Ryan Marinelli
Responsible Development of Offensive AI
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:As AI advances, broader consensus is needed to determine research priorities. This endeavor discusses offensive AI and provides guidance by leveraging Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and interpretability techniques. The objective is to more effectively establish priorities that balance societal benefits against risks. The two forms of offensive AI evaluated in this study are vulnerability detection agents, which solve Capture- The-Flag challenges, and AI-powered malware.
Harnessing Chain-of-Thought Metadata for Task Routing and Adversarial Prompt Detection
Mar 27, 2025

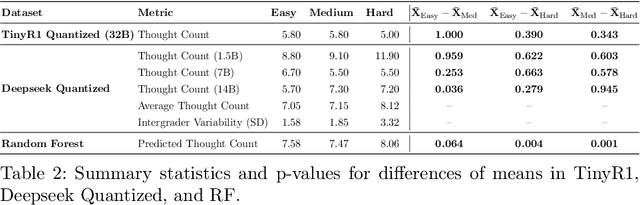

Abstract:In this work, we propose a metric called Number of Thoughts (NofT) to determine the difficulty of tasks pre-prompting and support Large Language Models (LLMs) in production contexts. By setting thresholds based on the number of thoughts, this metric can discern the difficulty of prompts and support more effective prompt routing. A 2% decrease in latency is achieved when routing prompts from the MathInstruct dataset through quantized, distilled versions of Deepseek with 1.7 billion, 7 billion, and 14 billion parameters. Moreover, this metric can be used to detect adversarial prompts used in prompt injection attacks with high efficacy. The Number of Thoughts can inform a classifier that achieves 95% accuracy in adversarial prompt detection. Our experiments ad datasets used are available on our GitHub page: https://github.com/rymarinelli/Number_Of_Thoughts/tree/main.
Dynamic Intelligence Assessment: Benchmarking LLMs on the Road to AGI with a Focus on Model Confidence
Oct 20, 2024



Abstract:As machine intelligence evolves, the need to test and compare the problem-solving abilities of different AI models grows. However, current benchmarks are often overly simplistic, allowing models to perform uniformly well, making it difficult to distinguish their capabilities. Additionally, benchmarks typically rely on static question-answer pairs, which models might memorize or guess. To address these limitations, we introduce the Dynamic Intelligence Assessment (DIA), a novel methodology for testing AI models using dynamic question templates and improved metrics across multiple disciplines such as mathematics, cryptography, cybersecurity, and computer science. The accompanying DIA-Bench dataset, which includes 150 diverse and challenging task templates with mutable parameters, is presented in various formats such as text, PDFs, compiled binaries, and visual puzzles. Our framework introduces four new metrics to assess a model's reliability and confidence across multiple attempts. These metrics revealed that even simple questions are frequently answered incorrectly when posed in varying forms, highlighting significant gaps in models' reliability. Notably, models like GPT-4o tended to overestimate their mathematical abilities, while ChatGPT-4o demonstrated better decision-making and performance through effective tool usage. We evaluated eight state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) using DIA-Bench, showing that current models struggle with complex tasks and often display unexpectedly low confidence, even with simpler questions. The DIA framework sets a new standard for assessing not only problem-solving but also a model's adaptive intelligence and ability to assess its own limitations. The dataset is publicly available on our project's website.
Analysis of Deep Learning Architectures and Efficacy of Detecting Forest Fires
Dec 08, 2022Abstract:The aim of this research is to review the state of computer vision as applied to combatting forest fires. My motivation to research this topic comes from the urgency with which new participants and stakeholders require guidance in this field. One of these new stakeholder groups are practitioners of machine learning that lack domain expertise. Introducing these new entrants to domain specific datasets and methods is critical to supporting this aim as general computer vision datasets are insufficient to support specialized research initiatives. The overarching aim of the research is to introduce datasets and methods to make them more accessible to the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge