Lucas C. Cordeiro
GPT, But Backwards: Exactly Inverting Language Model Outputs
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:While existing auditing techniques attempt to identify potential unwanted behaviours in large language models (LLMs), we address the complementary forensic problem of reconstructing the exact input that led to an existing LLM output - enabling post-incident analysis and potentially the detection of fake output reports. We formalize exact input reconstruction as a discrete optimisation problem with a unique global minimum and introduce SODA, an efficient gradient-based algorithm that operates on a continuous relaxation of the input search space with periodic restarts and parameter decay. Through comprehensive experiments on LLMs ranging in size from 33M to 3B parameters, we demonstrate that SODA significantly outperforms existing approaches. We succeed in fully recovering 79.5% of shorter out-of-distribution inputs from next-token logits, without a single false positive, but struggle to extract private information from the outputs of longer (15+ token) input sequences. This suggests that standard deployment practices may currently provide adequate protection against malicious use of our method. Our code is available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15539879.
Vulnerability Detection: From Formal Verification to Large Language Models and Hybrid Approaches: A Comprehensive Overview
Mar 13, 2025


Abstract:Software testing and verification are critical for ensuring the reliability and security of modern software systems. Traditionally, formal verification techniques, such as model checking and theorem proving, have provided rigorous frameworks for detecting bugs and vulnerabilities. However, these methods often face scalability challenges when applied to complex, real-world programs. Recently, the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has introduced a new paradigm for software analysis, leveraging their ability to understand insecure coding practices. Although LLMs demonstrate promising capabilities in tasks such as bug prediction and invariant generation, they lack the formal guarantees of classical methods. This paper presents a comprehensive study of state-of-the-art software testing and verification, focusing on three key approaches: classical formal methods, LLM-based analysis, and emerging hybrid techniques, which combine their strengths. We explore each approach's strengths, limitations, and practical applications, highlighting the potential of hybrid systems to address the weaknesses of standalone methods. We analyze whether integrating formal rigor with LLM-driven insights can enhance the effectiveness and scalability of software verification, exploring their viability as a pathway toward more robust and adaptive testing frameworks.
CASTLE: Benchmarking Dataset for Static Code Analyzers and LLMs towards CWE Detection
Mar 12, 2025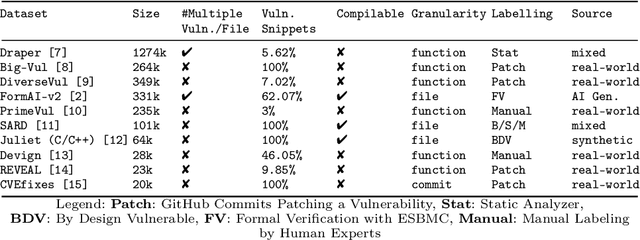
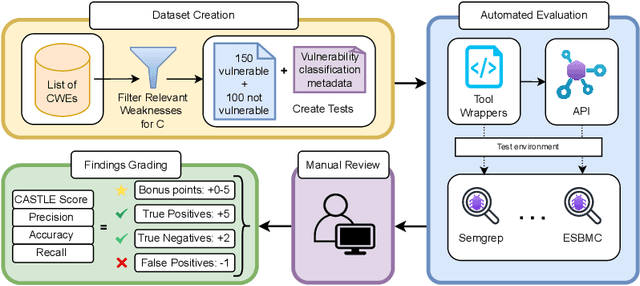
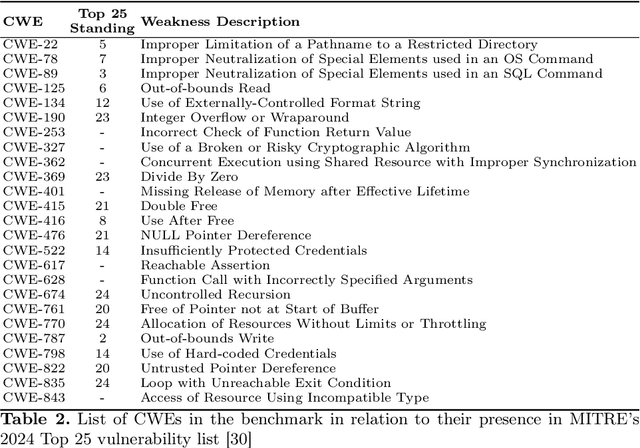
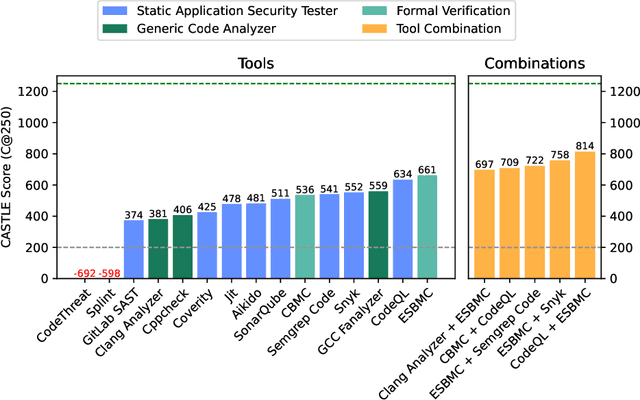
Abstract:Identifying vulnerabilities in source code is crucial, especially in critical software components. Existing methods such as static analysis, dynamic analysis, formal verification, and recently Large Language Models are widely used to detect security flaws. This paper introduces CASTLE (CWE Automated Security Testing and Low-Level Evaluation), a benchmarking framework for evaluating the vulnerability detection capabilities of different methods. We assess 13 static analysis tools, 10 LLMs, and 2 formal verification tools using a hand-crafted dataset of 250 micro-benchmark programs covering 25 common CWEs. We propose the CASTLE Score, a novel evaluation metric to ensure fair comparison. Our results reveal key differences: ESBMC (a formal verification tool) minimizes false positives but struggles with vulnerabilities beyond model checking, such as weak cryptography or SQL injection. Static analyzers suffer from high false positives, increasing manual validation efforts for developers. LLMs perform exceptionally well in the CASTLE dataset when identifying vulnerabilities in small code snippets. However, their accuracy declines, and hallucinations increase as the code size grows. These results suggest that LLMs could play a pivotal role in future security solutions, particularly within code completion frameworks, where they can provide real-time guidance to prevent vulnerabilities. The dataset is accessible at https://github.com/CASTLE-Benchmark.
Neural Network Verification is a Programming Language Challenge
Jan 10, 2025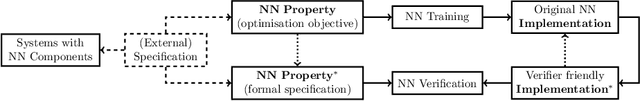
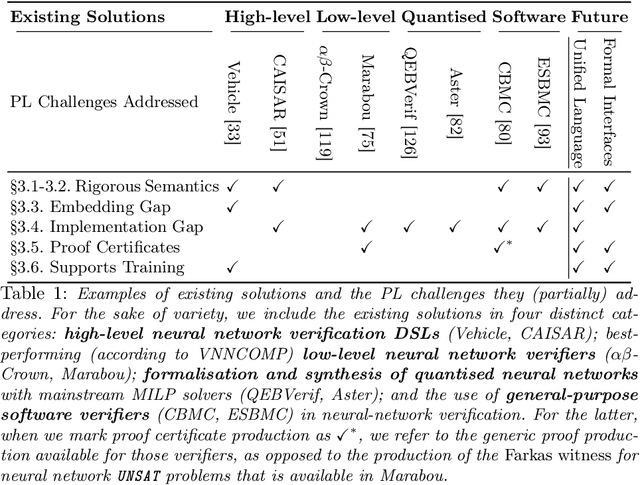
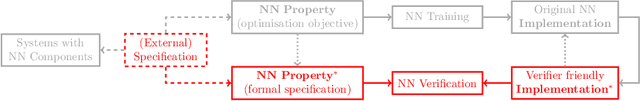

Abstract:Neural network verification is a new and rapidly developing field of research. So far, the main priority has been establishing efficient verification algorithms and tools, while proper support from the programming language perspective has been considered secondary or unimportant. Yet, there is mounting evidence that insights from the programming language community may make a difference in the future development of this domain. In this paper, we formulate neural network verification challenges as programming language challenges and suggest possible future solutions.
* Accepted at ESOP 2025, European Symposium on Programming Languages
Dynamic Intelligence Assessment: Benchmarking LLMs on the Road to AGI with a Focus on Model Confidence
Oct 20, 2024



Abstract:As machine intelligence evolves, the need to test and compare the problem-solving abilities of different AI models grows. However, current benchmarks are often overly simplistic, allowing models to perform uniformly well, making it difficult to distinguish their capabilities. Additionally, benchmarks typically rely on static question-answer pairs, which models might memorize or guess. To address these limitations, we introduce the Dynamic Intelligence Assessment (DIA), a novel methodology for testing AI models using dynamic question templates and improved metrics across multiple disciplines such as mathematics, cryptography, cybersecurity, and computer science. The accompanying DIA-Bench dataset, which includes 150 diverse and challenging task templates with mutable parameters, is presented in various formats such as text, PDFs, compiled binaries, and visual puzzles. Our framework introduces four new metrics to assess a model's reliability and confidence across multiple attempts. These metrics revealed that even simple questions are frequently answered incorrectly when posed in varying forms, highlighting significant gaps in models' reliability. Notably, models like GPT-4o tended to overestimate their mathematical abilities, while ChatGPT-4o demonstrated better decision-making and performance through effective tool usage. We evaluated eight state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) using DIA-Bench, showing that current models struggle with complex tasks and often display unexpectedly low confidence, even with simpler questions. The DIA framework sets a new standard for assessing not only problem-solving but also a model's adaptive intelligence and ability to assess its own limitations. The dataset is publicly available on our project's website.
Synthetic Data Aided Federated Learning Using Foundation Models
Jul 06, 2024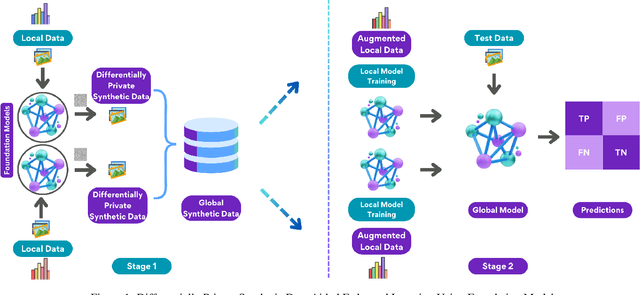
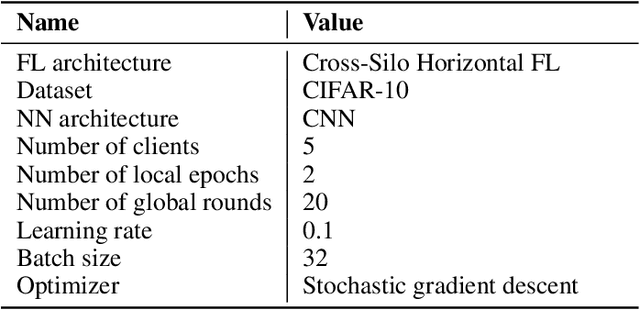
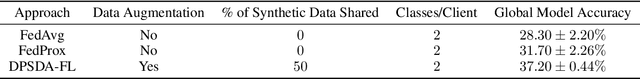
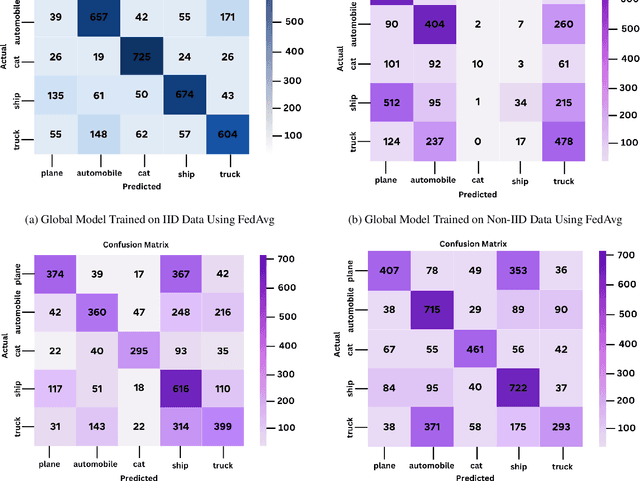
Abstract:In heterogeneous scenarios where the data distribution amongst the Federated Learning (FL) participants is Non-Independent and Identically distributed (Non-IID), FL suffers from the well known problem of data heterogeneity. This leads the performance of FL to be significantly degraded, as the global model tends to struggle to converge. To solve this problem, we propose Differentially Private Synthetic Data Aided Federated Learning Using Foundation Models (DPSDA-FL), a novel data augmentation strategy that aids in homogenizing the local data present on the clients' side. DPSDA-FL improves the training of the local models by leveraging differentially private synthetic data generated from foundation models. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach by evaluating it on the benchmark image dataset: CIFAR-10. Our experimental results have shown that DPSDA-FL can improve class recall and classification accuracy of the global model by up to 26% and 9%, respectively, in FL with Non-IID issues.
Automated Repair of AI Code with Large Language Models and Formal Verification
May 14, 2024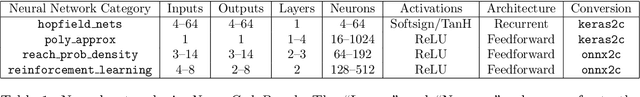

Abstract:The next generation of AI systems requires strong safety guarantees. This report looks at the software implementation of neural networks and related memory safety properties, including NULL pointer deference, out-of-bound access, double-free, and memory leaks. Our goal is to detect these vulnerabilities, and automatically repair them with the help of large language models. To this end, we first expand the size of NeuroCodeBench, an existing dataset of neural network code, to about 81k programs via an automated process of program mutation. Then, we verify the memory safety of the mutated neural network implementations with ESBMC, a state-of-the-art software verifier. Whenever ESBMC spots a vulnerability, we invoke a large language model to repair the source code. For the latest task, we compare the performance of various state-of-the-art prompt engineering techniques, and an iterative approach that repeatedly calls the large language model.
Do Neutral Prompts Produce Insecure Code? FormAI-v2 Dataset: Labelling Vulnerabilities in Code Generated by Large Language Models
Apr 29, 2024Abstract:This study provides a comparative analysis of state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs), analyzing how likely they generate vulnerabilities when writing simple C programs using a neutral zero-shot prompt. We address a significant gap in the literature concerning the security properties of code produced by these models without specific directives. N. Tihanyi et al. introduced the FormAI dataset at PROMISE '23, containing 112,000 GPT-3.5-generated C programs, with over 51.24% identified as vulnerable. We expand that work by introducing the FormAI-v2 dataset comprising 265,000 compilable C programs generated using various LLMs, including robust models such as Google's GEMINI-pro, OpenAI's GPT-4, and TII's 180 billion-parameter Falcon, to Meta's specialized 13 billion-parameter CodeLLama2 and various other compact models. Each program in the dataset is labelled based on the vulnerabilities detected in its source code through formal verification using the Efficient SMT-based Context-Bounded Model Checker (ESBMC). This technique eliminates false positives by delivering a counterexample and ensures the exclusion of false negatives by completing the verification process. Our study reveals that at least 63.47% of the generated programs are vulnerable. The differences between the models are minor, as they all display similar coding errors with slight variations. Our research highlights that while LLMs offer promising capabilities for code generation, deploying their output in a production environment requires risk assessment and validation.
Tasks People Prompt: A Taxonomy of LLM Downstream Tasks in Software Verification and Falsification Approaches
Apr 14, 2024Abstract:Prompting has become one of the main approaches to leverage emergent capabilities of Large Language Models [Brown et al. NeurIPS 2020, Wei et al. TMLR 2022, Wei et al. NeurIPS 2022]. During the last year, researchers and practitioners have been playing with prompts to see how to make the most of LLMs. By homogeneously dissecting 80 papers, we investigate in deep how software testing and verification research communities have been abstractly architecting their LLM-enabled solutions. More precisely, first, we want to validate whether downstream tasks are an adequate concept to convey the blueprint of prompt-based solutions. We also aim at identifying number and nature of such tasks in solutions. For such goal, we develop a novel downstream task taxonomy that enables pinpointing some engineering patterns in a rather varied spectrum of Software Engineering problems that encompasses testing, fuzzing, debugging, vulnerability detection, static analysis and program verification approaches.
NeuroCodeBench: a plain C neural network benchmark for software verification
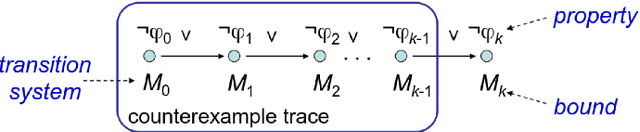
Sep 07, 2023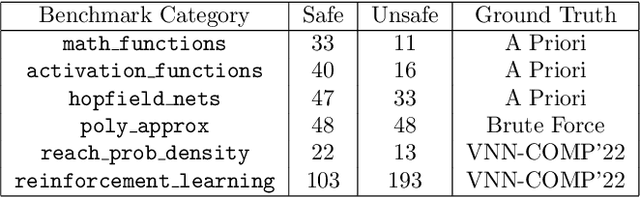
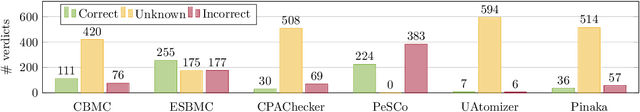
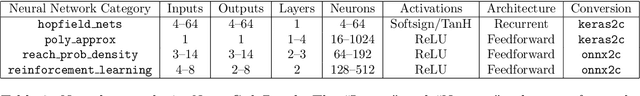
Abstract:Safety-critical systems with neural network components require strong guarantees. While existing neural network verification techniques have shown great progress towards this goal, they cannot prove the absence of software faults in the network implementation. This paper presents NeuroCodeBench - a verification benchmark for neural network code written in plain C. It contains 32 neural networks with 607 safety properties divided into 6 categories: maths library, activation functions, error-correcting networks, transfer function approximation, probability density estimation and reinforcement learning. Our preliminary evaluation shows that state-of-the-art software verifiers struggle to provide correct verdicts, due to their incomplete support of the standard C mathematical library and the complexity of larger neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge