Masoud Monajatipoor
Medical Vision-Language Pre-Training for Brain Abnormalities
Apr 27, 2024Abstract:Vision-language models have become increasingly powerful for tasks that require an understanding of both visual and linguistic elements, bridging the gap between these modalities. In the context of multimodal clinical AI, there is a growing need for models that possess domain-specific knowledge, as existing models often lack the expertise required for medical applications. In this paper, we take brain abnormalities as an example to demonstrate how to automatically collect medical image-text aligned data for pretraining from public resources such as PubMed. In particular, we present a pipeline that streamlines the pre-training process by initially collecting a large brain image-text dataset from case reports and published journals and subsequently constructing a high-performance vision-language model tailored to specific medical tasks. We also investigate the unique challenge of mapping subfigures to subcaptions in the medical domain. We evaluated the resulting model with quantitative and qualitative intrinsic evaluations. The resulting dataset and our code can be found here https://github.com/masoud-monajati/MedVL_pretraining_pipeline
LLMs in Biomedicine: A study on clinical Named Entity Recognition
Apr 10, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable versatility in various NLP tasks but encounter distinct challenges in biomedicine due to medical language complexities and data scarcity. This paper investigates the application of LLMs in the medical domain by exploring strategies to enhance their performance for the Named-Entity Recognition (NER) task. Specifically, our study reveals the importance of meticulously designed prompts in biomedicine. Strategic selection of in-context examples yields a notable improvement, showcasing ~15-20\% increase in F1 score across all benchmark datasets for few-shot clinical NER. Additionally, our findings suggest that integrating external resources through prompting strategies can bridge the gap between general-purpose LLM proficiency and the specialized demands of medical NER. Leveraging a medical knowledge base, our proposed method inspired by Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) can boost the F1 score of LLMs for zero-shot clinical NER. We will release the code upon publication.
MetaVL: Transferring In-Context Learning Ability From Language Models to Vision-Language Models
Jun 02, 2023



Abstract:Large-scale language models have shown the ability to adapt to a new task via conditioning on a few demonstrations (i.e., in-context learning). However, in the vision-language domain, most large-scale pre-trained vision-language (VL) models do not possess the ability to conduct in-context learning. How can we enable in-context learning for VL models? In this paper, we study an interesting hypothesis: can we transfer the in-context learning ability from the language domain to VL domain? Specifically, we first meta-trains a language model to perform in-context learning on NLP tasks (as in MetaICL); then we transfer this model to perform VL tasks by attaching a visual encoder. Our experiments suggest that indeed in-context learning ability can be transferred cross modalities: our model considerably improves the in-context learning capability on VL tasks and can even compensate for the size of the model significantly. On VQA, OK-VQA, and GQA, our method could outperform the baseline model while having 20 times fewer parameters.
How well can Text-to-Image Generative Models understand Ethical Natural Language Interventions?
Oct 27, 2022Abstract:Text-to-image generative models have achieved unprecedented success in generating high-quality images based on natural language descriptions. However, it is shown that these models tend to favor specific social groups when prompted with neutral text descriptions (e.g., 'a photo of a lawyer'). Following Zhao et al. (2021), we study the effect on the diversity of the generated images when adding ethical intervention that supports equitable judgment (e.g., 'if all individuals can be a lawyer irrespective of their gender') in the input prompts. To this end, we introduce an Ethical NaTural Language Interventions in Text-to-Image GENeration (ENTIGEN) benchmark dataset to evaluate the change in image generations conditional on ethical interventions across three social axes -- gender, skin color, and culture. Through ENTIGEN framework, we find that the generations from minDALL.E, DALL.E-mini and Stable Diffusion cover diverse social groups while preserving the image quality. Preliminary studies indicate that a large change in the model predictions is triggered by certain phrases such as 'irrespective of gender' in the context of gender bias in the ethical interventions. We release code and annotated data at https://github.com/Hritikbansal/entigen_emnlp.
MAGIC: Mask-Guided Image Synthesis by Inverting a Quasi-Robust Classifier
Sep 23, 2022



Abstract:We offer a method for one-shot image synthesis that allows controlling manipulations of a single image by inverting a quasi-robust classifier equipped with strong regularizers. Our proposed method, entitled Magic, samples structured gradients from a pre-trained quasi-robust classifier to better preserve the input semantics while preserving its classification accuracy, thereby guaranteeing credibility in the synthesis. Unlike current methods that use complex primitives to supervise the process or use attention maps as a weak supervisory signal, Magic aggregates gradients over the input, driven by a guide binary mask that enforces a strong, spatial prior. Magic implements a series of manipulations with a single framework achieving shape and location control, intense non-rigid shape deformations, and copy/move operations in the presence of repeating objects and gives users firm control over the synthesis by requiring simply specifying binary guide masks. Our study and findings are supported by various qualitative comparisons with the state-of-the-art on the same images sampled from ImageNet and quantitative analysis using machine perception along with a user survey of 100+ participants that endorse our synthesis quality.
GeoMLAMA: Geo-Diverse Commonsense Probing on Multilingual Pre-Trained Language Models
May 24, 2022



Abstract:Recent work has shown that Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs) have the ability to store the relational knowledge from pre-training data in their model parameters. However, it is not clear up to what extent do PLMs store geo-diverse commonsense knowledge, the knowledge associated with a culture and only shared locally. For instance, the color of bridal dress is white in American weddings whereas it is red in Chinese weddings. Here, we wish to probe if PLMs can predict red and white as the color of the bridal dress when queried for American and Chinese weddings, respectively. To this end, we introduce a framework for geo-diverse commonsense probing on multilingual PLMs (mPLMs) and introduce a corresponding benchmark Geo-diverse Commonsense Multilingual Language Model Analysis (GeoMLAMA) dataset. GeoMLAMA contains 3125 prompts in English, Chinese, Hindi, Persian, and Swahili, with a wide coverage of concepts shared by people from American, Chinese, Indian, Iranian and Kenyan cultures. We benchmark 11 standard mPLMs which include variants of mBERT, XLM, mT5, and XGLM on GeoMLAMA. Interestingly, we find that 1) larger mPLM variants do not necessarily store geo-diverse concepts better than its smaller variant; 2) mPLMs are not intrinsically biased towards knowledge from the Western countries (the United States); 3) the native language of a country may not be the best language to probe its knowledge and 4) a language may better probe knowledge about a non-native country than its native country.
Harms of Gender Exclusivity and Challenges in Non-Binary Representation in Language Technologies
Aug 27, 2021



Abstract:Gender is widely discussed in the context of language tasks and when examining the stereotypes propagated by language models. However, current discussions primarily treat gender as binary, which can perpetuate harms such as the cyclical erasure of non-binary gender identities. These harms are driven by model and dataset biases, which are consequences of the non-recognition and lack of understanding of non-binary genders in society. In this paper, we explain the complexity of gender and language around it, and survey non-binary persons to understand harms associated with the treatment of gender as binary in English language technologies. We also detail how current language representations (e.g., GloVe, BERT) capture and perpetuate these harms and related challenges that need to be acknowledged and addressed for representations to equitably encode gender information.
BERTHop: An Effective Vision-and-Language Model for Chest X-ray Disease Diagnosis
Aug 10, 2021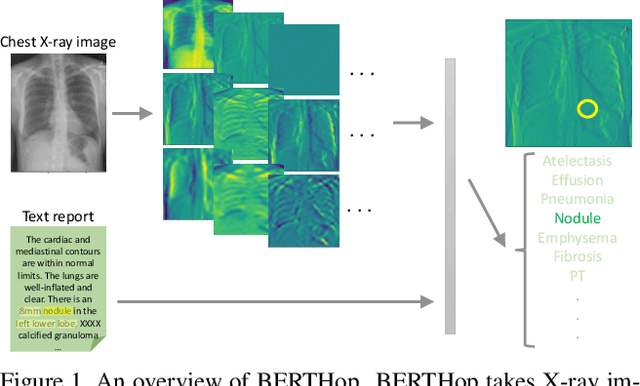
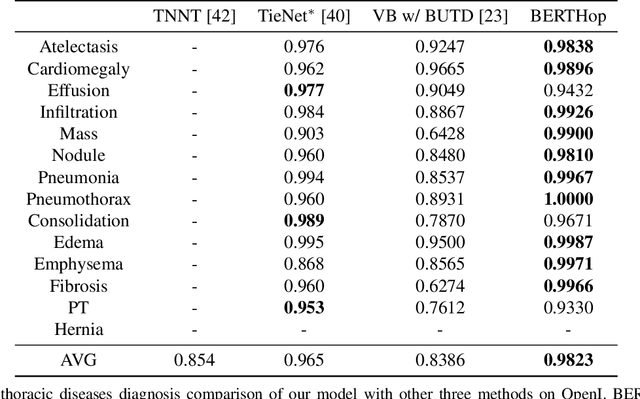
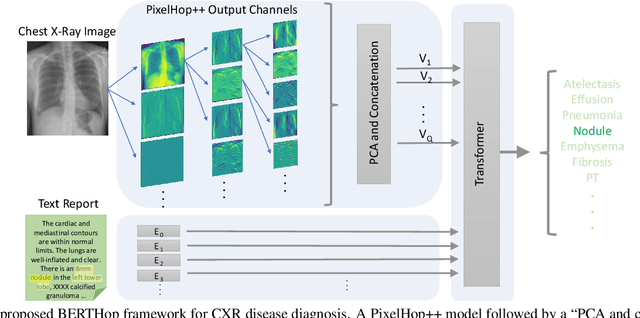
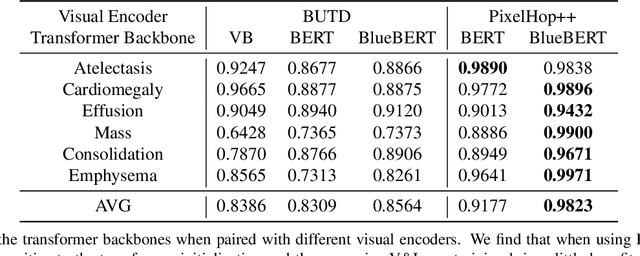
Abstract:Vision-and-language(V&L) models take image and text as input and learn to capture the associations between them. Prior studies show that pre-trained V&L models can significantly improve the model performance for downstream tasks such as Visual Question Answering (VQA). However, V&L models are less effective when applied in the medical domain (e.g., on X-ray images and clinical notes) due to the domain gap. In this paper, we investigate the challenges of applying pre-trained V&L models in medical applications. In particular, we identify that the visual representation in general V&L models is not suitable for processing medical data. To overcome this limitation, we propose BERTHop, a transformer-based model based on PixelHop++ and VisualBERT, for better capturing the associations between the two modalities. Experiments on the OpenI dataset, a commonly used thoracic disease diagnosis benchmark, show that BERTHop achieves an average Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 98.12% which is 1.62% higher than state-of-the-art (SOTA) while it is trained on a 9 times smaller dataset.
Successive Subspace Learning: An Overview
Feb 27, 2021
Abstract:Successive Subspace Learning (SSL) offers a light-weight unsupervised feature learning method based on inherent statistical properties of data units (e.g. image pixels and points in point cloud sets). It has shown promising results, especially on small datasets. In this paper, we intuitively explain this method, provide an overview of its development, and point out some open questions and challenges for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge