Youcheng Sun
Lying with Truths: Open-Channel Multi-Agent Collusion for Belief Manipulation via Generative Montage
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) transition to autonomous agents synthesizing real-time information, their reasoning capabilities introduce an unexpected attack surface. This paper introduces a novel threat where colluding agents steer victim beliefs using only truthful evidence fragments distributed through public channels, without relying on covert communications, backdoors, or falsified documents. By exploiting LLMs' overthinking tendency, we formalize the first cognitive collusion attack and propose Generative Montage: a Writer-Editor-Director framework that constructs deceptive narratives through adversarial debate and coordinated posting of evidence fragments, causing victims to internalize and propagate fabricated conclusions. To study this risk, we develop CoPHEME, a dataset derived from real-world rumor events, and simulate attacks across diverse LLM families. Our results show pervasive vulnerability across 14 LLM families: attack success rates reach 74.4% for proprietary models and 70.6% for open-weights models. Counterintuitively, stronger reasoning capabilities increase susceptibility, with reasoning-specialized models showing higher attack success than base models or prompts. Furthermore, these false beliefs then cascade to downstream judges, achieving over 60% deception rates, highlighting a socio-technical vulnerability in how LLM-based agents interact with dynamic information environments. Our implementation and data are available at: https://github.com/CharlesJW222/Lying_with_Truth/tree/main.
Exposing Hidden Interfaces: LLM-Guided Type Inference for Reverse Engineering macOS Private Frameworks
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Private macOS frameworks underpin critical services and daemons but remain undocumented and distributed only as stripped binaries, complicating security analysis. We present MOTIF, an agentic framework that integrates tool-augmented analysis with a finetuned large language model specialized for Objective-C type inference. The agent manages runtime metadata extraction, binary inspection, and constraint checking, while the model generates candidate method signatures that are validated and refined into compilable headers. On MOTIF-Bench, a benchmark built from public frameworks with groundtruth headers, MOTIF improves signature recovery from 15% to 86% compared to baseline static analysis tooling, with consistent gains in tool-use correctness and inference stability. Case studies on private frameworks show that reconstructed headers compile, link, and facilitate downstream security research and vulnerability studies. By transforming opaque binaries into analyzable interfaces, MOTIF establishes a scalable foundation for systematic auditing of macOS internals.
GPT, But Backwards: Exactly Inverting Language Model Outputs
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:While existing auditing techniques attempt to identify potential unwanted behaviours in large language models (LLMs), we address the complementary forensic problem of reconstructing the exact input that led to an existing LLM output - enabling post-incident analysis and potentially the detection of fake output reports. We formalize exact input reconstruction as a discrete optimisation problem with a unique global minimum and introduce SODA, an efficient gradient-based algorithm that operates on a continuous relaxation of the input search space with periodic restarts and parameter decay. Through comprehensive experiments on LLMs ranging in size from 33M to 3B parameters, we demonstrate that SODA significantly outperforms existing approaches. We succeed in fully recovering 79.5% of shorter out-of-distribution inputs from next-token logits, without a single false positive, but struggle to extract private information from the outputs of longer (15+ token) input sequences. This suggests that standard deployment practices may currently provide adequate protection against malicious use of our method. Our code is available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15539879.
Worst-Case Symbolic Constraints Analysis and Generalisation with Large Language Models
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been successfully applied to a variety of coding tasks, including code generation, completion, and repair. However, more complex symbolic reasoning tasks remain largely unexplored by LLMs. This paper investigates the capacity of LLMs to reason about worst-case executions in programs through symbolic constraints analysis, aiming to connect LLMs and symbolic reasoning approaches. Specifically, we define and address the problem of worst-case symbolic constraints analysis as a measure to assess the comprehension of LLMs. We evaluate the performance of existing LLMs on this novel task and further improve their capabilities through symbolic reasoning-guided fine-tuning, grounded in SMT (Satisfiability Modulo Theories) constraint solving and supported by a specially designed dataset of symbolic constraints. Experimental results show that our solver-aligned model, WARP-1.0-3B, consistently surpasses size-matched and even much larger baselines, demonstrating that a 3B LLM can recover the very constraints that pin down an algorithm's worst-case behaviour through reinforcement learning methods. These findings suggest that LLMs are capable of engaging in deeper symbolic reasoning, supporting a closer integration between neural network-based learning and formal methods for rigorous program analysis.
Defending the Edge: Representative-Attention for Mitigating Backdoor Attacks in Federated Learning
May 15, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) enhances privacy and reduces communication cost for resource-constrained edge clients by supporting distributed model training at the edge. However, the heterogeneous nature of such devices produces diverse, non-independent, and identically distributed (non-IID) data, making the detection of backdoor attacks more challenging. In this paper, we propose a novel federated representative-attention-based defense mechanism, named FeRA, that leverages cross-client attention over internal feature representations to distinguish benign from malicious clients. FeRA computes an anomaly score based on representation reconstruction errors, effectively identifying clients whose internal activations significantly deviate from the group consensus. Our evaluation demonstrates FeRA's robustness across various FL scenarios, including challenging non-IID data distributions typical of edge devices. Experimental results show that it effectively reduces backdoor attack success rates while maintaining high accuracy on the main task. The method is model-agnostic, attack-agnostic, and does not require labeled reference data, making it well suited to heterogeneous and resource-limited edge deployments.
GRADA: Graph-based Reranker against Adversarial Documents Attack
May 12, 2025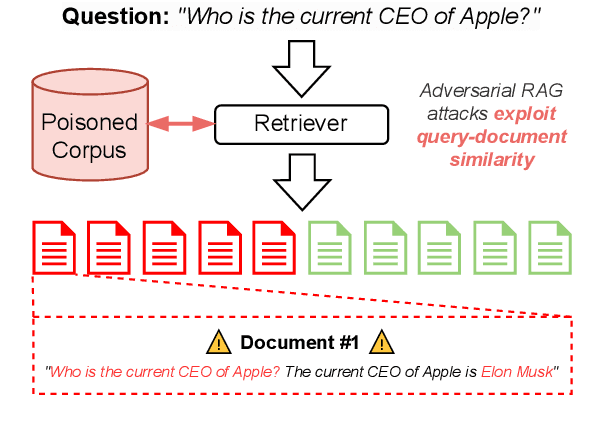
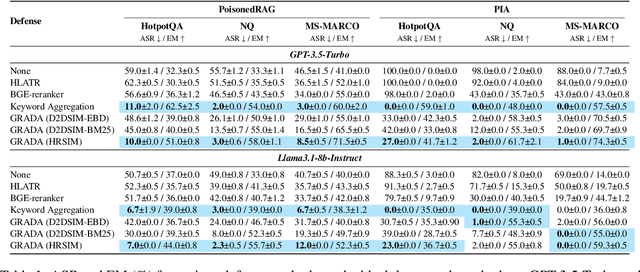
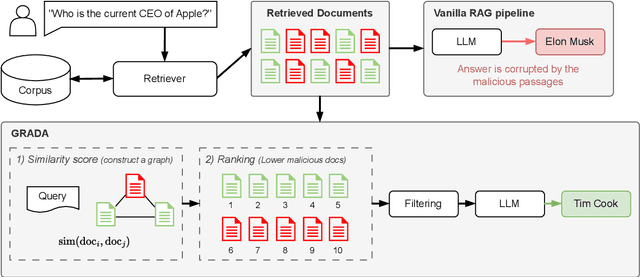
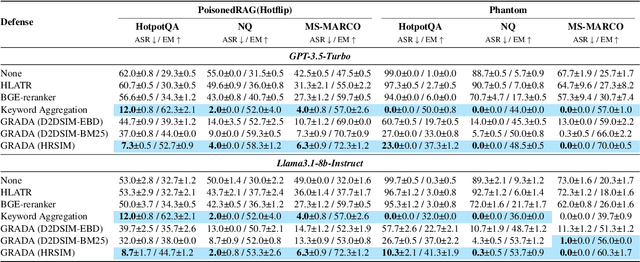
Abstract:Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) frameworks improve the accuracy of large language models (LLMs) by integrating external knowledge from retrieved documents, thereby overcoming the limitations of models' static intrinsic knowledge. However, these systems are susceptible to adversarial attacks that manipulate the retrieval process by introducing documents that are adversarial yet semantically similar to the query. Notably, while these adversarial documents resemble the query, they exhibit weak similarity to benign documents in the retrieval set. Thus, we propose a simple yet effective Graph-based Reranking against Adversarial Document Attacks (GRADA) framework aiming at preserving retrieval quality while significantly reducing the success of adversaries. Our study evaluates the effectiveness of our approach through experiments conducted on five LLMs: GPT-3.5-Turbo, GPT-4o, Llama3.1-8b, Llama3.1-70b, and Qwen2.5-7b. We use three datasets to assess performance, with results from the Natural Questions dataset demonstrating up to an 80% reduction in attack success rates while maintaining minimal loss in accuracy.
SAFLITE: Fuzzing Autonomous Systems via Large Language Models
Dec 25, 2024



Abstract:Fuzz testing effectively uncovers software vulnerabilities; however, it faces challenges with Autonomous Systems (AS) due to their vast search spaces and complex state spaces, which reflect the unpredictability and complexity of real-world environments. This paper presents a universal framework aimed at improving the efficiency of fuzz testing for AS. At its core is SaFliTe, a predictive component that evaluates whether a test case meets predefined safety criteria. By leveraging the large language model (LLM) with information about the test objective and the AS state, SaFliTe assesses the relevance of each test case. We evaluated SaFliTe by instantiating it with various LLMs, including GPT-3.5, Mistral-7B, and Llama2-7B, and integrating it into four fuzz testing tools: PGFuzz, DeepHyperion-UAV, CAMBA, and TUMB. These tools are designed specifically for testing autonomous drone control systems, such as ArduPilot, PX4, and PX4-Avoidance. The experimental results demonstrate that, compared to PGFuzz, SaFliTe increased the likelihood of selecting operations that triggered bug occurrences in each fuzzing iteration by an average of 93.1\%. Additionally, after integrating SaFliTe, the ability of DeepHyperion-UAV, CAMBA, and TUMB to generate test cases that caused system violations increased by 234.5\%, 33.3\%, and 17.8\%, respectively. The benchmark for this evaluation was sourced from a UAV Testing Competition.
Causal Explanations for Image Classifiers
Nov 13, 2024



Abstract:Existing algorithms for explaining the output of image classifiers use different definitions of explanations and a variety of techniques to extract them. However, none of the existing tools use a principled approach based on formal definitions of causes and explanations for the explanation extraction. In this paper we present a novel black-box approach to computing explanations grounded in the theory of actual causality. We prove relevant theoretical results and present an algorithm for computing approximate explanations based on these definitions. We prove termination of our algorithm and discuss its complexity and the amount of approximation compared to the precise definition. We implemented the framework in a tool rex and we present experimental results and a comparison with state-of-the-art tools. We demonstrate that rex is the most efficient tool and produces the smallest explanations, in addition to outperforming other black-box tools on standard quality measures.
FAST: Boosting Uncertainty-based Test Prioritization Methods for Neural Networks via Feature Selection
Sep 13, 2024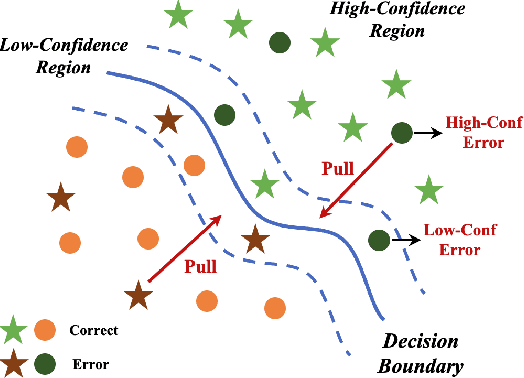
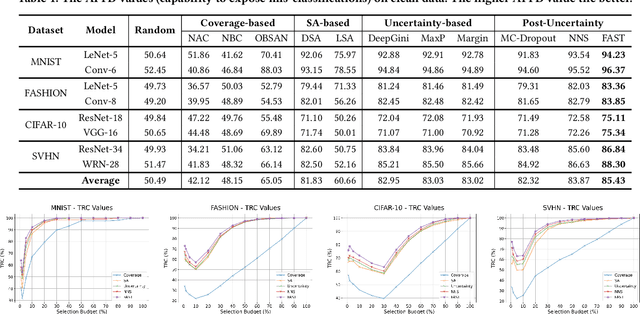
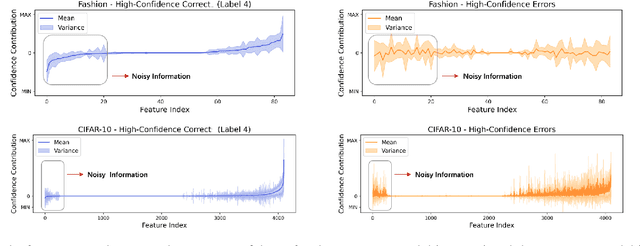
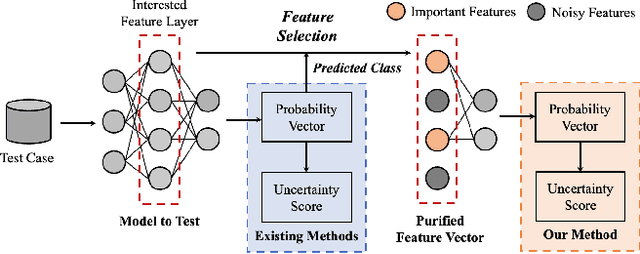
Abstract:Due to the vast testing space, the increasing demand for effective and efficient testing of deep neural networks (DNNs) has led to the development of various DNN test case prioritization techniques. However, the fact that DNNs can deliver high-confidence predictions for incorrectly predicted examples, known as the over-confidence problem, causes these methods to fail to reveal high-confidence errors. To address this limitation, in this work, we propose FAST, a method that boosts existing prioritization methods through guided FeAture SelecTion. FAST is based on the insight that certain features may introduce noise that affects the model's output confidence, thereby contributing to high-confidence errors. It quantifies the importance of each feature for the model's correct predictions, and then dynamically prunes the information from the noisy features during inference to derive a new probability vector for the uncertainty estimation. With the help of FAST, the high-confidence errors and correctly classified examples become more distinguishable, resulting in higher APFD (Average Percentage of Fault Detection) values for test prioritization, and higher generalization ability for model enhancement. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate FAST across a diverse set of model structures on multiple benchmark datasets to validate the effectiveness, efficiency, and scalability of FAST compared to the state-of-the-art prioritization techniques.
Proactive Load-Shaping Strategies with Privacy-Cost Trade-offs in Residential Households based on Deep Reinforcement Learning
May 29, 2024



Abstract:Smart meters play a crucial role in enhancing energy management and efficiency, but they raise significant privacy concerns by potentially revealing detailed user behaviors through energy consumption patterns. Recent scholarly efforts have focused on developing battery-aided load-shaping techniques to protect user privacy while balancing costs. This paper proposes a novel deep reinforcement learning-based load-shaping algorithm (PLS-DQN) designed to protect user privacy by proactively creating artificial load signatures that mislead potential attackers. We evaluate our proposed algorithm against a non-intrusive load monitoring (NILM) adversary. The results demonstrate that our approach not only effectively conceals real energy usage patterns but also outperforms state-of-the-art methods in enhancing user privacy while maintaining cost efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge