Markus Strohmaier
University of Mannheim, GESIS - Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences, Complexity Science Hub
QSTN: A Modular Framework for Robust Questionnaire Inference with Large Language Models
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:We introduce QSTN, an open-source Python framework for systematically generating responses from questionnaire-style prompts to support in-silico surveys and annotation tasks with large language models (LLMs). QSTN enables robust evaluation of questionnaire presentation, prompt perturbations, and response generation methods. Our extensive evaluation ($>40 $ million survey responses) shows that question structure and response generation methods have a significant impact on the alignment of generated survey responses with human answers, and can be obtained for a fraction of the compute cost. In addition, we offer a no-code user interface that allows researchers to set up robust experiments with LLMs without coding knowledge. We hope that QSTN will support the reproducibility and reliability of LLM-based research in the future.
What Do Temporal Graph Learning Models Learn?
Oct 10, 2025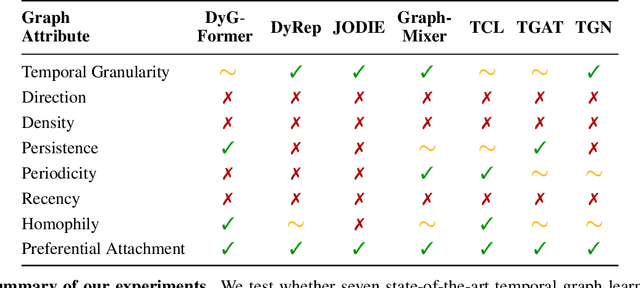
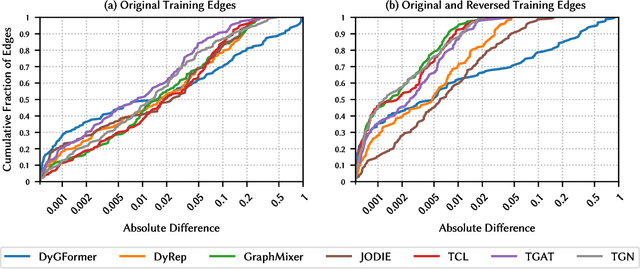
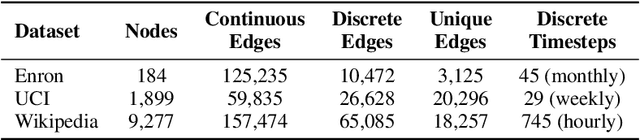
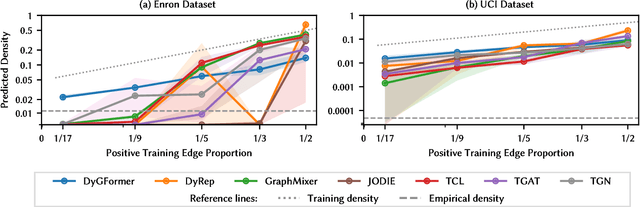
Abstract:Learning on temporal graphs has become a central topic in graph representation learning, with numerous benchmarks indicating the strong performance of state-of-the-art models. However, recent work has raised concerns about the reliability of benchmark results, noting issues with commonly used evaluation protocols and the surprising competitiveness of simple heuristics. This contrast raises the question of which properties of the underlying graphs temporal graph learning models actually use to form their predictions. We address this by systematically evaluating seven models on their ability to capture eight fundamental attributes related to the link structure of temporal graphs. These include structural characteristics such as density, temporal patterns such as recency, and edge formation mechanisms such as homophily. Using both synthetic and real-world datasets, we analyze how well models learn these attributes. Our findings reveal a mixed picture: models capture some attributes well but fail to reproduce others. With this, we expose important limitations. Overall, we believe that our results provide practical insights for the application of temporal graph learning models, and motivate more interpretability-driven evaluations in temporal graph learning research.
Prompt Perturbations Reveal Human-Like Biases in LLM Survey Responses
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used as proxies for human subjects in social science surveys, but their reliability and susceptibility to known response biases are poorly understood. This paper investigates the response robustness of LLMs in normative survey contexts -- we test nine diverse LLMs on questions from the World Values Survey (WVS), applying a comprehensive set of 11 perturbations to both question phrasing and answer option structure, resulting in over 167,000 simulated interviews. In doing so, we not only reveal LLMs' vulnerabilities to perturbations but also reveal that all tested models exhibit a consistent \textit{recency bias} varying in intensity, disproportionately favoring the last-presented answer option. While larger models are generally more robust, all models remain sensitive to semantic variations like paraphrasing and to combined perturbations. By applying a set of perturbations, we reveal that LLMs partially align with survey response biases identified in humans. This underscores the critical importance of prompt design and robustness testing when using LLMs to generate synthetic survey data.
Persona-driven Simulation of Voting Behavior in the European Parliament with Large Language Models
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) display remarkable capabilities to understand or even produce political discourse, but have been found to consistently display a progressive left-leaning bias. At the same time, so-called persona or identity prompts have been shown to produce LLM behavior that aligns with socioeconomic groups that the base model is not aligned with. In this work, we analyze whether zero-shot persona prompting with limited information can accurately predict individual voting decisions and, by aggregation, accurately predict positions of European groups on a diverse set of policies. We evaluate if predictions are stable towards counterfactual arguments, different persona prompts and generation methods. Finally, we find that we can simulate voting behavior of Members of the European Parliament reasonably well with a weighted F1 score of approximately 0.793. Our persona dataset of politicians in the 2024 European Parliament and our code are available at https://github.com/dess-mannheim/european_parliament_simulation.
Local Contrastive Editing of Gender Stereotypes
Oct 23, 2024Abstract:Stereotypical bias encoded in language models (LMs) poses a threat to safe language technology, yet our understanding of how bias manifests in the parameters of LMs remains incomplete. We introduce local contrastive editing that enables the localization and editing of a subset of weights in a target model in relation to a reference model. We deploy this approach to identify and modify subsets of weights that are associated with gender stereotypes in LMs. Through a series of experiments, we demonstrate that local contrastive editing can precisely localize and control a small subset (< 0.5%) of weights that encode gender bias. Our work (i) advances our understanding of how stereotypical biases can manifest in the parameter space of LMs and (ii) opens up new avenues for developing parameter-efficient strategies for controlling model properties in a contrastive manner.
Extracting Affect Aggregates from Longitudinal Social Media Data with Temporal Adapters for Large Language Models
Sep 26, 2024Abstract:This paper proposes temporally aligned Large Language Models (LLMs) as a tool for longitudinal analysis of social media data. We fine-tune Temporal Adapters for Llama 3 8B on full timelines from a panel of British Twitter users, and extract longitudinal aggregates of emotions and attitudes with established questionnaires. We validate our estimates against representative British survey data and find strong positive, significant correlations for several collective emotions. The obtained estimates are robust across multiple training seeds and prompt formulations, and in line with collective emotions extracted using a traditional classification model trained on labeled data. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to extend the analysis of affect in LLMs to a longitudinal setting through Temporal Adapters. Our work enables new approaches towards the longitudinal analysis of social media data.
ReSi: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Representational Similarity Measures
Aug 01, 2024



Abstract:Measuring the similarity of different representations of neural architectures is a fundamental task and an open research challenge for the machine learning community. This paper presents the first comprehensive benchmark for evaluating representational similarity measures based on well-defined groundings of similarity. The representational similarity (ReSi) benchmark consists of (i) six carefully designed tests for similarity measures, (ii) 23 similarity measures, (iii) eleven neural network architectures, and (iv) six datasets, spanning over the graph, language, and vision domains. The benchmark opens up several important avenues of research on representational similarity that enable novel explorations and applications of neural architectures. We demonstrate the utility of the ReSi benchmark by conducting experiments on various neural network architectures, real world datasets and similarity measures. All components of the benchmark are publicly available and thereby facilitate systematic reproduction and production of research results. The benchmark is extensible, future research can build on and further expand it. We believe that the ReSi benchmark can serve as a sound platform catalyzing future research that aims to systematically evaluate existing and explore novel ways of comparing representations of neural architectures.
Recommendation Fairness in Social Networks Over Time
Feb 05, 2024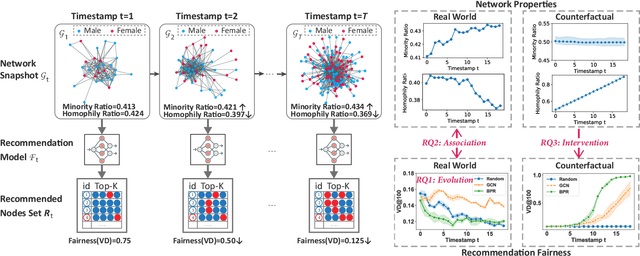
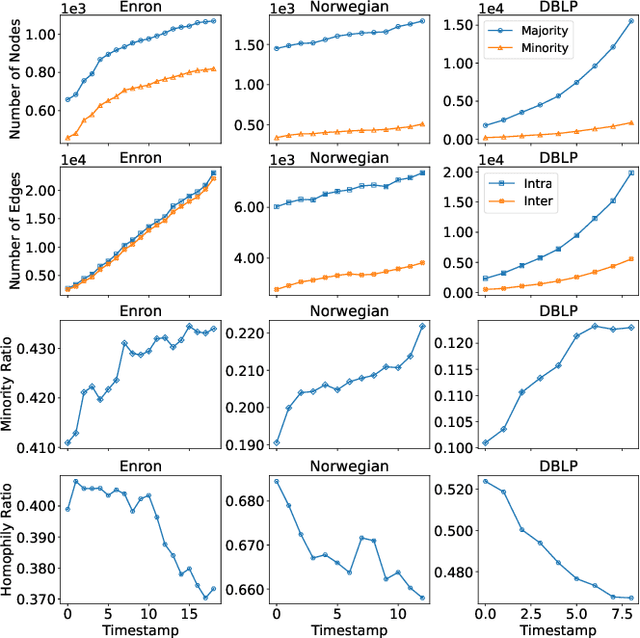
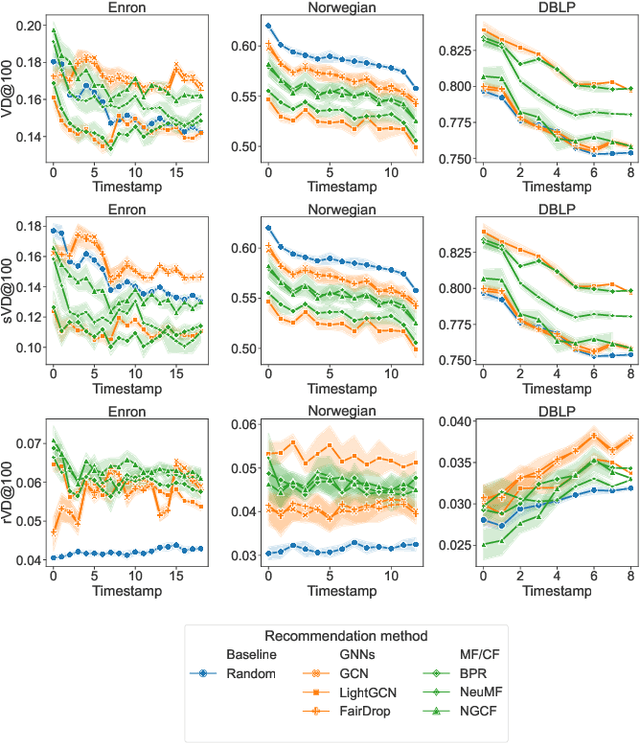
Abstract:In social recommender systems, it is crucial that the recommendation models provide equitable visibility for different demographic groups, such as gender or race. Most existing research has addressed this problem by only studying individual static snapshots of networks that typically change over time. To address this gap, we study the evolution of recommendation fairness over time and its relation to dynamic network properties. We examine three real-world dynamic networks by evaluating the fairness of six recommendation algorithms and analyzing the association between fairness and network properties over time. We further study how interventions on network properties influence fairness by examining counterfactual scenarios with alternative evolution outcomes and differing network properties. Our results on empirical datasets suggest that recommendation fairness improves over time, regardless of the recommendation method. We also find that two network properties, minority ratio, and homophily ratio, exhibit stable correlations with fairness over time. Our counterfactual study further suggests that an extreme homophily ratio potentially contributes to unfair recommendations even with a balanced minority ratio. Our work provides insights into the evolution of fairness within dynamic networks in social science. We believe that our findings will help system operators and policymakers to better comprehend the implications of temporal changes and interventions targeting fairness in social networks.
Similarity of Neural Network Models: A Survey of Functional and Representational Measures
May 10, 2023Abstract:Measuring similarity of neural networks has become an issue of great importance and research interest to understand and utilize differences of neural networks. While there are several perspectives on how neural networks can be similar, we specifically focus on two complementing perspectives, i.e., (i) representational similarity, which considers how activations of intermediate neural layers differ, and (ii) functional similarity, which considers how models differ in their outputs. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive overview of these two families of similarity measures for neural network models. In addition to providing detailed descriptions of existing measures, we summarize and discuss results on the properties and relationships of these measures, and point to open research problems. Further, we provide practical recommendations that can guide researchers as well as practitioners in applying the measures. We hope our work lays a foundation for our community to engage in more systematic research on the properties, nature and applicability of similarity measures for neural network models.
Toxic comments reduce the activity of volunteer editors on Wikipedia
Apr 26, 2023Abstract:Wikipedia is one of the most successful collaborative projects in history. It is the largest encyclopedia ever created, with millions of users worldwide relying on it as the first source of information as well as for fact-checking and in-depth research. As Wikipedia relies solely on the efforts of its volunteer-editors, its success might be particularly affected by toxic speech. In this paper, we analyze all 57 million comments made on user talk pages of 8.5 million editors across the six most active language editions of Wikipedia to study the potential impact of toxicity on editors' behaviour. We find that toxic comments consistently reduce the activity of editors, leading to an estimated loss of 0.5-2 active days per user in the short term. This amounts to multiple human-years of lost productivity when considering the number of active contributors to Wikipedia. The effects of toxic comments are even greater in the long term, as they significantly increase the risk of editors leaving the project altogether. Using an agent-based model, we demonstrate that toxicity attacks on Wikipedia have the potential to impede the progress of the entire project. Our results underscore the importance of mitigating toxic speech on collaborative platforms such as Wikipedia to ensure their continued success.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge