the generalization capabilities of the fine-tuned model on downstream tasks. We apply our theoretical framework to analyze generalization bound of two distinct scenarios: Context Encoder pre-training with deep neural networks and Masked Autoencoder pre-training with deep transformers, followed by fine-tuning on a binary classification task. Finally, inspired by our findings, we propose a novel regularization method during pre-training to further enhances the generalization of fine-tuned model. Overall, our results contribute to a better understanding of unsupervised pre-training and fine-tuning paradigm, and can shed light on the design of more effective pre-training algorithms.
On the Generalization Capability of Temporal Graph Learning Algorithms: Theoretical Insights and a Simpler Method
Feb 26, 2024



Abstract:Temporal Graph Learning (TGL) has become a prevalent technique across diverse real-world applications, especially in domains where data can be represented as a graph and evolves over time. Although TGL has recently seen notable progress in algorithmic solutions, its theoretical foundations remain largely unexplored. This paper aims at bridging this gap by investigating the generalization ability of different TGL algorithms (e.g., GNN-based, RNN-based, and memory-based methods) under the finite-wide over-parameterized regime. We establish the connection between the generalization error of TGL algorithms and "the number of layers/steps" in the GNN-/RNN-based TGL methods and "the feature-label alignment (FLA) score", where FLA can be used as a proxy for the expressive power and explains the performance of memory-based methods. Guided by our theoretical analysis, we propose Simplified-Temporal-Graph-Network, which enjoys a small generalization error, improved overall performance, and lower model complexity. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Our theoretical findings and proposed algorithm offer essential insights into TGL from a theoretical standpoint, laying the groundwork for the designing practical TGL algorithms in future studies.
Distributed Personalized Empirical Risk Minimization
Oct 26, 2023
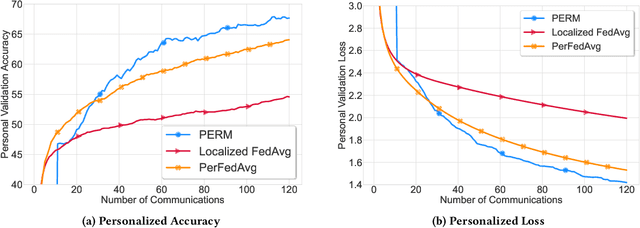

Abstract:This paper advocates a new paradigm Personalized Empirical Risk Minimization (PERM) to facilitate learning from heterogeneous data sources without imposing stringent constraints on computational resources shared by participating devices. In PERM, we aim to learn a distinct model for each client by learning who to learn with and personalizing the aggregation of local empirical losses by effectively estimating the statistical discrepancy among data distributions, which entails optimal statistical accuracy for all local distributions and overcomes the data heterogeneity issue. To learn personalized models at scale, we propose a distributed algorithm that replaces the standard model averaging with model shuffling to simultaneously optimize PERM objectives for all devices. This also allows us to learn distinct model architectures (e.g., neural networks with different numbers of parameters) for different clients, thus confining underlying memory and compute resources of individual clients. We rigorously analyze the convergence of the proposed algorithm and conduct experiments that corroborate the effectiveness of the proposed paradigm.
Stochastic Quantum Sampling for Non-Logconcave Distributions and Estimating Partition Functions
Oct 17, 2023Abstract:We present quantum algorithms for sampling from non-logconcave probability distributions in the form of $\pi(x) \propto \exp(-\beta f(x))$. Here, $f$ can be written as a finite sum $f(x):= \frac{1}{N}\sum_{k=1}^N f_k(x)$. Our approach is based on quantum simulated annealing on slowly varying Markov chains derived from unadjusted Langevin algorithms, removing the necessity for function evaluations which can be computationally expensive for large data sets in mixture modeling and multi-stable systems. We also incorporate a stochastic gradient oracle that implements the quantum walk operators inexactly by only using mini-batch gradients. As a result, our stochastic gradient based algorithm only accesses small subsets of data points in implementing the quantum walk. One challenge of quantizing the resulting Markov chains is that they do not satisfy the detailed balance condition in general. Consequently, the mixing time of the algorithm cannot be expressed in terms of the spectral gap of the transition density, making the quantum algorithms nontrivial to analyze. To overcome these challenges, we first build a hypothetical Markov chain that is reversible, and also converges to the target distribution. Then, we quantified the distance between our algorithm's output and the target distribution by using this hypothetical chain as a bridge to establish the total complexity. Our quantum algorithms exhibit polynomial speedups in terms of both dimension and precision dependencies when compared to the best-known classical algorithms.
Understanding Deep Gradient Leakage via Inversion Influence Functions
Sep 22, 2023Abstract:Deep Gradient Leakage (DGL) is a highly effective attack that recovers private training images from gradient vectors. This attack casts significant privacy challenges on distributed learning from clients with sensitive data, where clients are required to share gradients. Defending against such attacks requires but lacks an understanding of when and how privacy leakage happens, mostly because of the black-box nature of deep networks. In this paper, we propose a novel Inversion Influence Function (I$^2$F) that establishes a closed-form connection between the recovered images and the private gradients by implicitly solving the DGL problem. Compared to directly solving DGL, I$^2$F is scalable for analyzing deep networks, requiring only oracle access to gradients and Jacobian-vector products. We empirically demonstrate that I$^2$F effectively approximated the DGL generally on different model architectures, datasets, attack implementations, and noise-based defenses. With this novel tool, we provide insights into effective gradient perturbation directions, the unfairness of privacy protection, and privacy-preferred model initialization. Our codes are provided in https://github.com/illidanlab/inversion-influence-function.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge