Martín Abadi
Google Brain
Adversarial Patch
May 17, 2018



Abstract:We present a method to create universal, robust, targeted adversarial image patches in the real world. The patches are universal because they can be used to attack any scene, robust because they work under a wide variety of transformations, and targeted because they can cause a classifier to output any target class. These adversarial patches can be printed, added to any scene, photographed, and presented to image classifiers; even when the patches are small, they cause the classifiers to ignore the other items in the scene and report a chosen target class. To reproduce the results from the paper, our code is available at https://github.com/tensorflow/cleverhans/tree/master/examples/adversarial_patch
Dynamic Control Flow in Large-Scale Machine Learning
May 04, 2018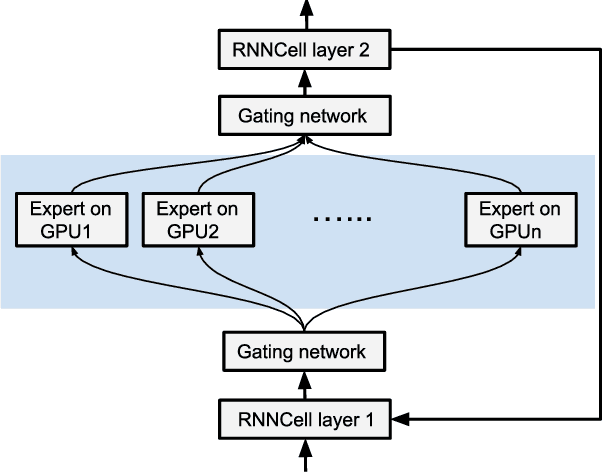
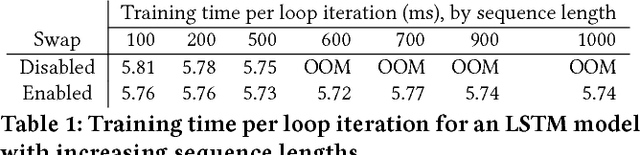
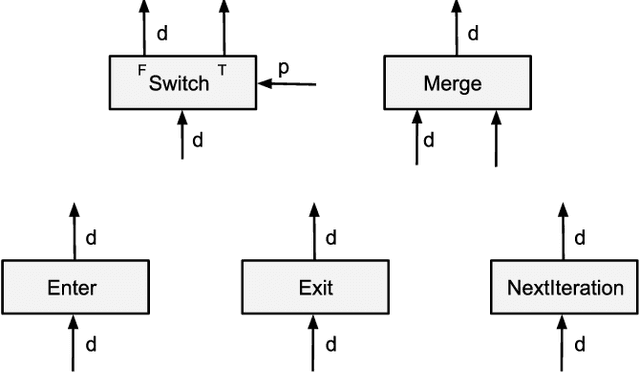
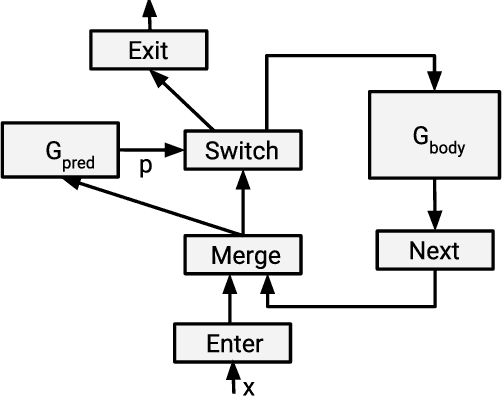
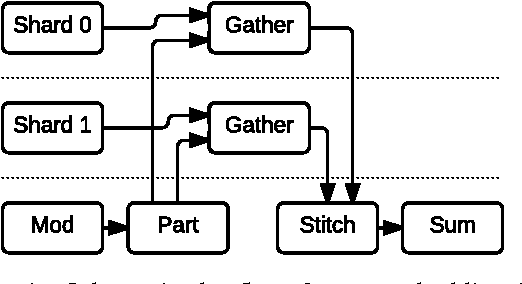
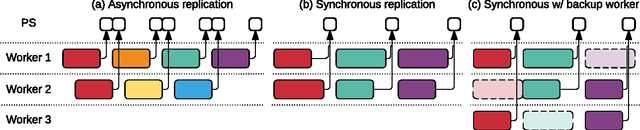
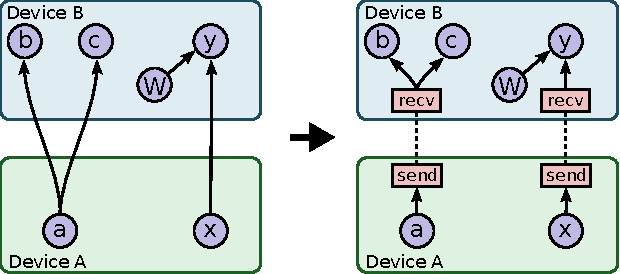
Abstract:Many recent machine learning models rely on fine-grained dynamic control flow for training and inference. In particular, models based on recurrent neural networks and on reinforcement learning depend on recurrence relations, data-dependent conditional execution, and other features that call for dynamic control flow. These applications benefit from the ability to make rapid control-flow decisions across a set of computing devices in a distributed system. For performance, scalability, and expressiveness, a machine learning system must support dynamic control flow in distributed and heterogeneous environments. This paper presents a programming model for distributed machine learning that supports dynamic control flow. We describe the design of the programming model, and its implementation in TensorFlow, a distributed machine learning system. Our approach extends the use of dataflow graphs to represent machine learning models, offering several distinctive features. First, the branches of conditionals and bodies of loops can be partitioned across many machines to run on a set of heterogeneous devices, including CPUs, GPUs, and custom ASICs. Second, programs written in our model support automatic differentiation and distributed gradient computations, which are necessary for training machine learning models that use control flow. Third, our choice of non-strict semantics enables multiple loop iterations to execute in parallel across machines, and to overlap compute and I/O operations. We have done our work in the context of TensorFlow, and it has been used extensively in research and production. We evaluate it using several real-world applications, and demonstrate its performance and scalability.
* Appeared in EuroSys 2018. 14 pages, 16 figures
On the Protection of Private Information in Machine Learning Systems: Two Recent Approaches
Aug 26, 2017Abstract:The recent, remarkable growth of machine learning has led to intense interest in the privacy of the data on which machine learning relies, and to new techniques for preserving privacy. However, older ideas about privacy may well remain valid and useful. This note reviews two recent works on privacy in the light of the wisdom of some of the early literature, in particular the principles distilled by Saltzer and Schroeder in the 1970s.
Semi-supervised Knowledge Transfer for Deep Learning from Private Training Data
Mar 03, 2017



Abstract:Some machine learning applications involve training data that is sensitive, such as the medical histories of patients in a clinical trial. A model may inadvertently and implicitly store some of its training data; careful analysis of the model may therefore reveal sensitive information. To address this problem, we demonstrate a generally applicable approach to providing strong privacy guarantees for training data: Private Aggregation of Teacher Ensembles (PATE). The approach combines, in a black-box fashion, multiple models trained with disjoint datasets, such as records from different subsets of users. Because they rely directly on sensitive data, these models are not published, but instead used as "teachers" for a "student" model. The student learns to predict an output chosen by noisy voting among all of the teachers, and cannot directly access an individual teacher or the underlying data or parameters. The student's privacy properties can be understood both intuitively (since no single teacher and thus no single dataset dictates the student's training) and formally, in terms of differential privacy. These properties hold even if an adversary can not only query the student but also inspect its internal workings. Compared with previous work, the approach imposes only weak assumptions on how teachers are trained: it applies to any model, including non-convex models like DNNs. We achieve state-of-the-art privacy/utility trade-offs on MNIST and SVHN thanks to an improved privacy analysis and semi-supervised learning.
Deep Learning with Differential Privacy
Oct 24, 2016

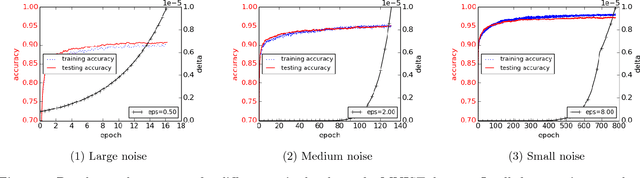

Abstract:Machine learning techniques based on neural networks are achieving remarkable results in a wide variety of domains. Often, the training of models requires large, representative datasets, which may be crowdsourced and contain sensitive information. The models should not expose private information in these datasets. Addressing this goal, we develop new algorithmic techniques for learning and a refined analysis of privacy costs within the framework of differential privacy. Our implementation and experiments demonstrate that we can train deep neural networks with non-convex objectives, under a modest privacy budget, and at a manageable cost in software complexity, training efficiency, and model quality.
Learning to Protect Communications with Adversarial Neural Cryptography
Oct 21, 2016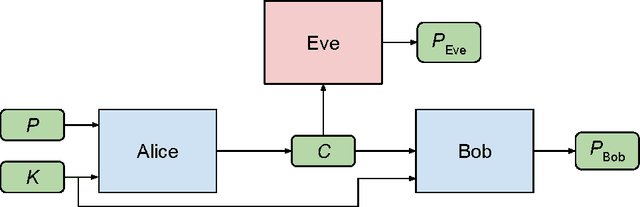
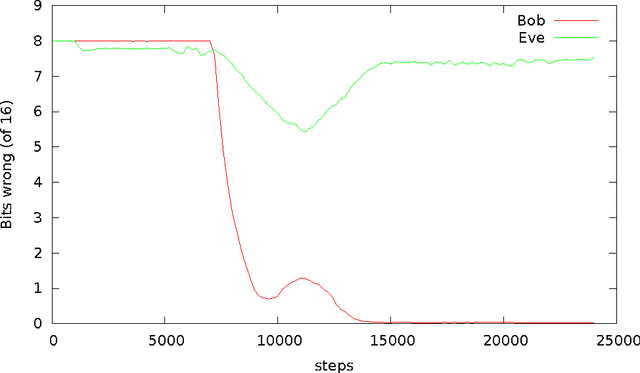
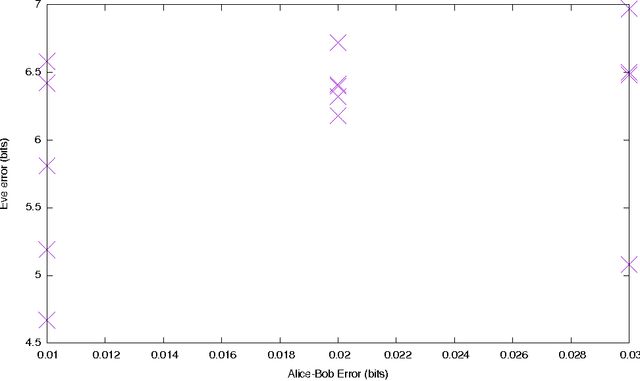
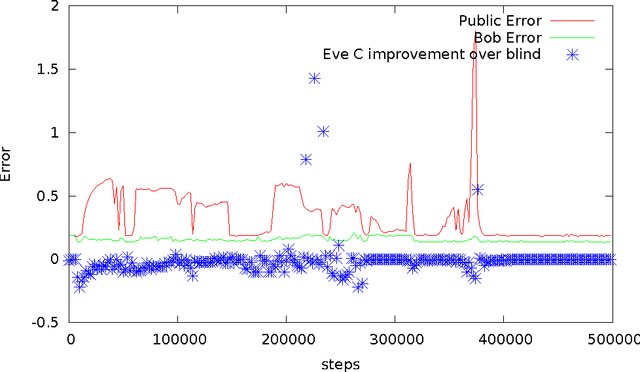
Abstract:We ask whether neural networks can learn to use secret keys to protect information from other neural networks. Specifically, we focus on ensuring confidentiality properties in a multiagent system, and we specify those properties in terms of an adversary. Thus, a system may consist of neural networks named Alice and Bob, and we aim to limit what a third neural network named Eve learns from eavesdropping on the communication between Alice and Bob. We do not prescribe specific cryptographic algorithms to these neural networks; instead, we train end-to-end, adversarially. We demonstrate that the neural networks can learn how to perform forms of encryption and decryption, and also how to apply these operations selectively in order to meet confidentiality goals.
TensorFlow: A system for large-scale machine learning
May 31, 2016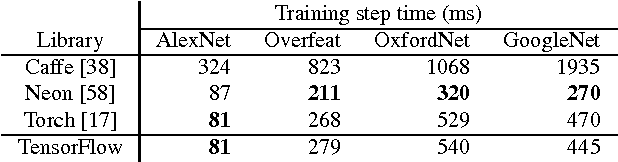
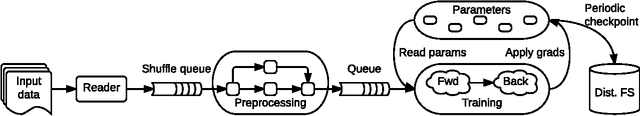
Abstract:TensorFlow is a machine learning system that operates at large scale and in heterogeneous environments. TensorFlow uses dataflow graphs to represent computation, shared state, and the operations that mutate that state. It maps the nodes of a dataflow graph across many machines in a cluster, and within a machine across multiple computational devices, including multicore CPUs, general-purpose GPUs, and custom designed ASICs known as Tensor Processing Units (TPUs). This architecture gives flexibility to the application developer: whereas in previous "parameter server" designs the management of shared state is built into the system, TensorFlow enables developers to experiment with novel optimizations and training algorithms. TensorFlow supports a variety of applications, with particularly strong support for training and inference on deep neural networks. Several Google services use TensorFlow in production, we have released it as an open-source project, and it has become widely used for machine learning research. In this paper, we describe the TensorFlow dataflow model in contrast to existing systems, and demonstrate the compelling performance that TensorFlow achieves for several real-world applications.
TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems
Mar 16, 2016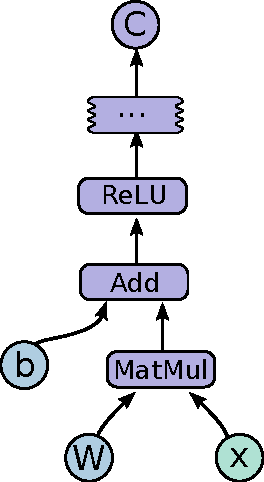
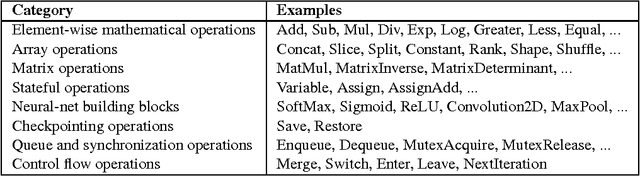
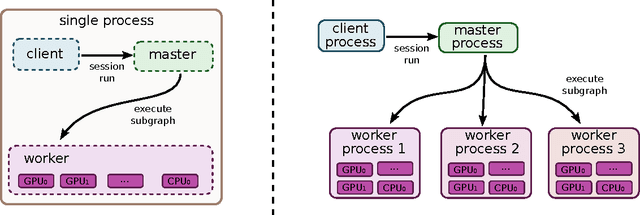
Abstract:TensorFlow is an interface for expressing machine learning algorithms, and an implementation for executing such algorithms. A computation expressed using TensorFlow can be executed with little or no change on a wide variety of heterogeneous systems, ranging from mobile devices such as phones and tablets up to large-scale distributed systems of hundreds of machines and thousands of computational devices such as GPU cards. The system is flexible and can be used to express a wide variety of algorithms, including training and inference algorithms for deep neural network models, and it has been used for conducting research and for deploying machine learning systems into production across more than a dozen areas of computer science and other fields, including speech recognition, computer vision, robotics, information retrieval, natural language processing, geographic information extraction, and computational drug discovery. This paper describes the TensorFlow interface and an implementation of that interface that we have built at Google. The TensorFlow API and a reference implementation were released as an open-source package under the Apache 2.0 license in November, 2015 and are available at www.tensorflow.org.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge