Does Knowledge Graph Really Matter for Recommender Systems?
Paper and Code
Apr 04, 2024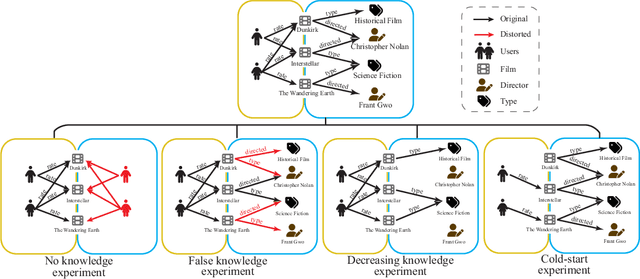
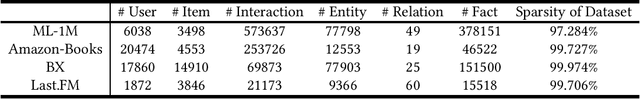
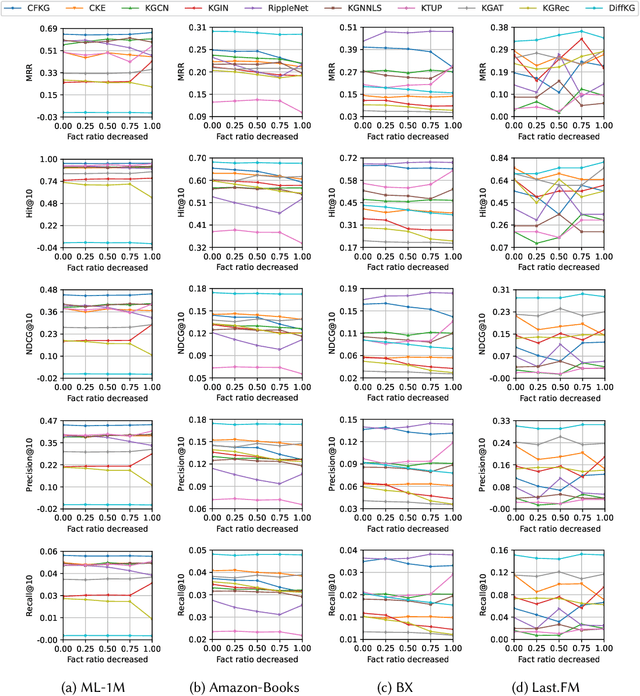
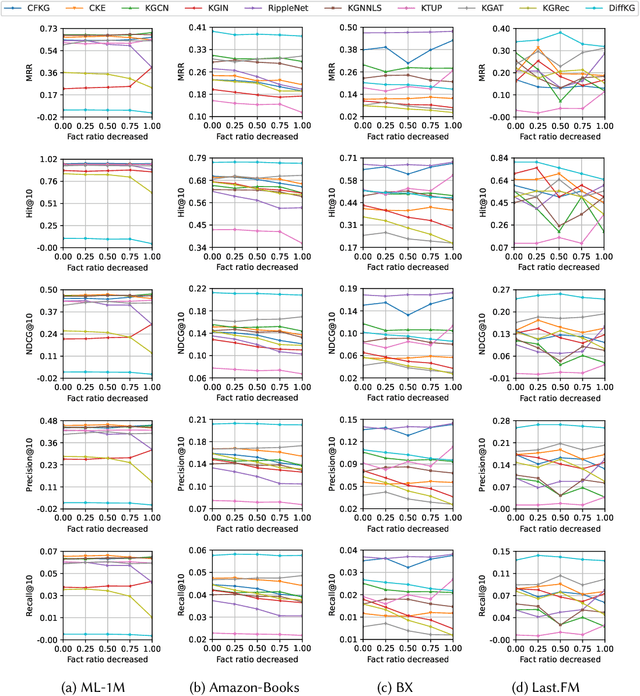
Recommender systems (RSs) are designed to provide personalized recommendations to users. Recently, knowledge graphs (KGs) have been widely introduced in RSs to improve recommendation accuracy. In this study, however, we demonstrate that RSs do not necessarily perform worse even if the KG is downgraded to the user-item interaction graph only (or removed). We propose an evaluation framework KG4RecEval to systematically evaluate how much a KG contributes to the recommendation accuracy of a KG-based RS, using our defined metric KGER (KG utilization efficiency in recommendation). We consider the scenarios where knowledge in a KG gets completely removed, randomly distorted and decreased, and also where recommendations are for cold-start users. Our extensive experiments on four commonly used datasets and a number of state-of-the-art KG-based RSs reveal that: to remove, randomly distort or decrease knowledge does not necessarily decrease recommendation accuracy, even for cold-start users. These findings inspire us to rethink how to better utilize knowledge from existing KGs, whereby we discuss and provide insights into what characteristics of datasets and KG-based RSs may help improve KG utilization efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge