Maximilian Ilse
Data Scaling Laws for Radiology Foundation Models
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Foundation vision encoders such as CLIP and DINOv2, trained on web-scale data, exhibit strong transfer performance across tasks and datasets. However, medical imaging foundation models remain constrained by smaller datasets, limiting our understanding of how data scale and pretraining paradigms affect performance in this setting. In this work, we systematically study continual pretraining of two vision encoders, MedImageInsight (MI2) and RAD-DINO representing the two major encoder paradigms CLIP and DINOv2, on up to 3.5M chest x-rays from a single institution, holding compute and evaluation protocols constant. We evaluate on classification (radiology findings, lines and tubes), segmentation (lines and tubes), and radiology report generation. While prior work has primarily focused on tasks related to radiology findings, we include lines and tubes tasks to counterbalance this bias and evaluate a model's ability to extract features that preserve continuity along elongated structures. Our experiments show that MI2 scales more effectively for finding-related tasks, while RAD-DINO is stronger on tube-related tasks. Surprisingly, continually pretraining MI2 with both reports and structured labels using UniCL improves performance, underscoring the value of structured supervision at scale. We further show that for some tasks, as few as 30k in-domain samples are sufficient to surpass open-weights foundation models. These results highlight the utility of center-specific continual pretraining, enabling medical institutions to derive significant performance gains by utilizing in-domain data.
MAIRA-Seg: Enhancing Radiology Report Generation with Segmentation-Aware Multimodal Large Language Models
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:There is growing interest in applying AI to radiology report generation, particularly for chest X-rays (CXRs). This paper investigates whether incorporating pixel-level information through segmentation masks can improve fine-grained image interpretation of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) for radiology report generation. We introduce MAIRA-Seg, a segmentation-aware MLLM framework designed to utilize semantic segmentation masks alongside CXRs for generating radiology reports. We train expert segmentation models to obtain mask pseudolabels for radiology-specific structures in CXRs. Subsequently, building on the architectures of MAIRA, a CXR-specialised model for report generation, we integrate a trainable segmentation tokens extractor that leverages these mask pseudolabels, and employ mask-aware prompting to generate draft radiology reports. Our experiments on the publicly available MIMIC-CXR dataset show that MAIRA-Seg outperforms non-segmentation baselines. We also investigate set-of-marks prompting with MAIRA and find that MAIRA-Seg consistently demonstrates comparable or superior performance. The results confirm that using segmentation masks enhances the nuanced reasoning of MLLMs, potentially contributing to better clinical outcomes.
MAIRA-2: Grounded Radiology Report Generation
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Radiology reporting is a complex task that requires detailed image understanding, integration of multiple inputs, including comparison with prior imaging, and precise language generation. This makes it ideal for the development and use of generative multimodal models. Here, we extend report generation to include the localisation of individual findings on the image - a task we call grounded report generation. Prior work indicates that grounding is important for clarifying image understanding and interpreting AI-generated text. Therefore, grounded reporting stands to improve the utility and transparency of automated report drafting. To enable evaluation of grounded reporting, we propose a novel evaluation framework - RadFact - leveraging the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). RadFact assesses the factuality of individual generated sentences, as well as correctness of generated spatial localisations when present. We introduce MAIRA-2, a large multimodal model combining a radiology-specific image encoder with a LLM, and trained for the new task of grounded report generation on chest X-rays. MAIRA-2 uses more comprehensive inputs than explored previously: the current frontal image, the current lateral image, the prior frontal image and prior report, as well as the Indication, Technique and Comparison sections of the current report. We demonstrate that these additions significantly improve report quality and reduce hallucinations, establishing a new state of the art on findings generation (without grounding) on MIMIC-CXR while demonstrating the feasibility of grounded reporting as a novel and richer task.
RAD-DINO: Exploring Scalable Medical Image Encoders Beyond Text Supervision
Jan 19, 2024Abstract:Language-supervised pre-training has proven to be a valuable method for extracting semantically meaningful features from images, serving as a foundational element in multimodal systems within the computer vision and medical imaging domains. However, resulting features are limited by the information contained within the text. This is particularly problematic in medical imaging, where radiologists' written findings focus on specific observations; a challenge compounded by the scarcity of paired imaging-text data due to concerns over leakage of personal health information. In this work, we fundamentally challenge the prevailing reliance on language supervision for learning general purpose biomedical imaging encoders. We introduce RAD-DINO, a biomedical image encoder pre-trained solely on unimodal biomedical imaging data that obtains similar or greater performance than state-of-the-art biomedical language supervised models on a diverse range of benchmarks. Specifically, the quality of learned representations is evaluated on standard imaging tasks (classification and semantic segmentation), and a vision-language alignment task (text report generation from images). To further demonstrate the drawback of language supervision, we show that features from RAD-DINO correlate with other medical records (e.g., sex or age) better than language-supervised models, which are generally not mentioned in radiology reports. Finally, we conduct a series of ablations determining the factors in RAD-DINO's performance; notably, we observe that RAD-DINO's downstream performance scales well with the quantity and diversity of training data, demonstrating that image-only supervision is a scalable approach for training a foundational biomedical image encoder.
RadEdit: stress-testing biomedical vision models via diffusion image editing
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:Biomedical imaging datasets are often small and biased, meaning that real-world performance of predictive models can be substantially lower than expected from internal testing. This work proposes using generative image editing to simulate dataset shifts and diagnose failure modes of biomedical vision models; this can be used in advance of deployment to assess readiness, potentially reducing cost and patient harm. Existing editing methods can produce undesirable changes, with spurious correlations learned due to the co-occurrence of disease and treatment interventions, limiting practical applicability. To address this, we train a text-to-image diffusion model on multiple chest X-ray datasets and introduce a new editing method RadEdit that uses multiple masks, if present, to constrain changes and ensure consistency in the edited images. We consider three types of dataset shifts: acquisition shift, manifestation shift, and population shift, and demonstrate that our approach can diagnose failures and quantify model robustness without additional data collection, complementing more qualitative tools for explainable AI.
Learning to Exploit Temporal Structure for Biomedical Vision-Language Processing
Jan 11, 2023


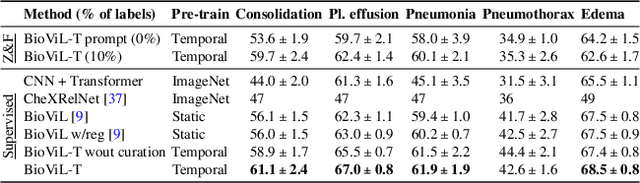
Abstract:Self-supervised learning in vision-language processing exploits semantic alignment between imaging and text modalities. Prior work in biomedical VLP has mostly relied on the alignment of single image and report pairs even though clinical notes commonly refer to prior images. This does not only introduce poor alignment between the modalities but also a missed opportunity to exploit rich self-supervision through existing temporal content in the data. In this work, we explicitly account for prior images and reports when available during both training and fine-tuning. Our approach, named BioViL-T, uses a CNN-Transformer hybrid multi-image encoder trained jointly with a text model. It is designed to be versatile to arising challenges such as pose variations and missing input images across time. The resulting model excels on downstream tasks both in single- and multi-image setups, achieving state-of-the-art performance on (I) progression classification, (II) phrase grounding, and (III) report generation, whilst offering consistent improvements on disease classification and sentence-similarity tasks. We release a novel multi-modal temporal benchmark dataset, MS-CXR-T, to quantify the quality of vision-language representations in terms of temporal semantics. Our experimental results show the advantages of incorporating prior images and reports to make most use of the data.
Efficient Causal Inference from Combined Observational and Interventional Data through Causal Reductions
Mar 08, 2021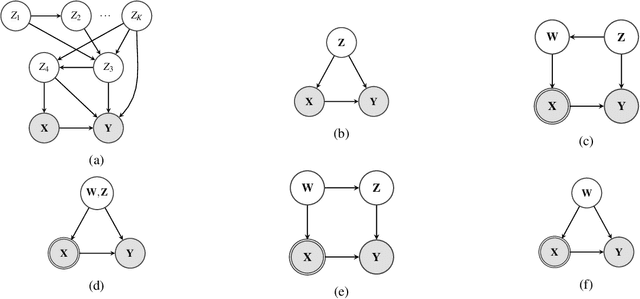
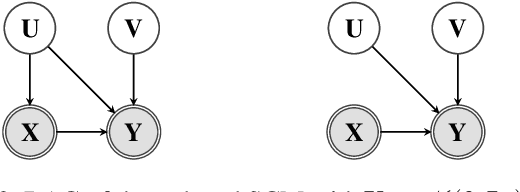
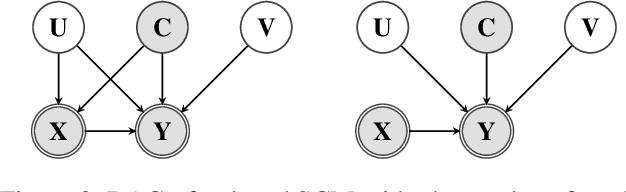
Abstract:Unobserved confounding is one of the main challenges when estimating causal effects. We propose a novel causal reduction method that replaces an arbitrary number of possibly high-dimensional latent confounders with a single latent confounder that lives in the same space as the treatment variable without changing the observational and interventional distributions entailed by the causal model. After the reduction, we parameterize the reduced causal model using a flexible class of transformations, so-called normalizing flows. We propose a learning algorithm to estimate the parameterized reduced model jointly from observational and interventional data. This allows us to estimate the causal effect in a principled way from combined data. We perform a series of experiments on data simulated using nonlinear causal mechanisms and find that we can often substantially reduce the number of interventional samples when adding observational training samples without sacrificing accuracy. Thus, adding observational data may help to more accurately estimate causal effects even in the presence of unobserved confounders.
Problems using deep generative models for probabilistic audio source separation
Nov 03, 2020
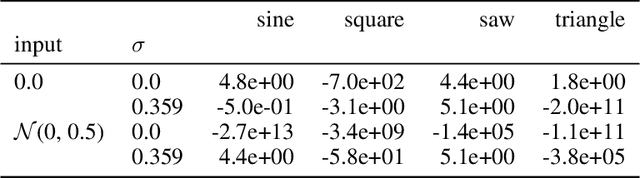
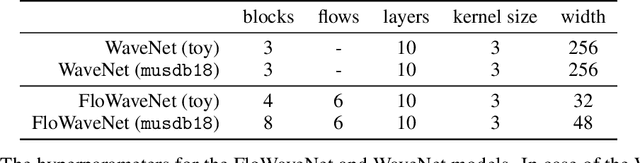
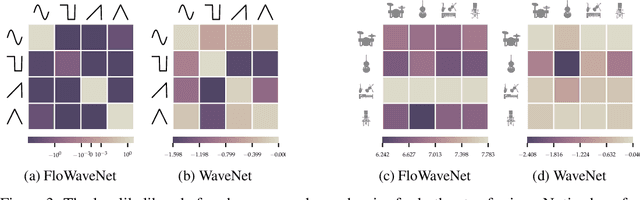
Abstract:Recent advancements in deep generative modeling make it possible to learn prior distributions from complex data that subsequently can be used for Bayesian inference. However, we find that distributions learned by deep generative models for audio signals do not exhibit the right properties that are necessary for tasks like audio source separation using a probabilistic approach. We observe that the learned prior distributions are either discriminative and extremely peaked or smooth and non-discriminative. We quantify this behavior for two types of deep generative models on two audio datasets.
Designing Data Augmentation for Simulating Interventions
May 06, 2020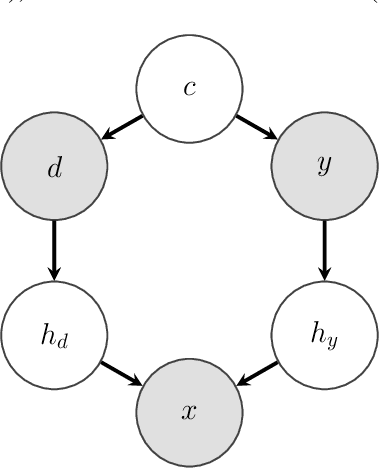
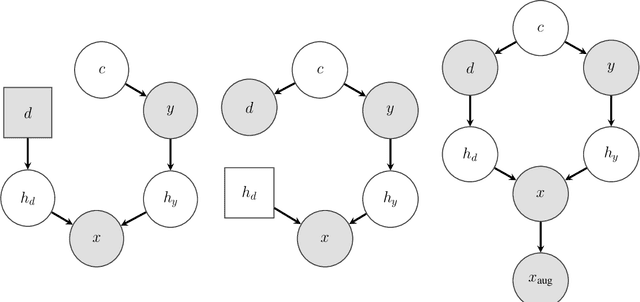
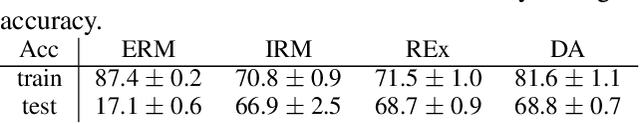
Abstract:Machine learning models trained with purely observational data and the principle of empirical risk minimization (Vapnik, 1992) can fail to generalize to unseen domains. In this paper, we focus on the case where the problem arises through spurious correlation between the observed domains and the actual task labels. We find that many domain generalization methods do not explicitly take this spurious correlation into account. Instead, especially in more application-oriented research areas like medical imaging or robotics, data augmentation techniques that are based on heuristics are used to learn domain invariant features. To bridge the gap between theory and practice, we develop a causal perspective on the problem of domain generalization. We argue that causal concepts can be used to explain the success of data augmentation by describing how they can weaken the spurious correlation between the observed domains and the task labels. We demonstrate that data augmentation can serve as a tool for simulating interventional data. Lastly, but unsurprisingly, we show that augmenting data improperly can cause a significant decrease in performance.
DIVA: Domain Invariant Variational Autoencoders
May 24, 2019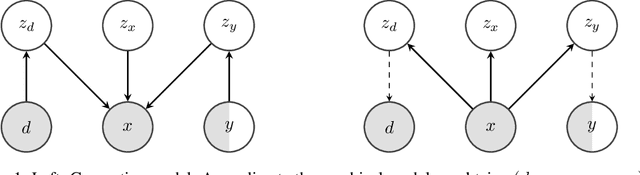
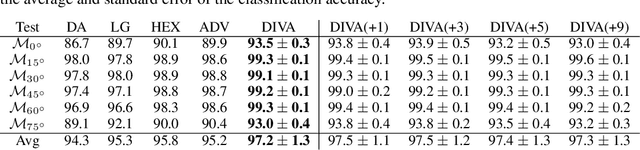
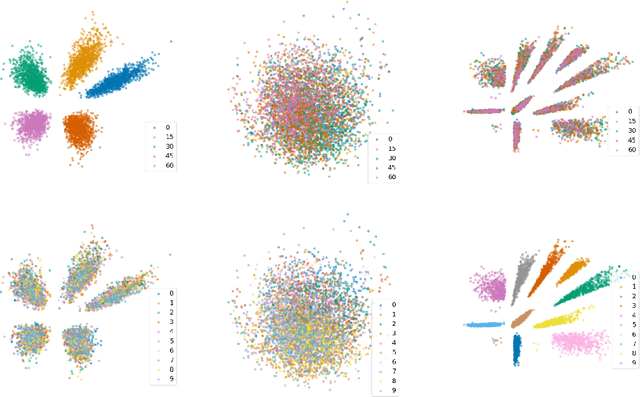
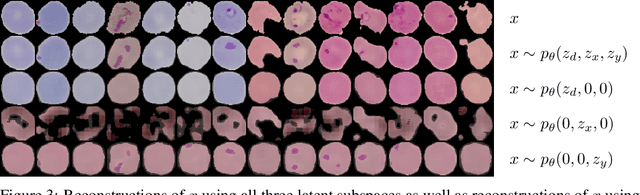
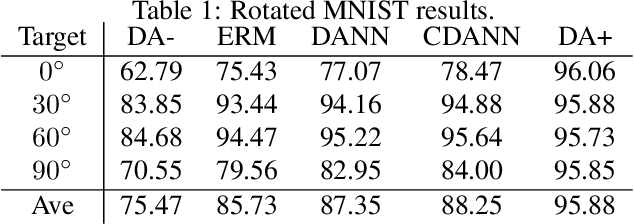
Abstract:We consider the problem of domain generalization, namely, how to learn representations given data from a set of domains that generalize to data from a previously unseen domain. We propose the Domain Invariant Variational Autoencoder (DIVA), a generative model that tackles this problem by learning three independent latent subspaces, one for the domain, one for the class, and one for any residual variations. We highlight that due to the generative nature of our model we can also incorporate unlabeled data from known or previously unseen domains. To the best of our knowledge this has not been done before in a domain generalization setting. This property is highly desirable in fields like medical imaging where labeled data is scarce. We experimentally evaluate our model on the rotated MNIST benchmark and a malaria cell images dataset where we show that (i) the learned subspaces are indeed complementary to each other, (ii) we improve upon recent works on this task and (iii) incorporating unlabelled data can boost the performance even further.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge