Lipeng He
Understanding and Preserving Safety in Fine-Tuned LLMs
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Fine-tuning is an essential and pervasive functionality for applying large language models (LLMs) to downstream tasks. However, it has the potential to substantially degrade safety alignment, e.g., by greatly increasing susceptibility to jailbreak attacks, even when the fine-tuning data is entirely harmless. Despite garnering growing attention in defense efforts during the fine-tuning stage, existing methods struggle with a persistent safety-utility dilemma: emphasizing safety compromises task performance, whereas prioritizing utility typically requires deep fine-tuning that inevitably leads to steep safety declination. In this work, we address this dilemma by shedding new light on the geometric interaction between safety- and utility-oriented gradients in safety-aligned LLMs. Through systematic empirical analysis, we uncover three key insights: (I) safety gradients lie in a low-rank subspace, while utility gradients span a broader high-dimensional space; (II) these subspaces are often negatively correlated, causing directional conflicts during fine-tuning; and (III) the dominant safety direction can be efficiently estimated from a single sample. Building upon these novel insights, we propose safety-preserving fine-tuning (SPF), a lightweight approach that explicitly removes gradient components conflicting with the low-rank safety subspace. Theoretically, we show that SPF guarantees utility convergence while bounding safety drift. Empirically, SPF consistently maintains downstream task performance and recovers nearly all pre-trained safety alignment, even under adversarial fine-tuning scenarios. Furthermore, SPF exhibits robust resistance to both deep fine-tuning and dynamic jailbreak attacks. Together, our findings provide new mechanistic understanding and practical guidance toward always-aligned LLM fine-tuning.
Safety at One Shot: Patching Fine-Tuned LLMs with A Single Instance
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Fine-tuning safety-aligned large language models (LLMs) can substantially compromise their safety. Previous approaches require many safety samples or calibration sets, which not only incur significant computational overhead during realignment but also lead to noticeable degradation in model utility. Contrary to this belief, we show that safety alignment can be fully recovered with only a single safety example, without sacrificing utility and at minimal cost. Remarkably, this recovery is effective regardless of the number of harmful examples used in fine-tuning or the size of the underlying model, and convergence is achieved within just a few epochs. Furthermore, we uncover the low-rank structure of the safety gradient, which explains why such efficient correction is possible. We validate our findings across five safety-aligned LLMs and multiple datasets, demonstrating the generality of our approach.
StructEval: Benchmarking LLMs' Capabilities to Generate Structural Outputs
May 26, 2025
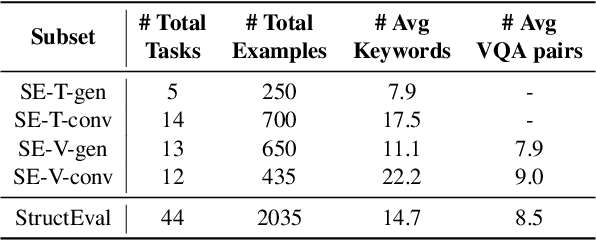

Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) become integral to software development workflows, their ability to generate structured outputs has become critically important. We introduce StructEval, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LLMs' capabilities in producing both non-renderable (JSON, YAML, CSV) and renderable (HTML, React, SVG) structured formats. Unlike prior benchmarks, StructEval systematically evaluates structural fidelity across diverse formats through two paradigms: 1) generation tasks, producing structured output from natural language prompts, and 2) conversion tasks, translating between structured formats. Our benchmark encompasses 18 formats and 44 types of task, with novel metrics for format adherence and structural correctness. Results reveal significant performance gaps, even state-of-the-art models like o1-mini achieve only 75.58 average score, with open-source alternatives lagging approximately 10 points behind. We find generation tasks more challenging than conversion tasks, and producing correct visual content more difficult than generating text-only structures.
Activation Approximations Can Incur Safety Vulnerabilities Even in Aligned LLMs: Comprehensive Analysis and Defense
Feb 02, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have showcased remarkable capabilities across various domains. Accompanying the evolving capabilities and expanding deployment scenarios of LLMs, their deployment challenges escalate due to their sheer scale and the advanced yet complex activation designs prevalent in notable model series, such as Llama, Gemma, and Mistral. These challenges have become particularly pronounced in resource-constrained deployment scenarios, where mitigating inference efficiency bottlenecks is imperative. Among various recent efforts, activation approximation has emerged as a promising avenue for pursuing inference efficiency, sometimes considered indispensable in applications such as private inference. Despite achieving substantial speedups with minimal impact on utility, even appearing sound and practical for real-world deployment, the safety implications of activation approximations remain unclear. In this work, we fill this critical gap in LLM safety by conducting the first systematic safety evaluation of activation approximations. Our safety vetting spans seven sota techniques across three popular categories, revealing consistent safety degradation across ten safety-aligned LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge