Sherman Siu
StructEval: Benchmarking LLMs' Capabilities to Generate Structural Outputs
May 26, 2025
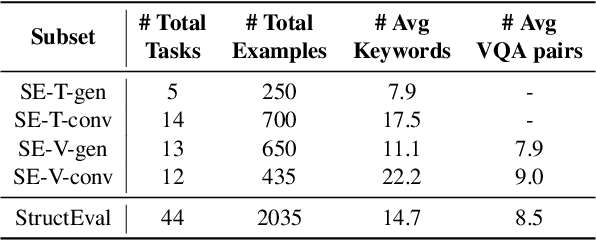
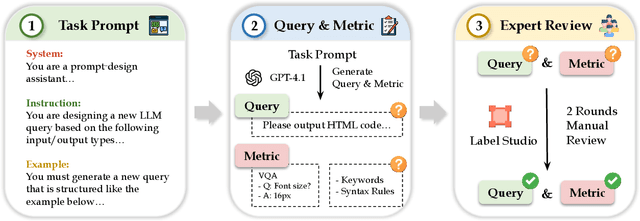

Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) become integral to software development workflows, their ability to generate structured outputs has become critically important. We introduce StructEval, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LLMs' capabilities in producing both non-renderable (JSON, YAML, CSV) and renderable (HTML, React, SVG) structured formats. Unlike prior benchmarks, StructEval systematically evaluates structural fidelity across diverse formats through two paradigms: 1) generation tasks, producing structured output from natural language prompts, and 2) conversion tasks, translating between structured formats. Our benchmark encompasses 18 formats and 44 types of task, with novel metrics for format adherence and structural correctness. Results reveal significant performance gaps, even state-of-the-art models like o1-mini achieve only 75.58 average score, with open-source alternatives lagging approximately 10 points behind. We find generation tasks more challenging than conversion tasks, and producing correct visual content more difficult than generating text-only structures.
MEGA-Bench: Scaling Multimodal Evaluation to over 500 Real-World Tasks
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:We present MEGA-Bench, an evaluation suite that scales multimodal evaluation to over 500 real-world tasks, to address the highly heterogeneous daily use cases of end users. Our objective is to optimize for a set of high-quality data samples that cover a highly diverse and rich set of multimodal tasks, while enabling cost-effective and accurate model evaluation. In particular, we collected 505 realistic tasks encompassing over 8,000 samples from 16 expert annotators to extensively cover the multimodal task space. Instead of unifying these problems into standard multi-choice questions (like MMMU, MMBench, and MMT-Bench), we embrace a wide range of output formats like numbers, phrases, code, \LaTeX, coordinates, JSON, free-form, etc. To accommodate these formats, we developed over 40 metrics to evaluate these tasks. Unlike existing benchmarks, MEGA-Bench offers a fine-grained capability report across multiple dimensions (e.g., application, input type, output format, skill), allowing users to interact with and visualize model capabilities in depth. We evaluate a wide variety of frontier vision-language models on MEGA-Bench to understand their capabilities across these dimensions.
VideoScore: Building Automatic Metrics to Simulate Fine-grained Human Feedback for Video Generation
Jun 24, 2024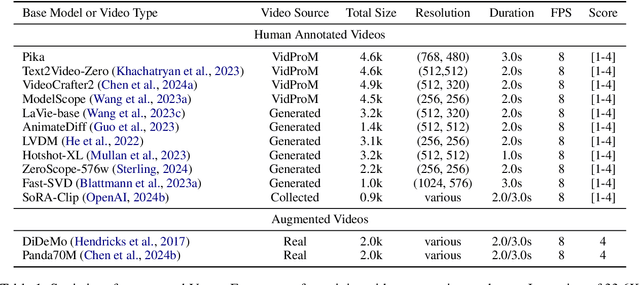

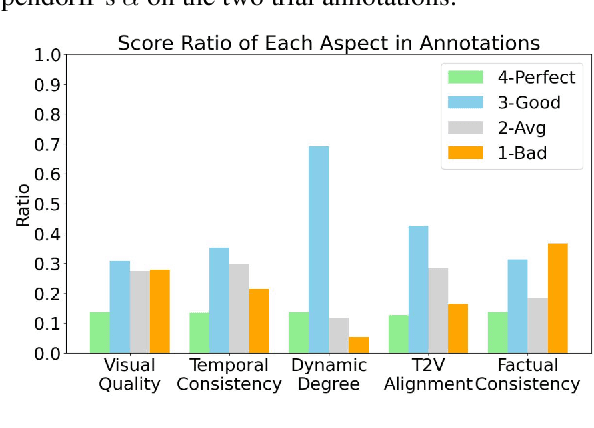

Abstract:The recent years have witnessed great advances in video generation. However, the development of automatic video metrics is lagging significantly behind. None of the existing metric is able to provide reliable scores over generated videos. The main barrier is the lack of large-scale human-annotated dataset. In this paper, we release VideoFeedback, the first large-scale dataset containing human-provided multi-aspect score over 37.6K synthesized videos from 11 existing video generative models. We train VideoScore (initialized from Mantis) based on VideoFeedback to enable automatic video quality assessment. Experiments show that the Spearman correlation between VideoScore and humans can reach 77.1 on VideoFeedback-test, beating the prior best metrics by about 50 points. Further result on other held-out EvalCrafter, GenAI-Bench, and VBench show that VideoScore has consistently much higher correlation with human judges than other metrics. Due to these results, we believe VideoScore can serve as a great proxy for human raters to (1) rate different video models to track progress (2) simulate fine-grained human feedback in Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) to improve current video generation models.
Towards automating Codenames spymasters with deep reinforcement learning
Dec 28, 2022Abstract:Although most reinforcement learning research has centered on competitive games, little work has been done on applying it to co-operative multiplayer games or text-based games. Codenames is a board game that involves both asymmetric co-operation and natural language processing, which makes it an excellent candidate for advancing RL research. To my knowledge, this work is the first to formulate Codenames as a Markov Decision Process and apply some well-known reinforcement learning algorithms such as SAC, PPO, and A2C to the environment. Although none of the above algorithms converge for the Codenames environment, neither do they converge for a simplified environment called ClickPixel, except when the board size is small.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge