Lukas Gosch
Exact Certification of (Graph) Neural Networks Against Label Poisoning
Nov 30, 2024



Abstract:Machine learning models are highly vulnerable to label flipping, i.e., the adversarial modification (poisoning) of training labels to compromise performance. Thus, deriving robustness certificates is important to guarantee that test predictions remain unaffected and to understand worst-case robustness behavior. However, for Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), the problem of certifying label flipping has so far been unsolved. We change this by introducing an exact certification method, deriving both sample-wise and collective certificates. Our method leverages the Neural Tangent Kernel (NTK) to capture the training dynamics of wide networks enabling us to reformulate the bilevel optimization problem representing label flipping into a Mixed-Integer Linear Program (MILP). We apply our method to certify a broad range of GNN architectures in node classification tasks. Thereby, concerning the worst-case robustness to label flipping: $(i)$ we establish hierarchies of GNNs on different benchmark graphs; $(ii)$ quantify the effect of architectural choices such as activations, depth and skip-connections; and surprisingly, $(iii)$ uncover a novel phenomenon of the robustness plateauing for intermediate perturbation budgets across all investigated datasets and architectures. While we focus on GNNs, our certificates are applicable to sufficiently wide NNs in general through their NTK. Thus, our work presents the first exact certificate to a poisoning attack ever derived for neural networks, which could be of independent interest.
Relaxing Graph Transformers for Adversarial Attacks
Jul 16, 2024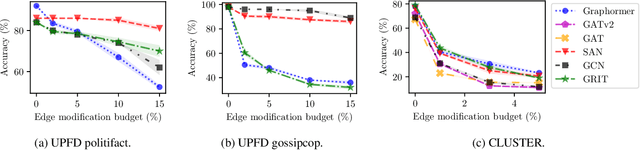
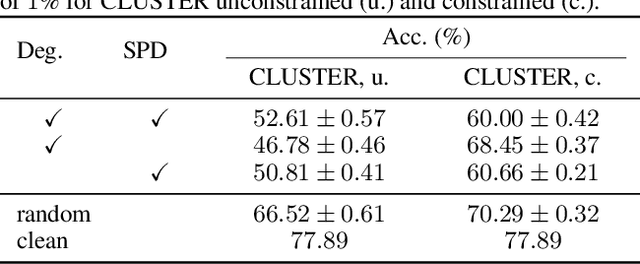
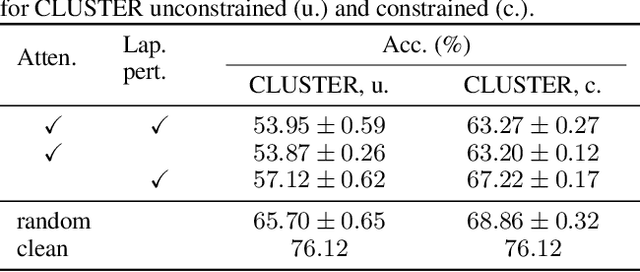
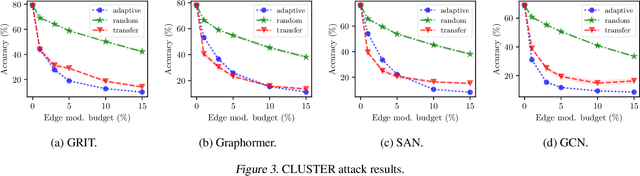
Abstract:Existing studies have shown that Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are vulnerable to adversarial attacks. Even though Graph Transformers (GTs) surpassed Message-Passing GNNs on several benchmarks, their adversarial robustness properties are unexplored. However, attacking GTs is challenging due to their Positional Encodings (PEs) and special attention mechanisms which can be difficult to differentiate. We overcome these challenges by targeting three representative architectures based on (1) random-walk PEs, (2) pair-wise-shortest-path PEs, and (3) spectral PEs - and propose the first adaptive attacks for GTs. We leverage our attacks to evaluate robustness to (a) structure perturbations on node classification; and (b) node injection attacks for (fake-news) graph classification. Our evaluation reveals that they can be catastrophically fragile and underlines our work's importance and the necessity for adaptive attacks.
Provable Robustness of (Graph) Neural Networks Against Data Poisoning and Backdoor Attacks
Jul 15, 2024
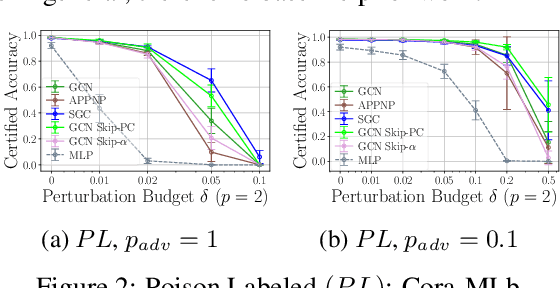
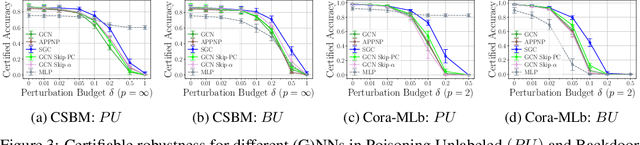
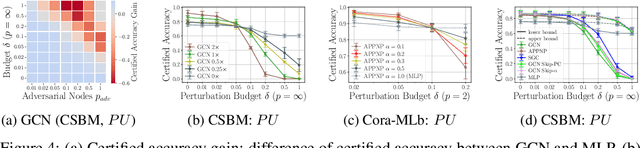
Abstract:Generalization of machine learning models can be severely compromised by data poisoning, where adversarial changes are applied to the training data, as well as backdoor attacks that additionally manipulate the test data. These vulnerabilities have led to interest in certifying (i.e., proving) that such changes up to a certain magnitude do not affect test predictions. We, for the first time, certify Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) against poisoning and backdoor attacks targeting the node features of a given graph. Our certificates are white-box and based upon $(i)$ the neural tangent kernel, which characterizes the training dynamics of sufficiently wide networks; and $(ii)$ a novel reformulation of the bilevel optimization problem describing poisoning as a mixed-integer linear program. Consequently, we leverage our framework to provide fundamental insights into the role of graph structure and its connectivity on the worst-case robustness behavior of convolution-based and PageRank-based GNNs. We note that our framework is more general and constitutes the first approach to derive white-box poisoning certificates for NNs, which can be of independent interest beyond graph-related tasks.
Assessing Robustness via Score-Based Adversarial Image Generation
Oct 06, 2023

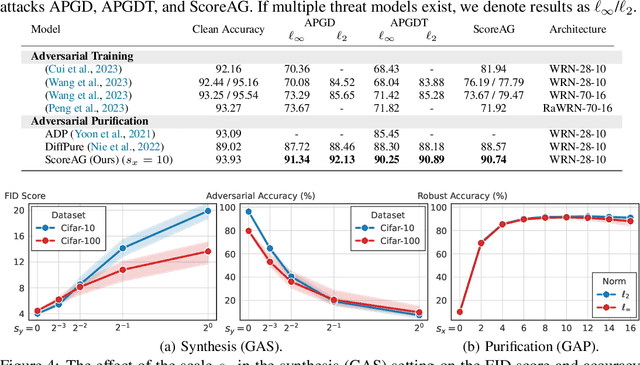
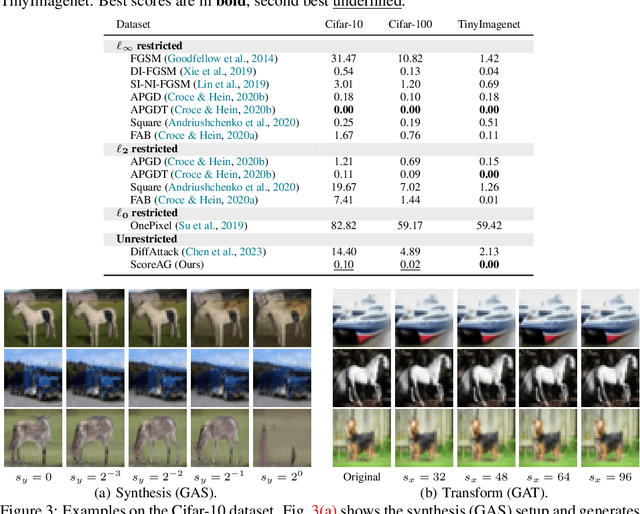
Abstract:Most adversarial attacks and defenses focus on perturbations within small $\ell_p$-norm constraints. However, $\ell_p$ threat models cannot capture all relevant semantic-preserving perturbations, and hence, the scope of robustness evaluations is limited. In this work, we introduce Score-Based Adversarial Generation (ScoreAG), a novel framework that leverages the advancements in score-based generative models to generate adversarial examples beyond $\ell_p$-norm constraints, so-called unrestricted adversarial examples, overcoming their limitations. Unlike traditional methods, ScoreAG maintains the core semantics of images while generating realistic adversarial examples, either by transforming existing images or synthesizing new ones entirely from scratch. We further exploit the generative capability of ScoreAG to purify images, empirically enhancing the robustness of classifiers. Our extensive empirical evaluation demonstrates that ScoreAG matches the performance of state-of-the-art attacks and defenses across multiple benchmarks. This work highlights the importance of investigating adversarial examples bounded by semantics rather than $\ell_p$-norm constraints. ScoreAG represents an important step towards more encompassing robustness assessments.
Expressivity of Graph Neural Networks Through the Lens of Adversarial Robustness
Aug 16, 2023
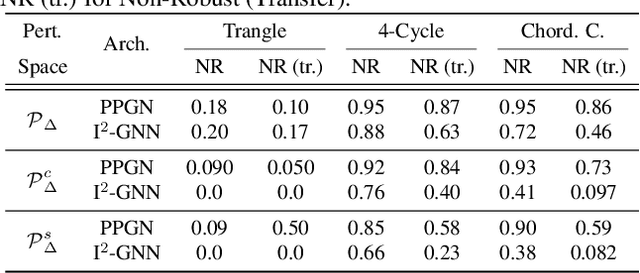
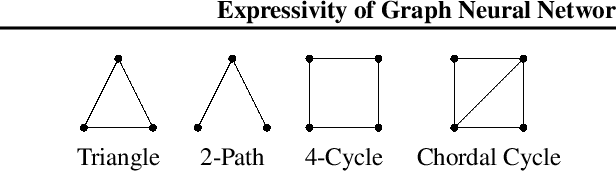
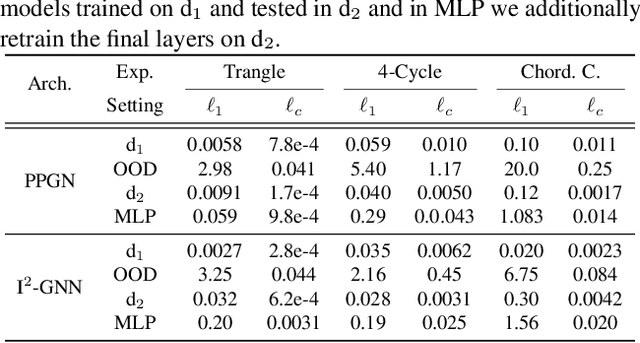
Abstract:We perform the first adversarial robustness study into Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) that are provably more powerful than traditional Message Passing Neural Networks (MPNNs). In particular, we use adversarial robustness as a tool to uncover a significant gap between their theoretically possible and empirically achieved expressive power. To do so, we focus on the ability of GNNs to count specific subgraph patterns, which is an established measure of expressivity, and extend the concept of adversarial robustness to this task. Based on this, we develop efficient adversarial attacks for subgraph counting and show that more powerful GNNs fail to generalize even to small perturbations to the graph's structure. Expanding on this, we show that such architectures also fail to count substructures on out-of-distribution graphs.
Adversarial Training for Graph Neural Networks
Jun 27, 2023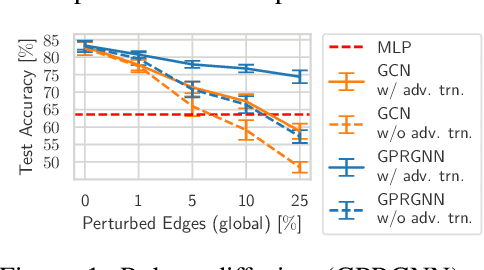
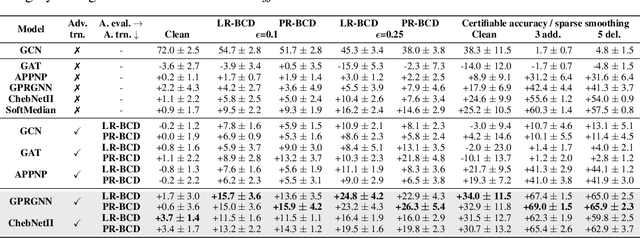
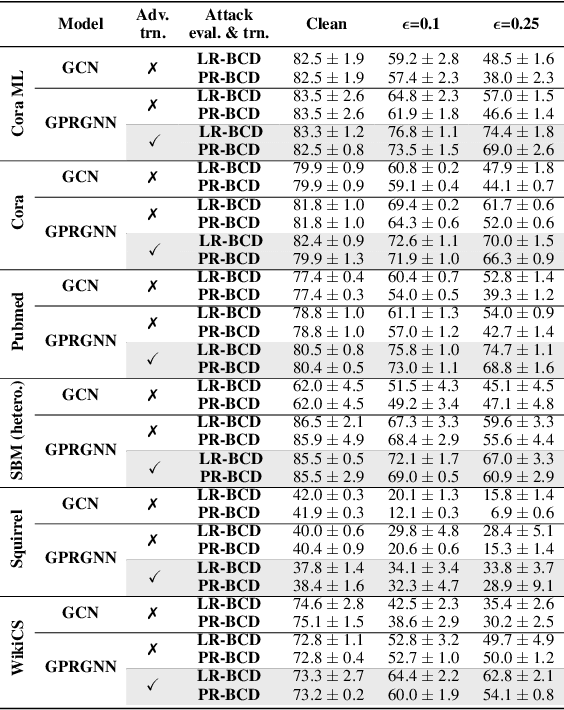
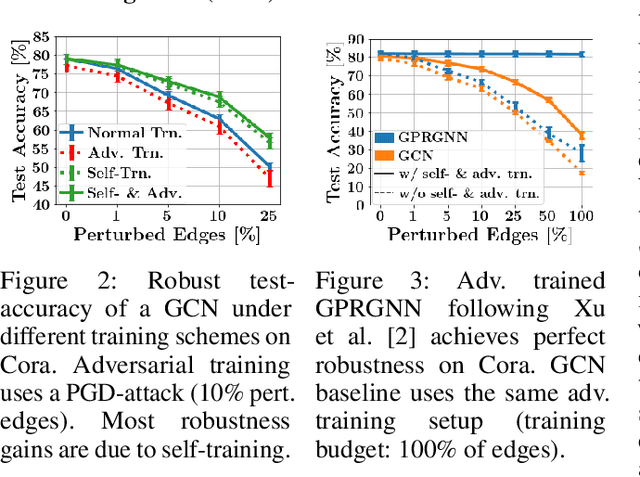
Abstract:Despite its success in the image domain, adversarial training does not (yet) stand out as an effective defense for Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) against graph structure perturbations. In the pursuit of fixing adversarial training (1) we show and overcome fundamental theoretical as well as practical limitations of the adopted graph learning setting in prior work; (2) we reveal that more flexible GNNs based on learnable graph diffusion are able to adjust to adversarial perturbations, while the learned message passing scheme is naturally interpretable; (3) we introduce the first attack for structure perturbations that, while targeting multiple nodes at once, is capable of handling global (graph-level) as well as local (node-level) constraints. Including these contributions, we demonstrate that adversarial training is a state-of-the-art defense against adversarial structure perturbations.
Revisiting Robustness in Graph Machine Learning
May 02, 2023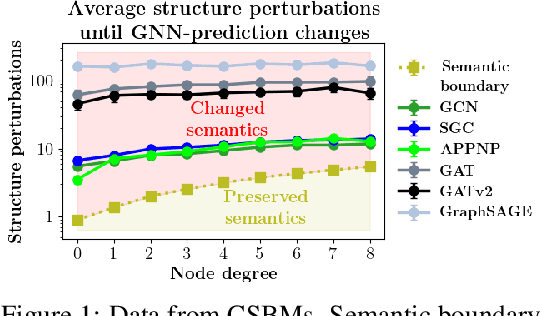
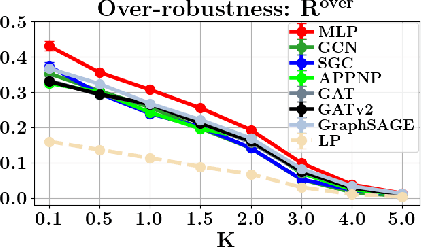
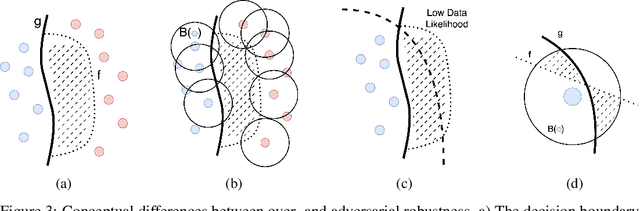

Abstract:Many works show that node-level predictions of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are unrobust to small, often termed adversarial, changes to the graph structure. However, because manual inspection of a graph is difficult, it is unclear if the studied perturbations always preserve a core assumption of adversarial examples: that of unchanged semantic content. To address this problem, we introduce a more principled notion of an adversarial graph, which is aware of semantic content change. Using Contextual Stochastic Block Models (CSBMs) and real-world graphs, our results uncover: $i)$ for a majority of nodes the prevalent perturbation models include a large fraction of perturbed graphs violating the unchanged semantics assumption; $ii)$ surprisingly, all assessed GNNs show over-robustness - that is robustness beyond the point of semantic change. We find this to be a complementary phenomenon to adversarial examples and show that including the label-structure of the training graph into the inference process of GNNs significantly reduces over-robustness, while having a positive effect on test accuracy and adversarial robustness. Theoretically, leveraging our new semantics-aware notion of robustness, we prove that there is no robustness-accuracy tradeoff for inductively classifying a newly added node.
Training Differentially Private Graph Neural Networks with Random Walk Sampling
Jan 02, 2023Abstract:Deep learning models are known to put the privacy of their training data at risk, which poses challenges for their safe and ethical release to the public. Differentially private stochastic gradient descent is the de facto standard for training neural networks without leaking sensitive information about the training data. However, applying it to models for graph-structured data poses a novel challenge: unlike with i.i.d. data, sensitive information about a node in a graph cannot only leak through its gradients, but also through the gradients of all nodes within a larger neighborhood. In practice, this limits privacy-preserving deep learning on graphs to very shallow graph neural networks. We propose to solve this issue by training graph neural networks on disjoint subgraphs of a given training graph. We develop three random-walk-based methods for generating such disjoint subgraphs and perform a careful analysis of the data-generating distributions to provide strong privacy guarantees. Through extensive experiments, we show that our method greatly outperforms the state-of-the-art baseline on three large graphs, and matches or outperforms it on four smaller ones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge