Fazlolah Mohaghegh
LLMs in Biomedicine: A study on clinical Named Entity Recognition
Apr 10, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable versatility in various NLP tasks but encounter distinct challenges in biomedicine due to medical language complexities and data scarcity. This paper investigates the application of LLMs in the medical domain by exploring strategies to enhance their performance for the Named-Entity Recognition (NER) task. Specifically, our study reveals the importance of meticulously designed prompts in biomedicine. Strategic selection of in-context examples yields a notable improvement, showcasing ~15-20\% increase in F1 score across all benchmark datasets for few-shot clinical NER. Additionally, our findings suggest that integrating external resources through prompting strategies can bridge the gap between general-purpose LLM proficiency and the specialized demands of medical NER. Leveraging a medical knowledge base, our proposed method inspired by Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) can boost the F1 score of LLMs for zero-shot clinical NER. We will release the code upon publication.
Machine Learning and Computer Vision Techniques to Predict Thermal Properties of Particulate Composites
Aug 27, 2020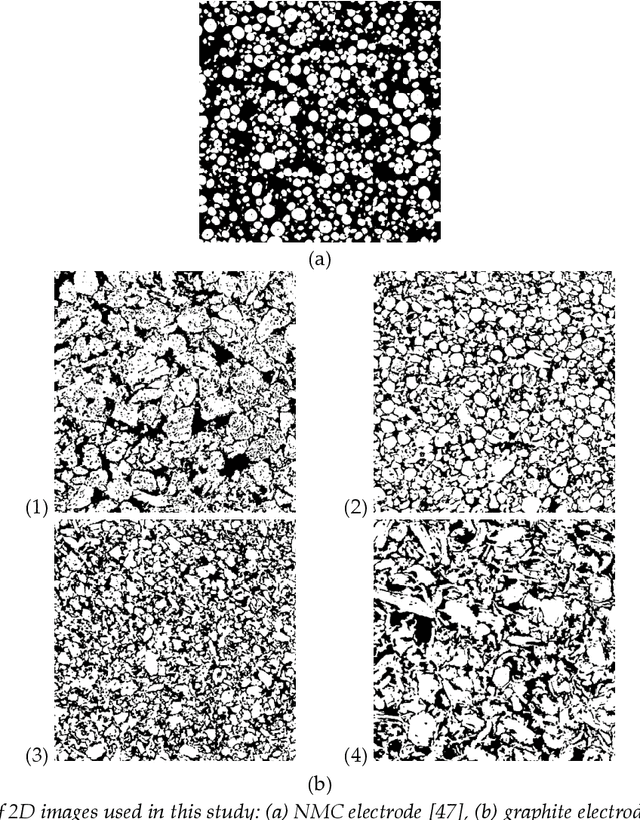
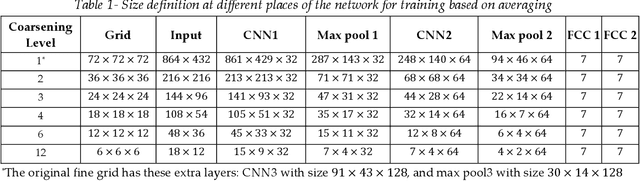
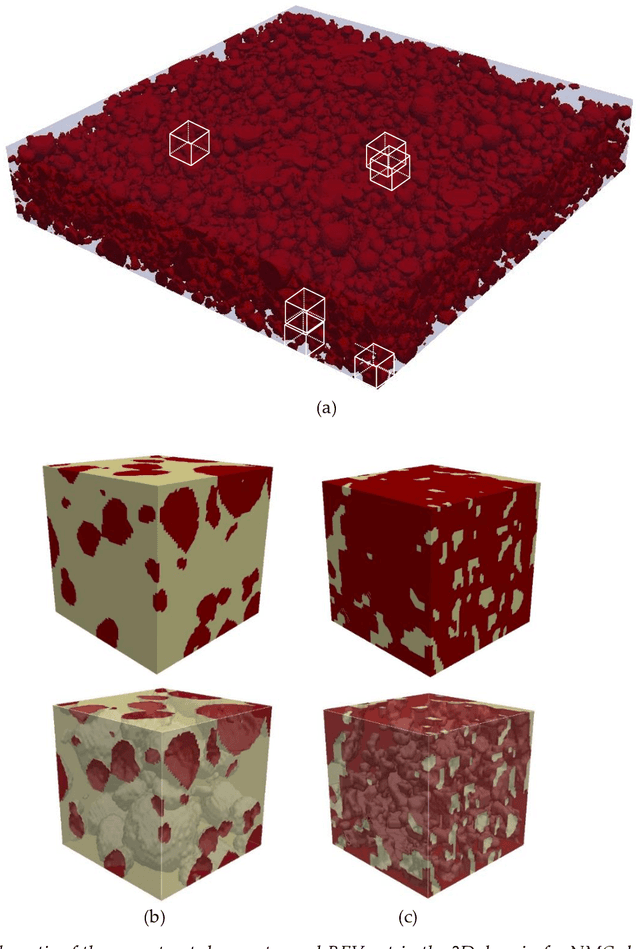
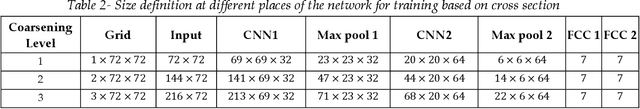
Abstract:Accurate thermal analysis of composites and porous media requires detailed characterization of local thermal properties in small scale. For some important applications such as lithium-ion batteries, changes in the properties during the operation makes the analysis even more challenging, necessitating a rapid characterization. We propose a new method to characterize the thermal properties of particulate composites based on actual micro-images. Our computer-vision-based approach constructs 3D images from stacks of 2D SEM images and then extracts several representative elemental volumes (REVs) from the reconstructed images at random places, which leads to having a range of geometrical features for different REVs. A deep learning algorithm is designed based on convolutional neural nets to take the shape of the geometry and result in the effective conductivity of the REV. The training of the network is performed in two methods: First, based on implementing a coarser grid that uses the average values of conductivities from the fine grid and the resulted effective conductivity from the DNS solution of the fine grid. The other method uses conductivity values on cross sections from each REV in different directions. The results of training based on averaging show that using a coarser grid in the network does not have a meaningful effect on the network error; however, it decreases the training time up to three orders of magnitude. We showed that one general network can make accurate predictions using different types of electrode images, representing the difference in the geometry and constituents. Moreover, training based on averaging is more accurate than training based on cross sections. The study of the robustness of implementing a machine learning technique in predicting the thermal percolation shows the prediction error is almost half of the error from predictions based on the volume fraction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge