Lifeng Wang
Yanyun-3: Enabling Cross-Platform Strategy Game Operation with Vision-Language Models
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Automated operation in cross-platform strategy games demands agents with robust generalization across diverse user interfaces and dynamic battlefield conditions. While vision-language models (VLMs) have shown considerable promise in multimodal reasoning, their application to complex human-computer interaction scenarios--such as strategy gaming--remains largely unexplored. Here, we introduce Yanyun-3, a general-purpose agent framework that, for the first time, enables autonomous cross-platform operation across three heterogeneous strategy game environments. By integrating the vision-language reasoning of Qwen2.5-VL with the precise execution capabilities of UI-TARS, Yanyun-3 successfully performs core tasks including target localization, combat resource allocation, and area control. Through systematic ablation studies, we evaluate the effects of various multimodal data combinations--static images, multi-image sequences, and videos--and propose the concept of combination granularity to differentiate between intra-sample fusion and inter-sample mixing strategies. We find that a hybrid strategy, which fuses multi-image and video data while mixing in static images (MV+S), substantially outperforms full fusion: it reduces inference time by 63% and boosts the BLEU-4 score by a factor of 12 (from 4.81% to 62.41%, approximately 12.98x). Operating via a closed-loop pipeline of screen capture, model inference, and action execution, the agent demonstrates strong real-time performance and cross-platform generalization. Beyond providing an efficient solution for strategy game automation, our work establishes a general paradigm for enhancing VLM performance through structured multimodal data organization, offering new insights into the interplay between static perception and dynamic reasoning in embodied intelligence.
Large Foundation Model for Ads Recommendation
Aug 20, 2025


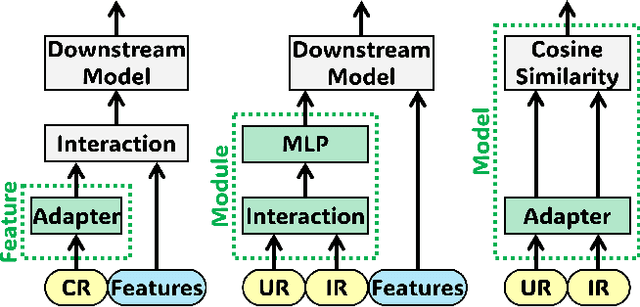
Abstract:Online advertising relies on accurate recommendation models, with recent advances using pre-trained large-scale foundation models (LFMs) to capture users' general interests across multiple scenarios and tasks. However, existing methods have critical limitations: they extract and transfer only user representations (URs), ignoring valuable item representations (IRs) and user-item cross representations (CRs); and they simply use a UR as a feature in downstream applications, which fails to bridge upstream-downstream gaps and overlooks more transfer granularities. In this paper, we propose LFM4Ads, an All-Representation Multi-Granularity transfer framework for ads recommendation. It first comprehensively transfers URs, IRs, and CRs, i.e., all available representations in the pre-trained foundation model. To effectively utilize the CRs, it identifies the optimal extraction layer and aggregates them into transferable coarse-grained forms. Furthermore, we enhance the transferability via multi-granularity mechanisms: non-linear adapters for feature-level transfer, an Isomorphic Interaction Module for module-level transfer, and Standalone Retrieval for model-level transfer. LFM4Ads has been successfully deployed in Tencent's industrial-scale advertising platform, processing tens of billions of daily samples while maintaining terabyte-scale model parameters with billions of sparse embedding keys across approximately two thousand features. Since its production deployment in Q4 2024, LFM4Ads has achieved 10+ successful production launches across various advertising scenarios, including primary ones like Weixin Moments and Channels. These launches achieve an overall GMV lift of 2.45% across the entire platform, translating to estimated annual revenue increases in the hundreds of millions of dollars.
A Knowledge-enhanced Pathology Vision-language Foundation Model for Cancer Diagnosis
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Deep learning has enabled the development of highly robust foundation models for various pathological tasks across diverse diseases and patient cohorts. Among these models, vision-language pre-training, which leverages large-scale paired data to align pathology image and text embedding spaces, and provides a novel zero-shot paradigm for downstream tasks. However, existing models have been primarily data-driven and lack the incorporation of domain-specific knowledge, which limits their performance in cancer diagnosis, especially for rare tumor subtypes. To address this limitation, we establish a Knowledge-enhanced Pathology (KEEP) foundation model that harnesses disease knowledge to facilitate vision-language pre-training. Specifically, we first construct a disease knowledge graph (KG) that covers 11,454 human diseases with 139,143 disease attributes, including synonyms, definitions, and hypernym relations. We then systematically reorganize the millions of publicly available noisy pathology image-text pairs, into 143K well-structured semantic groups linked through the hierarchical relations of the disease KG. To derive more nuanced image and text representations, we propose a novel knowledge-enhanced vision-language pre-training approach that integrates disease knowledge into the alignment within hierarchical semantic groups instead of unstructured image-text pairs. Validated on 18 diverse benchmarks with more than 14,000 whole slide images (WSIs), KEEP achieves state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot cancer diagnostic tasks. Notably, for cancer detection, KEEP demonstrates an average sensitivity of 89.8% at a specificity of 95.0% across 7 cancer types. For cancer subtyping, KEEP achieves a median balanced accuracy of 0.456 in subtyping 30 rare brain cancers, indicating strong generalizability for diagnosing rare tumors.
Spatial-spectral Cell-free Networks: A Large-scale Case Study
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:This paper studies the large-scale cell-free networks where dense distributed access points (APs) serve many users. As a promising next-generation network architecture, cell-free networks enable ultra-reliable connections and minimal fading/blockage, which are much favorable to the millimeter wave and Terahertz transmissions. However, conventional beam management with large phased arrays in a cell is very time-consuming in the higher-frequencies, and could be worsened when deploying a large number of coordinated APs in the cell-free systems. To tackle this challenge, the spatial-spectral cell-free networks with the leaky-wave antennas are established by coupling the propagation angles with frequencies. The beam training overhead in this direction can be significantly reduced through exploiting such spatial-spectral coupling effects. In the considered large-scale spatial-spectral cell-free networks, a novel subchannel allocation solution at sub-terahertz bands is proposed by leveraging the relationship between cross-entropy method and mixture model. Since initial access and AP clustering play a key role in achieving scalable large-scale cell-free networks, a hierarchical AP clustering solution is proposed to make the joint initial access and cluster formation, which is adaptive and has no need to initialize the number of AP clusters. After AP clustering, a subchannel allocation solution is devised to manage the interference between AP clusters. Numerical results are presented to confirm the efficiency of the proposed solutions and indicate that besides subchannel allocation, AP clustering can also have a big impact on the large-scale cell-free network performance at sub-terahertz bands.
Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning Empowered Task Offloading in V2I Networks
May 18, 2024Abstract:Edge computing plays an essential role in the vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) networks, where vehicles offload their intensive computation tasks to the road-side units for saving energy and reduce the latency. This paper designs the optimal task offloading policy to address the concerns involving processing delay, energy consumption and edge computing cost. Each computation task consisting of some interdependent sub-tasks is characterized as a directed acyclic graph (DAG). In such dynamic networks, a novel hierarchical Offloading scheme is proposed by leveraging deep reinforcement learning (DRL). The inter-dependencies among the DAGs of the computation tasks are extracted using a graph neural network with attention mechanism. A parameterized DRL algorithm is developed to deal with the hierarchical action space containing both discrete and continuous actions. Simulation results with a real-world car speed dataset demonstrate that the proposed scheme can effectively reduce the system overhead.
Scalable Multiuser Immersive Communications with Multi-numerology and Mini-slot
Sep 16, 2023



Abstract:This paper studies multiuser immersive communications networks in which different user equipment may demand various extended reality (XR) services. In such heterogeneous networks, time-frequency resource allocation needs to be more adaptive since XR services are usually multi-modal and latency-sensitive. To this end, we develop a scalable time-frequency resource allocation method based on multi-numerology and mini-slot. To appropriately determining the discrete parameters of multi-numerology and mini-slot for multiuser immersive communications, the proposed method first presents a novel flexible time-frequency resource block configuration, then it leverages the deep reinforcement learning to maximize the total quality-of-experience (QoE) under different users' QoE constraints. The results confirm the efficiency and scalability of the proposed time-frequency resource allocation method.
Evaluating Modules in Graph Contrastive Learning
Jun 15, 2021



Abstract:The recent emergence of contrastive learning approaches facilitates the research on graph representation learning (GRL), introducing graph contrastive learning (GCL) into the literature. These methods contrast semantically similar and dissimilar sample pairs to encode the semantics into node or graph embeddings. However, most existing works only performed model-level evaluation, and did not explore the combination space of modules for more comprehensive and systematic studies. For effective module-level evaluation, we propose a framework that decomposes GCL models into four modules: (1) a sampler to generate anchor, positive and negative data samples (nodes or graphs); (2) an encoder and a readout function to get sample embeddings; (3) a discriminator to score each sample pair (anchor-positive and anchor-negative); and (4) an estimator to define the loss function. Based on this framework, we conduct controlled experiments over a wide range of architectural designs and hyperparameter settings on node and graph classification tasks. Specifically, we manage to quantify the impact of a single module, investigate the interaction between modules, and compare the overall performance with current model architectures. Our key findings include a set of module-level guidelines for GCL, e.g., simple samplers from LINE and DeepWalk are strong and robust; an MLP encoder associated with Sum readout could achieve competitive performance on graph classification. Finally, we release our implementations and results as OpenGCL, a modularized toolkit that allows convenient reproduction, standard model and module evaluation, and easy extension.
GEAR: Graph-based Evidence Aggregating and Reasoning for Fact Verification
Jul 22, 2019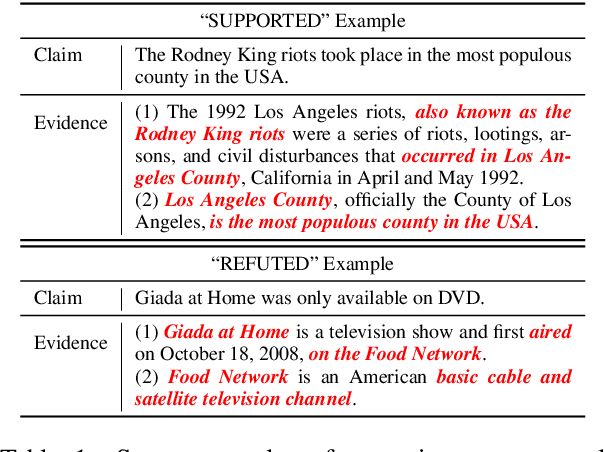
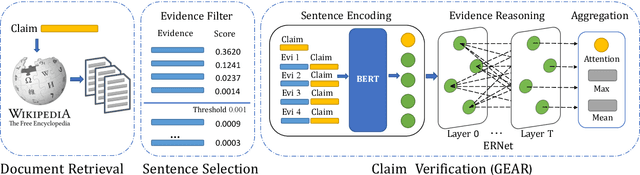
Abstract:Fact verification (FV) is a challenging task which requires to retrieve relevant evidence from plain text and use the evidence to verify given claims. Many claims require to simultaneously integrate and reason over several pieces of evidence for verification. However, previous work employs simple models to extract information from evidence without letting evidence communicate with each other, e.g., merely concatenate the evidence for processing. Therefore, these methods are unable to grasp sufficient relational and logical information among the evidence. To alleviate this issue, we propose a graph-based evidence aggregating and reasoning (GEAR) framework which enables information to transfer on a fully-connected evidence graph and then utilizes different aggregators to collect multi-evidence information. We further employ BERT, an effective pre-trained language representation model, to improve the performance. Experimental results on a large-scale benchmark dataset FEVER have demonstrated that GEAR could leverage multi-evidence information for FV and thus achieves the promising result with a test FEVER score of 67.10%. Our code is available at https://github.com/thunlp/GEAR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge