Kyeongha Rho
LAVCap: LLM-based Audio-Visual Captioning using Optimal Transport
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:Automated audio captioning is a task that generates textual descriptions for audio content, and recent studies have explored using visual information to enhance captioning quality. However, current methods often fail to effectively fuse audio and visual data, missing important semantic cues from each modality. To address this, we introduce LAVCap, a large language model (LLM)-based audio-visual captioning framework that effectively integrates visual information with audio to improve audio captioning performance. LAVCap employs an optimal transport-based alignment loss to bridge the modality gap between audio and visual features, enabling more effective semantic extraction. Additionally, we propose an optimal transport attention module that enhances audio-visual fusion using an optimal transport assignment map. Combined with the optimal training strategy, experimental results demonstrate that each component of our framework is effective. LAVCap outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods on the AudioCaps dataset, without relying on large datasets or post-processing. Code is available at https://github.com/NAVER-INTEL-Co-Lab/gaudi-lavcap.
EquiAV: Leveraging Equivariance for Audio-Visual Contrastive Learning
Mar 14, 2024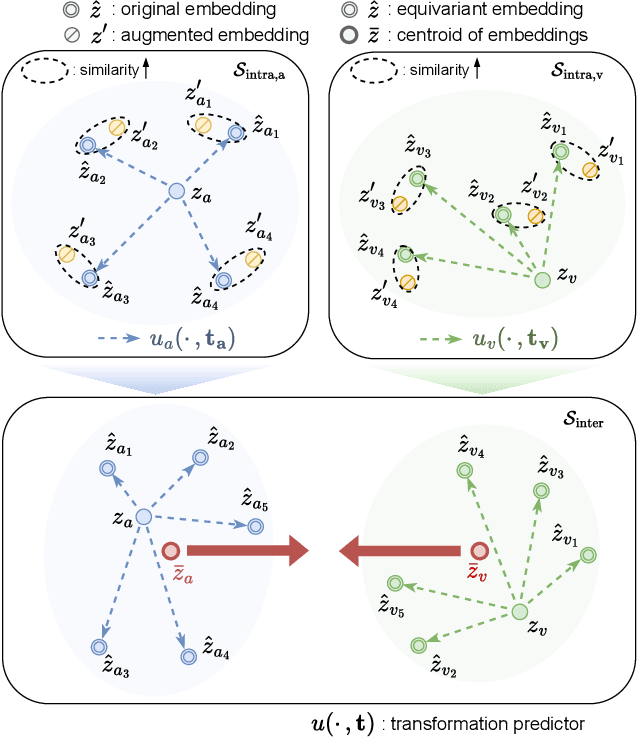

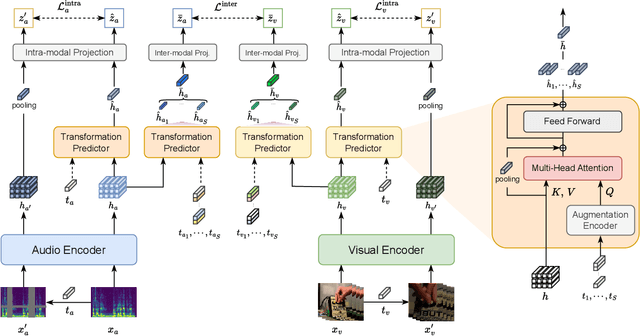

Abstract:Recent advancements in self-supervised audio-visual representation learning have demonstrated its potential to capture rich and comprehensive representations. However, despite the advantages of data augmentation verified in many learning methods, audio-visual learning has struggled to fully harness these benefits, as augmentations can easily disrupt the correspondence between input pairs. To address this limitation, we introduce EquiAV, a novel framework that leverages equivariance for audio-visual contrastive learning. Our approach begins with extending equivariance to audio-visual learning, facilitated by a shared attention-based transformation predictor. It enables the aggregation of features from diverse augmentations into a representative embedding, providing robust supervision. Notably, this is achieved with minimal computational overhead. Extensive ablation studies and qualitative results verify the effectiveness of our method. EquiAV outperforms previous works across various audio-visual benchmarks.
TalkNCE: Improving Active Speaker Detection with Talk-Aware Contrastive Learning
Sep 21, 2023



Abstract:The goal of this work is Active Speaker Detection (ASD), a task to determine whether a person is speaking or not in a series of video frames. Previous works have dealt with the task by exploring network architectures while learning effective representations has been less explored. In this work, we propose TalkNCE, a novel talk-aware contrastive loss. The loss is only applied to part of the full segments where a person on the screen is actually speaking. This encourages the model to learn effective representations through the natural correspondence of speech and facial movements. Our loss can be jointly optimized with the existing objectives for training ASD models without the need for additional supervision or training data. The experiments demonstrate that our loss can be easily integrated into the existing ASD frameworks, improving their performance. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performances on AVA-ActiveSpeaker and ASW datasets.
That's What I Said: Fully-Controllable Talking Face Generation
Apr 06, 2023Abstract:The goal of this paper is to synthesise talking faces with controllable facial motions. To achieve this goal, we propose two key ideas. The first is to establish a canonical space where every face has the same motion patterns but different identities. The second is to navigate a multimodal motion space that only represents motion-related features while eliminating identity information. To disentangle identity and motion, we introduce an orthogonality constraint between the two different latent spaces. From this, our method can generate natural-looking talking faces with fully controllable facial attributes and accurate lip synchronisation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art results in terms of both visual quality and lip-sync score. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to develop a talking face generation framework that can accurately manifest full target facial motions including lip, head pose, and eye movements in the generated video without any additional supervision beyond RGB video with audio.
NTIRE 2020 Challenge on Real Image Denoising: Dataset, Methods and Results
May 08, 2020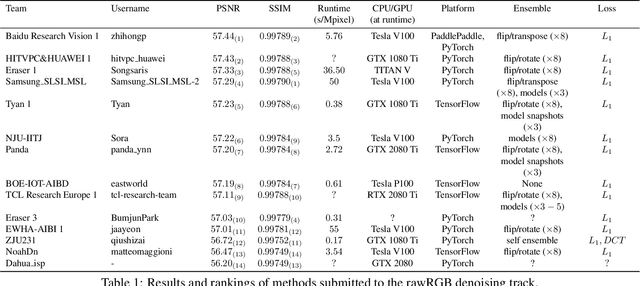
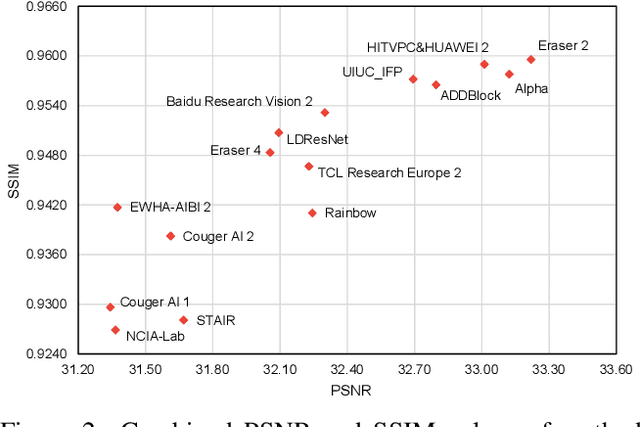
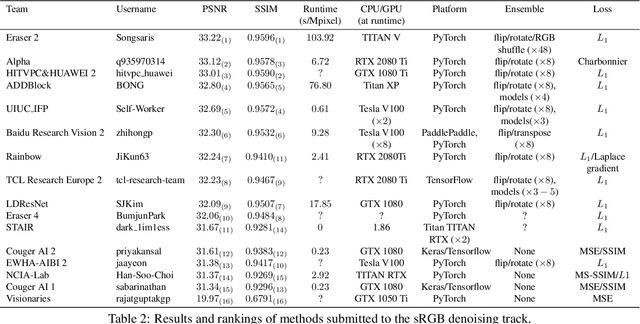
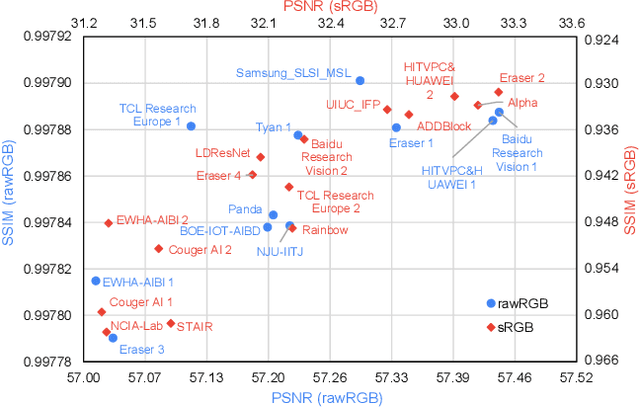
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2020 challenge on real image denoising with focus on the newly introduced dataset, the proposed methods and their results. The challenge is a new version of the previous NTIRE 2019 challenge on real image denoising that was based on the SIDD benchmark. This challenge is based on a newly collected validation and testing image datasets, and hence, named SIDD+. This challenge has two tracks for quantitatively evaluating image denoising performance in (1) the Bayer-pattern rawRGB and (2) the standard RGB (sRGB) color spaces. Each track ~250 registered participants. A total of 22 teams, proposing 24 methods, competed in the final phase of the challenge. The proposed methods by the participating teams represent the current state-of-the-art performance in image denoising targeting real noisy images. The newly collected SIDD+ datasets are publicly available at: https://bit.ly/siddplus_data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge