Lean Wang
mHC: Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Recently, studies exemplified by Hyper-Connections (HC) have extended the ubiquitous residual connection paradigm established over the past decade by expanding the residual stream width and diversifying connectivity patterns. While yielding substantial performance gains, this diversification fundamentally compromises the identity mapping property intrinsic to the residual connection, which causes severe training instability and restricted scalability, and additionally incurs notable memory access overhead. To address these challenges, we propose Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections (mHC), a general framework that projects the residual connection space of HC onto a specific manifold to restore the identity mapping property, while incorporating rigorous infrastructure optimization to ensure efficiency. Empirical experiments demonstrate that mHC is effective for training at scale, offering tangible performance improvements and superior scalability. We anticipate that mHC, as a flexible and practical extension of HC, will contribute to a deeper understanding of topological architecture design and suggest promising directions for the evolution of foundational models.
TimeChat-Online: 80% Visual Tokens are Naturally Redundant in Streaming Videos
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth of online video platforms, particularly live streaming services, has created an urgent need for real-time video understanding systems. These systems must process continuous video streams and respond to user queries instantaneously, presenting unique challenges for current Video Large Language Models (VideoLLMs). While existing VideoLLMs excel at processing complete videos, they face significant limitations in streaming scenarios due to their inability to handle dense, redundant frames efficiently. We introduce TimeChat-Online, a novel online VideoLLM that revolutionizes real-time video interaction. At its core lies our innovative Differential Token Drop (DTD) module, which addresses the fundamental challenge of visual redundancy in streaming videos. Drawing inspiration from human visual perception's Change Blindness phenomenon, DTD preserves meaningful temporal changes while filtering out static, redundant content between frames. Remarkably, our experiments demonstrate that DTD achieves an 82.8% reduction in video tokens while maintaining 98% performance on StreamingBench, revealing that over 80% of visual content in streaming videos is naturally redundant without requiring language guidance. To enable seamless real-time interaction, we present TimeChat-Online-139K, a comprehensive streaming video dataset featuring diverse interaction patterns including backward-tracing, current-perception, and future-responding scenarios. TimeChat-Online's unique Proactive Response capability, naturally achieved through continuous monitoring of video scene transitions via DTD, sets it apart from conventional approaches. Our extensive evaluation demonstrates TimeChat-Online's superior performance on streaming benchmarks (StreamingBench and OvOBench) and maintaining competitive results on long-form video tasks such as Video-MME and MLVU.
DeepSeek-V3 Technical Report
Dec 27, 2024



Abstract:We present DeepSeek-V3, a strong Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language model with 671B total parameters with 37B activated for each token. To achieve efficient inference and cost-effective training, DeepSeek-V3 adopts Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) and DeepSeekMoE architectures, which were thoroughly validated in DeepSeek-V2. Furthermore, DeepSeek-V3 pioneers an auxiliary-loss-free strategy for load balancing and sets a multi-token prediction training objective for stronger performance. We pre-train DeepSeek-V3 on 14.8 trillion diverse and high-quality tokens, followed by Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning stages to fully harness its capabilities. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that DeepSeek-V3 outperforms other open-source models and achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source models. Despite its excellent performance, DeepSeek-V3 requires only 2.788M H800 GPU hours for its full training. In addition, its training process is remarkably stable. Throughout the entire training process, we did not experience any irrecoverable loss spikes or perform any rollbacks. The model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3.
Temporal Reasoning Transfer from Text to Video
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:Video Large Language Models (Video LLMs) have shown promising capabilities in video comprehension, yet they struggle with tracking temporal changes and reasoning about temporal relationships. While previous research attributed this limitation to the ineffective temporal encoding of visual inputs, our diagnostic study reveals that video representations contain sufficient information for even small probing classifiers to achieve perfect accuracy. Surprisingly, we find that the key bottleneck in Video LLMs' temporal reasoning capability stems from the underlying LLM's inherent difficulty with temporal concepts, as evidenced by poor performance on textual temporal question-answering tasks. Building on this discovery, we introduce the Textual Temporal reasoning Transfer (T3). T3 synthesizes diverse temporal reasoning tasks in pure text format from existing image-text datasets, addressing the scarcity of video samples with complex temporal scenarios. Remarkably, without using any video data, T3 enhances LongVA-7B's temporal understanding, yielding a 5.3 absolute accuracy improvement on the challenging TempCompass benchmark, which enables our model to outperform ShareGPT4Video-8B trained on 28,000 video samples. Additionally, the enhanced LongVA-7B model achieves competitive performance on comprehensive video benchmarks. For example, it achieves a 49.7 accuracy on the Temporal Reasoning task of Video-MME, surpassing powerful large-scale models such as InternVL-Chat-V1.5-20B and VILA1.5-40B. Further analysis reveals a strong correlation between textual and video temporal task performance, validating the efficacy of transferring temporal reasoning abilities from text to video domains.
Auxiliary-Loss-Free Load Balancing Strategy for Mixture-of-Experts
Aug 28, 2024



Abstract:For Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models, an unbalanced expert load will lead to routing collapse or increased computational overhead. Existing methods commonly employ an auxiliary loss to encourage load balance, but a large auxiliary loss will introduce non-negligible interference gradients into training and thus impair the model performance. In order to control load balance while not producing undesired gradients during training, we propose Loss-Free Balancing, featured by an auxiliary-loss-free load balancing strategy. To be specific, before the top-K routing decision, Loss-Free Balancing will first apply an expert-wise bias to the routing scores of each expert. By dynamically updating the bias of each expert according to its recent load, Loss-Free Balancing can consistently maintain a balanced distribution of expert load. In addition, since Loss-Free Balancing does not produce any interference gradients, it also elevates the upper bound of model performance gained from MoE training. We validate the performance of Loss-Free Balancing on MoE models with up to 3B parameters trained on up to 200B tokens. Experimental results show that Loss-Free Balancing achieves both better performance and better load balance compared with traditional auxiliary-loss-controlled load balancing strategies.
DeCo: Decoupling Token Compression from Semantic Abstraction in Multimodal Large Language Models
May 31, 2024



Abstract:The visual projector, which bridges the vision and language modalities and facilitates cross-modal alignment, serves as a crucial component in MLLMs. However, measuring the effectiveness of projectors in vision-language alignment remains under-explored, which currently can only be inferred from the performance of MLLMs on downstream tasks. Motivated by the problem, this study examines the projector module by interpreting the vision-language semantic flow within MLLMs. Specifically, we trace back the semantic relevance flow from generated language tokens to raw visual encoder patches and the intermediate outputs produced by projectors. Our findings reveal that compressive projectors (e.g., QFormer), abstract visual patches into a limited set of semantic concepts, such as objects or attributes, resulting in a 'double abstraction' phenomenon. This involves a first visual semantic abstraction by the projector referring to pre-defined query tokens, and a second extraction by the LLM based on text instructions. The double abstraction is inefficient in training and will result in cumulative vision semantics deficiency. To mitigate this issue, we propose the key insight of 'Decouple Compression from Abstraction (DeCo), that is compressing the visual token number at the patch level by projectors and allowing the LLM to handle visual semantic abstraction entirely. Consequently, we adopt a simple compressor, i.e., 2D Adaptive Pooling, to downsample visual patches in a parameter-free manner. Empirical evaluation demonstrates that DeCo surpasses traditional compressive projectors regarding both performance and efficiency. It achieves performance gains of 0.9%, 7.1%, and 2.9% across the MLLM Benchmarks, Visual Localization, and Open-ended VQA tasks with fewer trainable parameters and faster convergence speed.
Towards Codable Text Watermarking for Large Language Models
Jul 29, 2023Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) generate texts with increasing fluency and realism, there is a growing need to identify the source of texts to prevent the abuse of LLMs. Text watermarking techniques have proven reliable in distinguishing whether a text is generated by LLMs by injecting hidden patterns into the generated texts. However, we argue that existing watermarking methods for LLMs are encoding-inefficient (only contain one bit of information - whether it is generated from an LLM or not) and cannot flexibly meet the diverse information encoding needs (such as encoding model version, generation time, user id, etc.) in different LLMs application scenarios. In this work, we conduct the first systematic study on the topic of Codable Text Watermarking for LLMs (CTWL) that allows text watermarks to carry more customizable information. First of all, we study the taxonomy of LLM watermarking technology and give a mathematical formulation for CTWL. Additionally, we provide a comprehensive evaluation system for CTWL: (1) watermarking success rate, (2) robustness against various corruptions, (3) coding rate of payload information, (4) encoding and decoding efficiency, (5) impacts on the quality of the generated text. To meet the requirements of these non-Pareto-improving metrics, we devise a CTWL method named Balance-Marking, based on the motivation of ensuring that available and unavailable vocabularies for encoding information have approximately equivalent probabilities. Compared to the random vocabulary partitioning extended from the existing work, a probability-balanced vocabulary partition can significantly improve the quality of the generated text. Extensive experimental results have shown that our method outperforms a direct baseline under comprehensive evaluation.
Label Words are Anchors: An Information Flow Perspective for Understanding In-Context Learning
May 23, 2023



Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) emerges as a promising capability of large language models (LLMs) by providing them with demonstration examples to perform diverse tasks. However, the underlying mechanism of how LLMs learn from the provided context remains under-explored. In this paper, we investigate the working mechanism of ICL through an information flow lens. Our findings reveal that label words in the demonstration examples function as anchors: (1) semantic information aggregates into label word representations during the shallow computation layers' processing; (2) the consolidated information in label words serves as a reference for LLMs' final predictions. Based on these insights, we introduce an anchor re-weighting method to improve ICL performance, a demonstration compression technique to expedite inference, and an analysis framework for diagnosing ICL errors in GPT2-XL. The promising applications of our findings again validate the uncovered ICL working mechanism and pave the way for future studies.
Gradient Knowledge Distillation for Pre-trained Language Models
Nov 02, 2022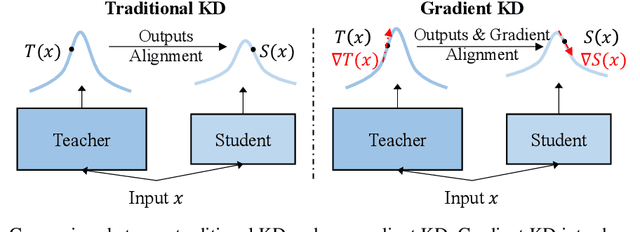

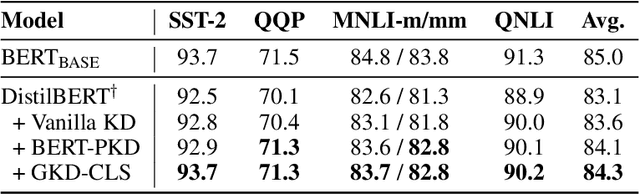

Abstract:Knowledge distillation (KD) is an effective framework to transfer knowledge from a large-scale teacher to a compact yet well-performing student. Previous KD practices for pre-trained language models mainly transfer knowledge by aligning instance-wise outputs between the teacher and student, while neglecting an important knowledge source, i.e., the gradient of the teacher. The gradient characterizes how the teacher responds to changes in inputs, which we assume is beneficial for the student to better approximate the underlying mapping function of the teacher. Therefore, we propose Gradient Knowledge Distillation (GKD) to incorporate the gradient alignment objective into the distillation process. Experimental results show that GKD outperforms previous KD methods regarding student performance. Further analysis shows that incorporating gradient knowledge makes the student behave more consistently with the teacher, improving the interpretability greatly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge