Elisabeth Lex
Modeling Behavioral Patterns in News Recommendations Using Fuzzy Neural Networks
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:News recommender systems are increasingly driven by black-box models, offering little transparency for editorial decision-making. In this work, we introduce a transparent recommender system that uses fuzzy neural networks to learn human-readable rules from behavioral data for predicting article clicks. By extracting the rules at configurable thresholds, we can control rule complexity and thus, the level of interpretability. We evaluate our approach on two publicly available news datasets (i.e., MIND and EB-NeRD) and show that we can accurately predict click behavior compared to several established baselines, while learning human-readable rules. Furthermore, we show that the learned rules reveal news consumption patterns, enabling editors to align content curation goals with target audience behavior.
Differentiable Fuzzy Neural Networks for Recommender Systems
May 09, 2025Abstract:As recommender systems become increasingly complex, transparency is essential to increase user trust, accountability, and regulatory compliance. Neuro-symbolic approaches that integrate symbolic reasoning with sub-symbolic learning offer a promising approach toward transparent and user-centric systems. In this work-in-progress, we investigate using fuzzy neural networks (FNNs) as a neuro-symbolic approach for recommendations that learn logic-based rules over predefined, human-readable atoms. Each rule corresponds to a fuzzy logic expression, making the recommender's decision process inherently transparent. In contrast to black-box machine learning methods, our approach reveals the reasoning behind a recommendation while maintaining competitive performance. We evaluate our method on a synthetic and MovieLens 1M datasets and compare it to state-of-the-art recommendation algorithms. Our results demonstrate that our approach accurately captures user behavior while providing a transparent decision-making process. Finally, the differentiable nature of this approach facilitates an integration with other neural models, enabling the development of hybrid, transparent recommender systems.
Hybrid Personalization Using Declarative and Procedural Memory Modules of the Cognitive Architecture ACT-R
May 08, 2025Abstract:Recommender systems often rely on sub-symbolic machine learning approaches that operate as opaque black boxes. These approaches typically fail to account for the cognitive processes that shape user preferences and decision-making. In this vision paper, we propose a hybrid user modeling framework based on the cognitive architecture ACT-R that integrates symbolic and sub-symbolic representations of human memory. Our goal is to combine ACT-R's declarative memory, which is responsible for storing symbolic chunks along sub-symbolic activations, with its procedural memory, which contains symbolic production rules. This integration will help simulate how users retrieve past experiences and apply decision-making strategies. With this approach, we aim to provide more transparent recommendations, enable rule-based explanations, and facilitate the modeling of cognitive biases. We argue that our approach has the potential to inform the design of a new generation of human-centered, psychology-informed recommender systems.
OnSET: Ontology and Semantic Exploration Toolkit
Apr 11, 2025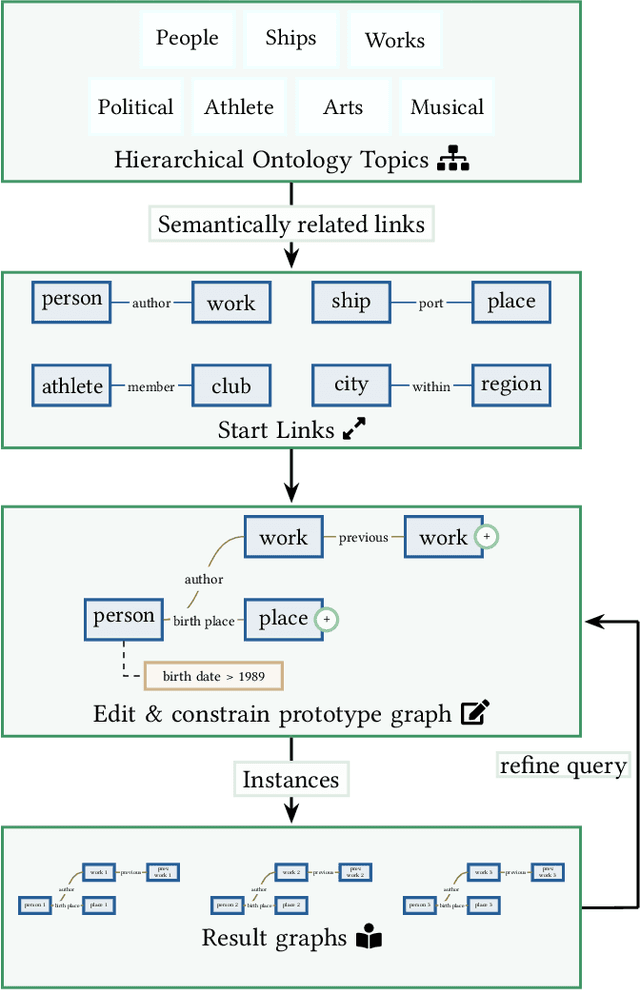
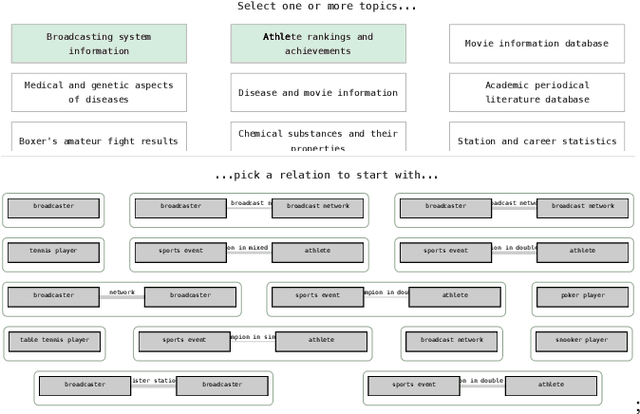
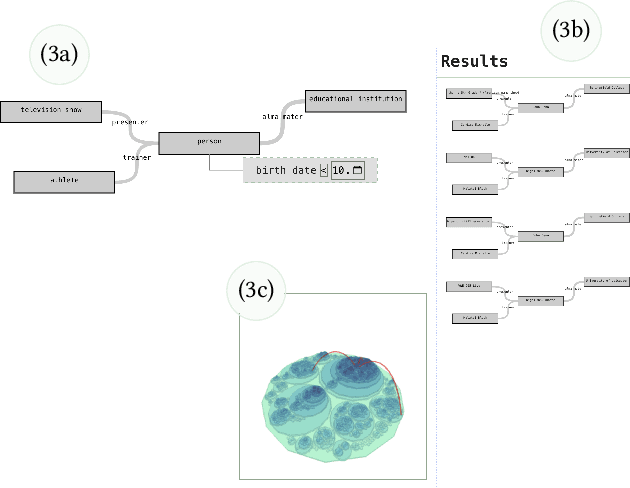
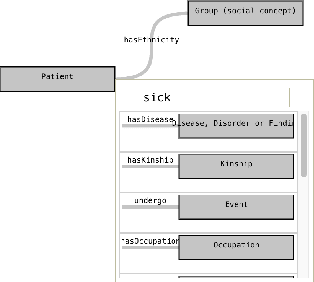
Abstract:Retrieval over knowledge graphs is usually performed using dedicated, complex query languages like SPARQL. We propose a novel system, Ontology and Semantic Exploration Toolkit (OnSET) that allows non-expert users to easily build queries with visual user guidance provided by topic modelling and semantic search throughout the application. OnSET allows users without any prior information about the ontology or networked knowledge to start exploring topics of interest over knowledge graphs, including the retrieval and detailed exploration of prototypical sub-graphs and their instances. Existing systems either focus on direct graph explorations or do not foster further exploration of the result set. We, however, provide a node-based editor that can extend on these missing properties of existing systems to support the search over big ontologies with sub-graph instances. Furthermore, OnSET combines efficient and open platforms to deploy the system on commodity hardware.
Making Alice Appear Like Bob: A Probabilistic Preference Obfuscation Method For Implicit Feedback Recommendation Models
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Users' interaction or preference data used in recommender systems carry the risk of unintentionally revealing users' private attributes (e.g., gender or race). This risk becomes particularly concerning when the training data contains user preferences that can be used to infer these attributes, especially if they align with common stereotypes. This major privacy issue allows malicious attackers or other third parties to infer users' protected attributes. Previous efforts to address this issue have added or removed parts of users' preferences prior to or during model training to improve privacy, which often leads to decreases in recommendation accuracy. In this work, we introduce SBO, a novel probabilistic obfuscation method for user preference data designed to improve the accuracy--privacy trade-off for such recommendation scenarios. We apply SBO to three state-of-the-art recommendation models (i.e., BPR, MultVAE, and LightGCN) and two popular datasets (i.e., MovieLens-1M and LFM-2B). Our experiments reveal that SBO outperforms comparable approaches with respect to the accuracy--privacy trade-off. Specifically, we can reduce the leakage of users' protected attributes while maintaining on-par recommendation accuracy.
Framing Analysis of Health-Related Narratives: Conspiracy versus Mainstream Media
Jan 18, 2024Abstract:Understanding how online media frame issues is crucial due to their impact on public opinion. Research on framing using natural language processing techniques mainly focuses on specific content features in messages and neglects their narrative elements. Also, the distinction between framing in different sources remains an understudied problem. We address those issues and investigate how the framing of health-related topics, such as COVID-19 and other diseases, differs between conspiracy and mainstream websites. We incorporate narrative information into the framing analysis by introducing a novel frame extraction approach based on semantic graphs. We find that health-related narratives in conspiracy media are predominantly framed in terms of beliefs, while mainstream media tend to present them in terms of science. We hope our work offers new ways for a more nuanced frame analysis.
The Impact of Differential Privacy on Recommendation Accuracy and Popularity Bias
Jan 15, 2024



Abstract:Collaborative filtering-based recommender systems leverage vast amounts of behavioral user data, which poses severe privacy risks. Thus, often, random noise is added to the data to ensure Differential Privacy (DP). However, to date, it is not well understood, in which ways this impacts personalized recommendations. In this work, we study how DP impacts recommendation accuracy and popularity bias, when applied to the training data of state-of-the-art recommendation models. Our findings are three-fold: First, we find that nearly all users' recommendations change when DP is applied. Second, recommendation accuracy drops substantially while recommended item popularity experiences a sharp increase, suggesting that popularity bias worsens. Third, we find that DP exacerbates popularity bias more severely for users who prefer unpopular items than for users that prefer popular items.
FrameFinder: Explorative Multi-Perspective Framing Extraction from News Headlines
Dec 14, 2023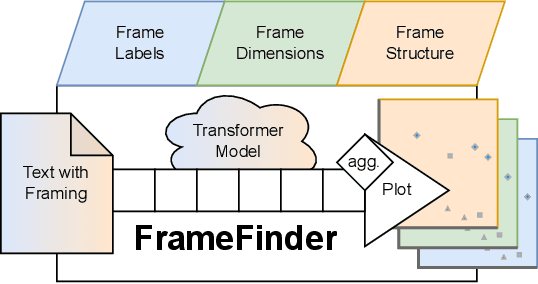
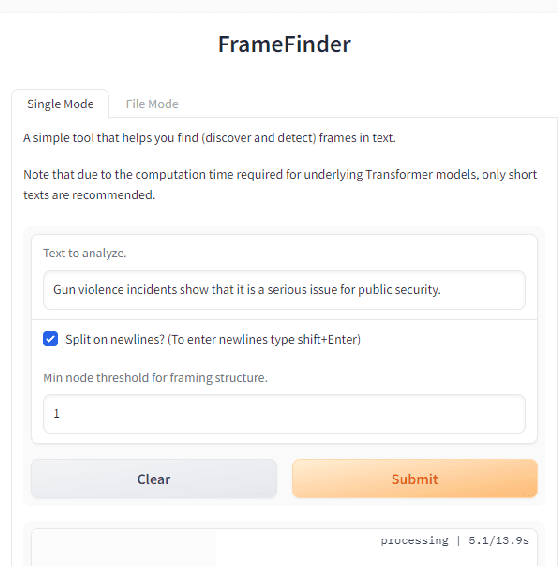
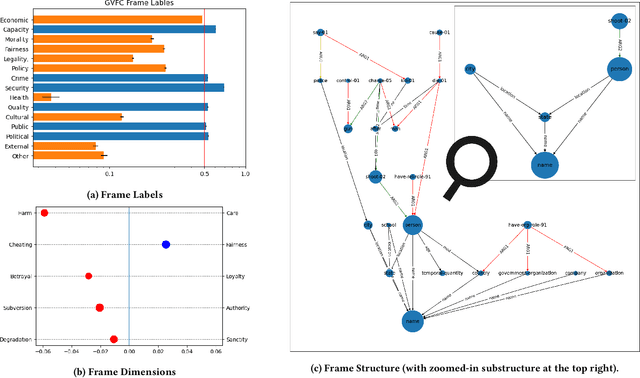
Abstract:Revealing the framing of news articles is an important yet neglected task in information seeking and retrieval. In the present work, we present FrameFinder, an open tool for extracting and analyzing frames in textual data. FrameFinder visually represents the frames of text from three perspectives, i.e., (i) frame labels, (ii) frame dimensions, and (iii) frame structure. By analyzing the well-established gun violence frame corpus, we demonstrate the merits of our proposed solution to support social science research and call for subsequent integration into information interactions.
* Accepted for publication at CHIIR'24
Beyond-Accuracy: A Review on Diversity, Serendipity and Fairness in Recommender Systems Based on Graph Neural Networks
Oct 03, 2023

Abstract:By providing personalized suggestions to users, recommender systems have become essential to numerous online platforms. Collaborative filtering, particularly graph-based approaches using Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), have demonstrated great results in terms of recommendation accuracy. However, accuracy may not always be the most important criterion for evaluating recommender systems' performance, since beyond-accuracy aspects such as recommendation diversity, serendipity, and fairness can strongly influence user engagement and satisfaction. This review paper focuses on addressing these dimensions in GNN-based recommender systems, going beyond the conventional accuracy-centric perspective. We begin by reviewing recent developments in approaches that improve not only the accuracy-diversity trade-off but also promote serendipity and fairness in GNN-based recommender systems. We discuss different stages of model development including data preprocessing, graph construction, embedding initialization, propagation layers, embedding fusion, score computation, and training methodologies. Furthermore, we present a look into the practical difficulties encountered in assuring diversity, serendipity, and fairness, while retaining high accuracy. Finally, we discuss potential future research directions for developing more robust GNN-based recommender systems that go beyond the unidimensional perspective of focusing solely on accuracy. This review aims to provide researchers and practitioners with an in-depth understanding of the multifaceted issues that arise when designing GNN-based recommender systems, setting our work apart by offering a comprehensive exploration of beyond-accuracy dimensions.
mCPT at SemEval-2023 Task 3: Multilingual Label-Aware Contrastive Pre-Training of Transformers for Few- and Zero-shot Framing Detection
Mar 17, 2023Abstract:This paper presents the winning system for the zero-shot Spanish framing detection task, which also achieves competitive places in eight additional languages. The challenge of the framing detection task lies in identifying a set of 14 frames when only a few or zero samples are available, i.e., a multilingual multi-label few- or zero-shot setting. Our developed solution employs a pre-training procedure based on multilingual Transformers using a label-aware contrastive loss function. In addition to describing the system, we perform an embedding space analysis and ablation study to demonstrate how our pre-training procedure supports framing detection to advance computational framing analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge