Matthew Graham
California Institute of Technology, USA
Accelerating Radiative Transfer for Planetary Atmospheres by Orders of Magnitude with a Transformer-Based Machine Learning Model
Oct 30, 2025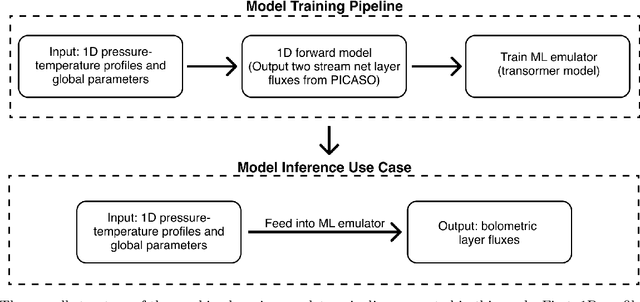
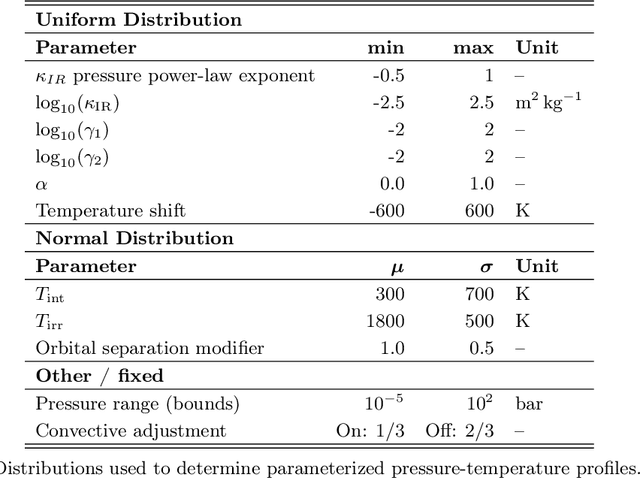
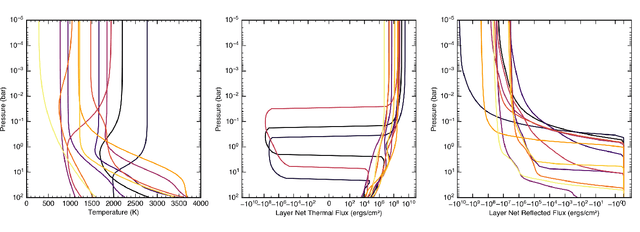
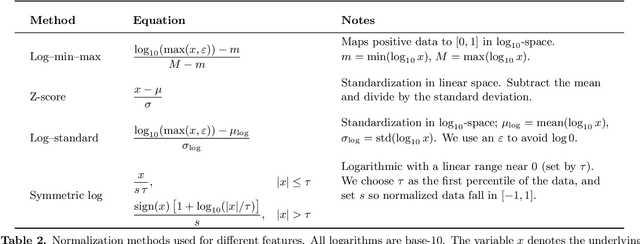
Abstract:Radiative transfer calculations are essential for modeling planetary atmospheres. However, standard methods are computationally demanding and impose accuracy-speed trade-offs. High computational costs force numerical simplifications in large models (e.g., General Circulation Models) that degrade the accuracy of the simulation. Radiative transfer calculations are an ideal candidate for machine learning emulation: fundamentally, it is a well-defined physical mapping from a static atmospheric profile to the resulting fluxes, and high-fidelity training data can be created from first principles calculations. We developed a radiative transfer emulator using an encoder-only transformer neural network architecture, trained on 1D profiles representative of solar-composition hot Jupiter atmospheres. Our emulator reproduced bolometric two-stream layer fluxes with mean test set errors of ~1% compared to the traditional method and achieved speedups of 100x. Emulating radiative transfer with machine learning opens up the possibility for faster and more accurate routines within planetary atmospheric models such as GCMs.
Building Machine Learning Challenges for Anomaly Detection in Science
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:Scientific discoveries are often made by finding a pattern or object that was not predicted by the known rules of science. Oftentimes, these anomalous events or objects that do not conform to the norms are an indication that the rules of science governing the data are incomplete, and something new needs to be present to explain these unexpected outliers. The challenge of finding anomalies can be confounding since it requires codifying a complete knowledge of the known scientific behaviors and then projecting these known behaviors on the data to look for deviations. When utilizing machine learning, this presents a particular challenge since we require that the model not only understands scientific data perfectly but also recognizes when the data is inconsistent and out of the scope of its trained behavior. In this paper, we present three datasets aimed at developing machine learning-based anomaly detection for disparate scientific domains covering astrophysics, genomics, and polar science. We present the different datasets along with a scheme to make machine learning challenges around the three datasets findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR). Furthermore, we present an approach that generalizes to future machine learning challenges, enabling the possibility of large, more compute-intensive challenges that can ultimately lead to scientific discovery.
Data Science and Machine Learning in Education
Jul 19, 2022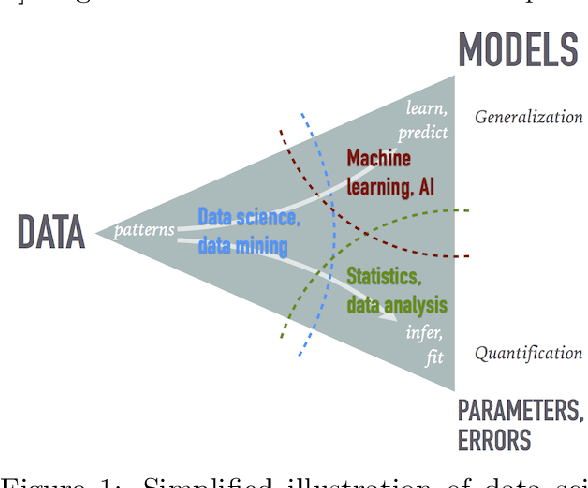
Abstract:The growing role of data science (DS) and machine learning (ML) in high-energy physics (HEP) is well established and pertinent given the complex detectors, large data, sets and sophisticated analyses at the heart of HEP research. Moreover, exploiting symmetries inherent in physics data have inspired physics-informed ML as a vibrant sub-field of computer science research. HEP researchers benefit greatly from materials widely available materials for use in education, training and workforce development. They are also contributing to these materials and providing software to DS/ML-related fields. Increasingly, physics departments are offering courses at the intersection of DS, ML and physics, often using curricula developed by HEP researchers and involving open software and data used in HEP. In this white paper, we explore synergies between HEP research and DS/ML education, discuss opportunities and challenges at this intersection, and propose community activities that will be mutually beneficial.
Enabling real-time multi-messenger astrophysics discoveries with deep learning
Nov 26, 2019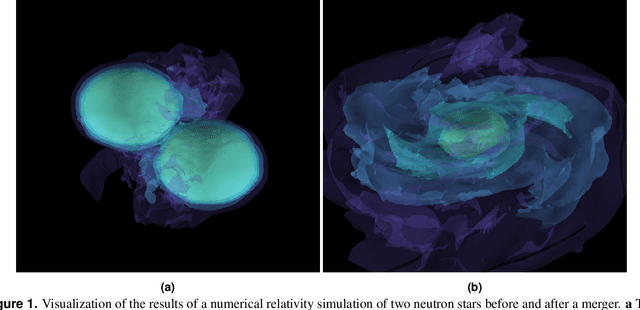
Abstract:Multi-messenger astrophysics is a fast-growing, interdisciplinary field that combines data, which vary in volume and speed of data processing, from many different instruments that probe the Universe using different cosmic messengers: electromagnetic waves, cosmic rays, gravitational waves and neutrinos. In this Expert Recommendation, we review the key challenges of real-time observations of gravitational wave sources and their electromagnetic and astroparticle counterparts, and make a number of recommendations to maximize their potential for scientific discovery. These recommendations refer to the design of scalable and computationally efficient machine learning algorithms; the cyber-infrastructure to numerically simulate astrophysical sources, and to process and interpret multi-messenger astrophysics data; the management of gravitational wave detections to trigger real-time alerts for electromagnetic and astroparticle follow-ups; a vision to harness future developments of machine learning and cyber-infrastructure resources to cope with the big-data requirements; and the need to build a community of experts to realize the goals of multi-messenger astrophysics.
* Invited Expert Recommendation for Nature Reviews Physics. The art work produced by E. A. Huerta and Shawn Rosofsky for this article was used by Carl Conway to design the cover of the October 2019 issue of Nature Reviews Physics
Recommendation or Discrimination?: Quantifying Distribution Parity in Information Retrieval Systems
Sep 13, 2019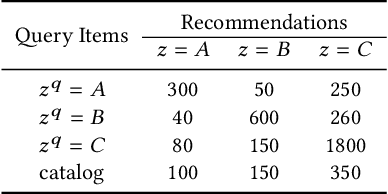


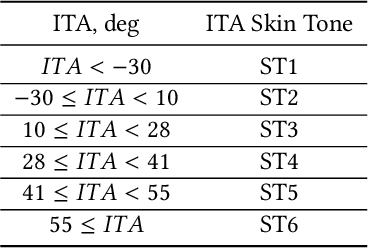
Abstract:Information retrieval (IR) systems often leverage query data to suggest relevant items to users. This introduces the possibility of unfairness if the query (i.e., input) and the resulting recommendations unintentionally correlate with latent factors that are protected variables (e.g., race, gender, and age). For instance, a visual search system for fashion recommendations may pick up on features of the human models rather than fashion garments when generating recommendations. In this work, we introduce a statistical test for "distribution parity" in the top-K IR results, which assesses whether a given set of recommendations is fair with respect to a specific protected variable. We evaluate our test using both simulated and empirical results. First, using artificially biased recommendations, we demonstrate the trade-off between statistically detectable bias and the size of the search catalog. Second, we apply our test to a visual search system for fashion garments, specifically testing for recommendation bias based on the skin tone of fashion models. Our distribution parity test can help ensure that IR systems' results are fair and produce a good experience for all users.
Deep Learning for Multi-Messenger Astrophysics: A Gateway for Discovery in the Big Data Era
Feb 01, 2019Abstract:This report provides an overview of recent work that harnesses the Big Data Revolution and Large Scale Computing to address grand computational challenges in Multi-Messenger Astrophysics, with a particular emphasis on real-time discovery campaigns. Acknowledging the transdisciplinary nature of Multi-Messenger Astrophysics, this document has been prepared by members of the physics, astronomy, computer science, data science, software and cyberinfrastructure communities who attended the NSF-, DOE- and NVIDIA-funded "Deep Learning for Multi-Messenger Astrophysics: Real-time Discovery at Scale" workshop, hosted at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications, October 17-19, 2018. Highlights of this report include unanimous agreement that it is critical to accelerate the development and deployment of novel, signal-processing algorithms that use the synergy between artificial intelligence (AI) and high performance computing to maximize the potential for scientific discovery with Multi-Messenger Astrophysics. We discuss key aspects to realize this endeavor, namely (i) the design and exploitation of scalable and computationally efficient AI algorithms for Multi-Messenger Astrophysics; (ii) cyberinfrastructure requirements to numerically simulate astrophysical sources, and to process and interpret Multi-Messenger Astrophysics data; (iii) management of gravitational wave detections and triggers to enable electromagnetic and astro-particle follow-ups; (iv) a vision to harness future developments of machine and deep learning and cyberinfrastructure resources to cope with the scale of discovery in the Big Data Era; (v) and the need to build a community that brings domain experts together with data scientists on equal footing to maximize and accelerate discovery in the nascent field of Multi-Messenger Astrophysics.
Deep-Learnt Classification of Light Curves
Sep 19, 2017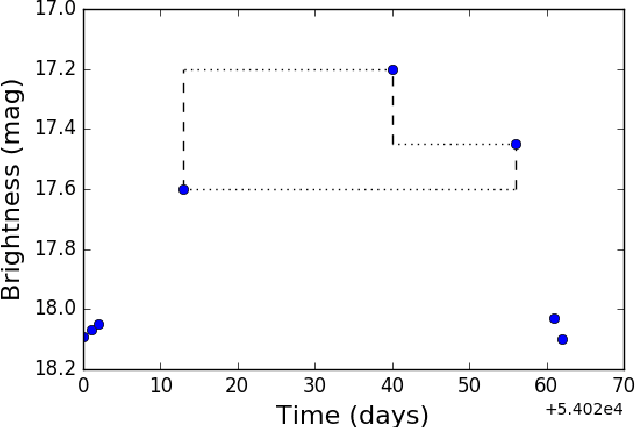
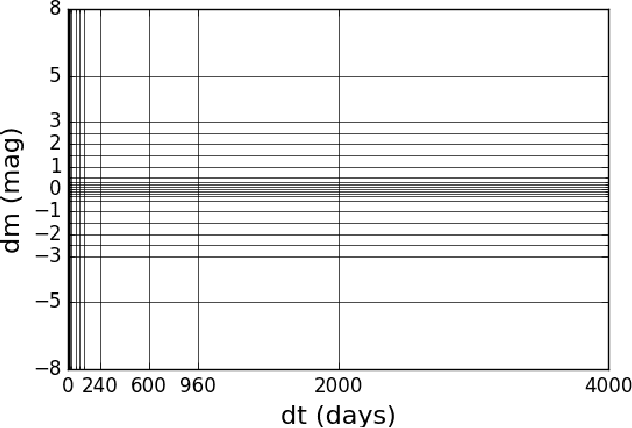
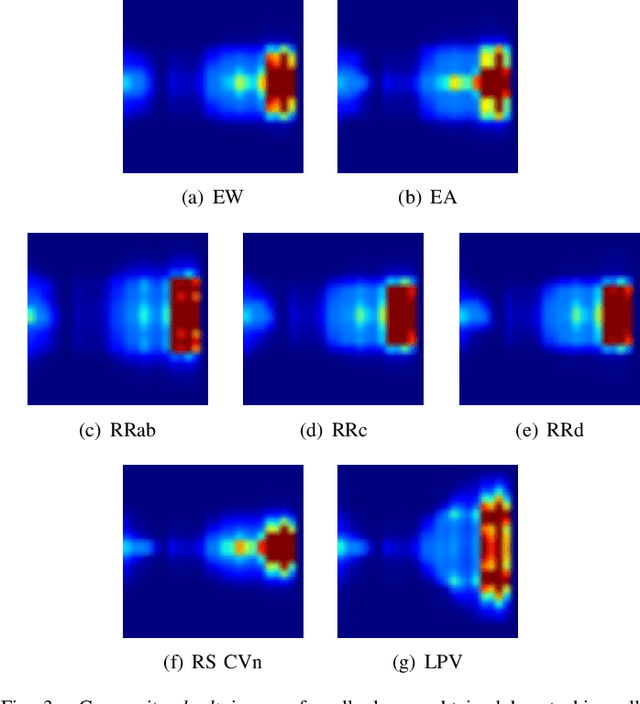
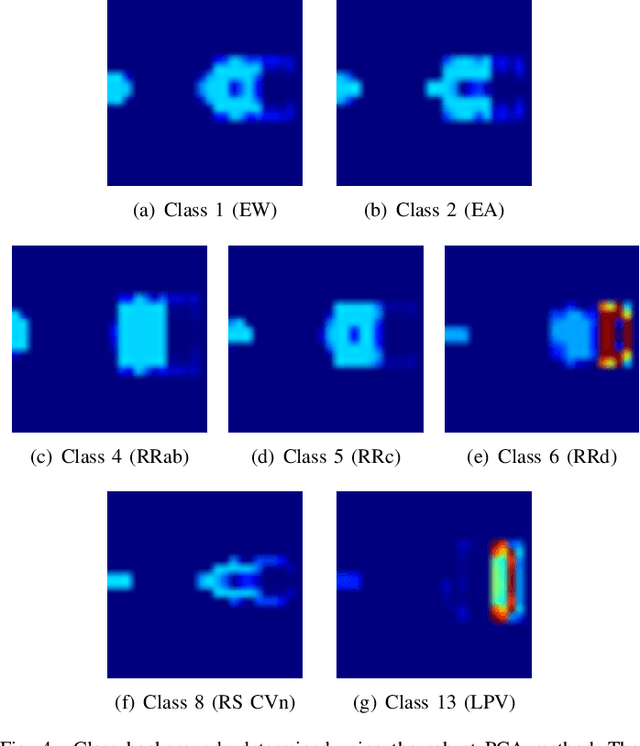
Abstract:Astronomy light curves are sparse, gappy, and heteroscedastic. As a result standard time series methods regularly used for financial and similar datasets are of little help and astronomers are usually left to their own instruments and techniques to classify light curves. A common approach is to derive statistical features from the time series and to use machine learning methods, generally supervised, to separate objects into a few of the standard classes. In this work, we transform the time series to two-dimensional light curve representations in order to classify them using modern deep learning techniques. In particular, we show that convolutional neural networks based classifiers work well for broad characterization and classification. We use labeled datasets of periodic variables from CRTS survey and show how this opens doors for a quick classification of diverse classes with several possible exciting extensions.
* 8 pages, 9 figures, 6 tables, 2 listings. Accepted to 2017 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge